Chapter: Mechanical : Quality Management : Introduction
Quality Management
Quality Management
1 Introduction
1.1 Prerequisite Discussions of Quality
2 Concept
2.1. Need for Quality
2.2. Evolution of quality
2.3. Defining quality
3 Dimensions of quality
3.1 Dimensions of service quality
3.2 Definition of TQM
4 Characteristics Of TQM
4.1 Basic Concepts of TQM
5 TQM Frame work or (ELEMENTS OF TQM)
6 Principles of tqm
7 Obstacles (barriers) in implementing tqm
8 Benefits of tqm
9 Contributions of Deming
10 The juran trilogy
11 Contributions of Crosby
11.1 Crosby’s fourteen points
INTRODUCTION
PREREQUISITE DISCUSSIONS
Quality is in its essence a way of management of the
organization.
Quality is conformance to
customer requirements. The requirements have many dimensions. The number of
quality experts also called quality gurus contributed to the evolution of
quality.
AN
INTRODUCTION:
A name itself is sufficient to describe everything but a bit
more clarification will add to a base for the description.
Total quality management is a management’s approach towards the quality, it can
be in regard
to products, customer satisfaction and
employees satisfaction. The concept of TQM
was developed by an American W. Edwards Deming and i.e.
why it is called as Deming’s concept of TQM .He introduced this concept
for improving the quality of various products and services. Earlier it was just
related with the quality of products which a organization is producing but now
other concepts like marketing, finance design, customer service has also joined
the area. Which means that now good numbers of things are there to manage. TQM
works on one belief that mistakes can be avoided and defects can be prevented.
And management should believe in watching each and every step.
TQM is now a day’s called
as TPM (total productivity management) and an organization needs to
consider ABCD for the effective application of TQM where A stands for accident
cure , B stands for breakdown , C stands for cost reduction and D stands for
damage. This policy of ABCD is in relation to product and if TQM needs to be
introduced a positive attitude from the side of management and employees is
required and then a collective effort will come up. TQM should give chance
for unleashing employee’s creativity and potential. The aim of TQM is to reduce
variations in quality of the products as well as in the working of whole
organization. For the successful implementation of TQM, an organization must
consider the commitment from all the level of organization. A concept of Six
sigma is a part of TQM. It is a strategy developed by Motorola and it
helps to detect the defects and to remove them.
TQM talks about the satisfaction of customer, supplier,
employees etc. and it requires continuous improvement. If the workers of an
organization are efficiently working then their morale will go up. TQM works
effectively if the organization works in a family manner. Here management is
like a father, employees are the children and manager is like mother and as father
and mother takes care for their home collectively the same way , management and
managers are supposed to take care for their organization with the help of tool
called TQM. Total quality management is called total because entire
organization is involved, Quality means degree of excellence. And management in
literal sense means getting things done by others. In a TQM effort, all members
of an organization participate in improving processes, products, services and
the culture in which they work. The earlier introduced quality management
concept is now taken over by Total quality management. To have effective TQM
the first requirement is strong internal motivation and emotional involvement
for implementation. So the concept of TQM talks about adopting the new policy,
creating quality products, eliminate defects, estimate for breakdown, accidents
etc . Hence TQM should be purpose driven so first the whole organization should
be willing to accept the change then only TQM can actually affect the
organization in a positive way.
CONCEPT
Need for quality:
The need for quality was felt,
during World War II due to the unprecedented need for manufacture goods. From
them on methodologies for assuring quality in products and services evolved
continuously finally lead to TQM.
Evolution
of quality (or) GURUS OF TQM:
SHEWHART - Control chart theory
- PDCA Cycle
DEMING - Statistical Process Control
JURAN - Concepts of SHEWHART
- Return on Investment (ROI)
FEIGANBAUM - Total Quality Control
- Management involvement
- Employee involvement
- Company wide quality control
ISHIKAWA - Cause and Effect Diagram
- Quality Circle concept
CROSBY - “Quality is Free”
- - Conformance to requirements
TAGUCHI - Loss Function concept
- Design
of Experiments
DEFINING
QUALITY:
Quality
is fitness for use
Quality
is conformance to requirements
Quality
is the totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that
bear on its ability to
satisfy
stated and implied needs of customer.
Quality
can be quantified as follows
Q = P / E
where,
Q = Quality
P = Performance
E = Expectation

DIMENSIONS
OF QUALITY:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Dimension Meaning
and Example
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Performance Primary product characteristics,
such as the brightness of the picture
Features Secondary characteristics, added
features, such as remote control
Conformance Meeting specifications or industry standards, workmanship
Reliability Consistency
of performance over time, average time of the unit to fail
Durability Useful
life, includes repair
Service
Resolution
of problems and complaints, ease of repair
Response Human –
to – human interface, such as the courtesy of the dealer
Aesthetics Sensory
characteristics, such as exterior finish
Reputation Past
performance and other intangibles, such as being ranked first
1.3.1 Dimensions of service quality
Reliability Refers to the dependability of the service providers and their
ability to keep
their promises.
Responsiveness Refers to the reaction time of the service.
Assurance Refers
the level of certainty a customer has regarding the quality of the service
provided.
Empathy Being
able to understand the needs of the customer as an individual.
Tangibles Similar
to the physical characteristics of quality of products.
Other Dimensions Time, Courtesy, Timeliness, consistency, accuracy,
credibility and security.
Total
Quality Management (TQM) is an enhancement to the traditional way of doing
business.
Definition
of TQM
Art of
managing the whole to achieve excellence.
Total - Made
up of the whole
Quality - Degree
of Excellence a Product or Service provides.
Management - Art
of handling, controlling, directing etc.
TQM is the application of quantitative methods and human
resources to improve all the processes within an organization and exceed CUSTOMER
NEEDS now and in the future.
CHARACTERISTICS
OF TQM
The above
definitions revealed the following characteristics of TQM :
1. TQM is a
customer oriented.
2. TQM
required a long term commitment for continuous improvement of all processes.
3. TQM is
teamwork.
4. TQM
requires the leadership of top management and continuous involvement.
5. TQM is a
strategy for continuous improving performance at all levels and in all areas of
responsibility.
Basic
Concepts of TQM:
1.
A committed and involved management.
2.
An unwavering focus on the customer both
internally and externally.
3.
Effective involvement and utilization of entire
work force,
4.
Continuous improvement of the business and
production process.
5.
Treating suppliers as partners.
6.
Establish performance measures for the processes.
ELEMENTS
OF TQM
A
framework summarizing the important elements of TQM discussed in this text.
Three
elements of TQM include
1. The
philosophical elements of TQM stress the operation of the company
using quality as the integrating element.
2. The
generic tools consist of various statistical process control
(SPC) methods that are used for problem solving and continuous
improvement by quality teams. Quality function deployment is typically used by
managers to drive the voice of the customer into the organization.
3.
Tools of the QC department consists
of statistical quality control (SQC) methods such as sampling
plans,
process capability and Taguchi methods.
TQM Frame work:
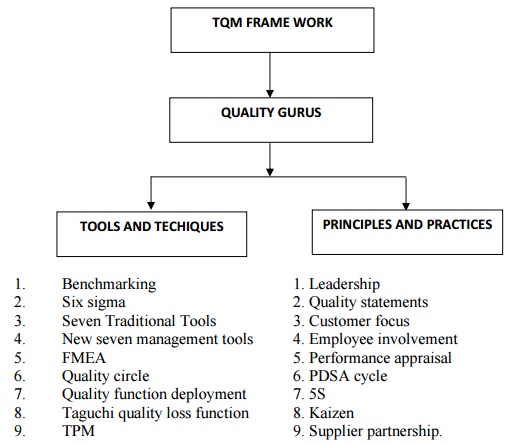
TOOLS AND T
1. Benchmarking
2. Six sigma
3. Seven Traditional Tools
4. New seven management tools
5. FMEA
6. Quality circle
7. Quality function deployment
8. Taguchi quality loss function
9. TPM
PRINCIPLESPRACT
1. Leadership
2. Quality statements
3. Customer focus
4. Employee involvement
5. Performance appraisal
6. PDSA cycle
7. 5S
8. Kaizen
9. Supplier partnership.
Approach:
Continuous
improvement process.
Measures:
Performance
Measures
PRINCIPLES
OF TQM
Ø Customer’s
requirements must be met the first time, every time.
Ø There
must be agreed requirements, for both internal and external customers.
Ø Everybody
must be involved, from all levels and across all functions.
Ø Regular
communication with staff at levels is must. Two way communication at all levels
must be promoted.
Identifying
training needs and relating them with individual capabilities and requirements
is must.
Ø Top
management’s participation and commitment is must.
Ø A culture
of continuous improvement must be established.
Ø Emphasis should
be placed on purchasing and supplier management
Ø Every job
must add value.
Ø Quality
improvement must eliminate wastes and reduce total cost.
Ø There
must be a focus on the prevention of problems.
Ø A culture
of promoting creativity must be established.
Ø Performance
measure is a must at organization, department and individual levels. It helps
to asses and meet objectives of quality.
Ø There
should be focus on team work.
OBSTACLES
(BARRIERS) IN IMPLEMENTING TQM :
Ø Lack of
Management Commitment
Ø Inability
to change Organizational culture
Ø Improper
planning
Ø Lack of
continuous training and education
Ø Incompatible
organizational structure and isolated individuals and departments
Ø Ineffective
measurement techniques and lack of access to data and results
Ø Paying
inadequate attention to internal and external customers
Ø Inadequate
use of empowerment and teamwork
Ø Failure
to continually improve
BENEFITS
OF TQM:
Ø Improved
quality
Ø Employee
participation
Ø Team work
Ø Working
relationships
Ø Customer
satisfaction
Ø Employee
satisfaction
Ø Productivity
Ø Communication
Ø Profitability
Ø Market
share
CONTRIBUTIONS
OF DEMING:
1.
Create and publish the Aims and Purposes of the
organization.
2.
Learn the New Philosophy.
3.
Understand the purpose of Inspection.
4.
Stop awarding business based on price alone.
5.
Improve constantly and forever the System.
6.
Institute Training.
7.
Teach and Institute Leadership.
8.
Drive out Fear, Create Trust and Create a climate
for innovation.
9.
Optimize the efforts of Teams, Groups and Staff
areas.
10.
Eliminate exhortations for the Work force.
11a. Eliminate numerical quotas for
the work force.
11b. Eliminate Management by
objectives.
12.
Remove Barriers that rob people of pride of
workmanship.
13.
Encourage Education and Self-improvement for
everyone.
14.
Take action to accomplish the transformation.
THE JURAN
TRILOGY
Juran
views quality as fitness for use.
Juran
Trilogy is designed to reduce the cost of quality over time.
1. QUALITY PLANNING
Ø Determine
internal & external customers.
Ø Their
needs are discovered.
Ø Develop
product / service features.
Ø Develop
the processes able to produce the product / service features.
Ø Transfer
plans to operations.
2. QUALITY CONTROL
Control
is used by operating forces to help meet the product, process and service
requirements.
It
consists of the following steps
1.
Determine items to be controlled.
2.
Set goals for the controls.
3.
Measure actual performance.
4.
Compare actual performance to goals.
5.
Act on the difference.
3.
QUALITY IMPROVEMENT
Aims to attain levels of performance that are higher than
current levels.
It
consists of the following steps
Ø Establishment
of quality council.
Ø Identify
the improvement projects.
Ø Establish
the project teams with a project leader.
Ø Provide
the team with the resources.
CONTRIBUTIONS
OF CROSBY:
The Four
absolutes of quality are
1. Quality
is defined as conformance to requirements.
2. The
system for causing Quality is prevention.
3. The
performance standard must be zero defects.
4. The
measurement of Quality is the Price of Nonconformance
Crosby’s
Fourteen Points:
1. Management
Commitment
2. Quality
Improvement Team
3. Quality
Measurement
4. Cost of
Quality Evaluation
5. Quality
Awareness
6. Corrective
Action
7. Establish
an Ad Hoc Committee for the Zero Defects Program
8. Supervisor
Training
9. Zero Defects
Day
10.Goal
Setting
11.Error
Cause Removal
12.Recognition
13.Quality
Councils
Do It Over Again
Related Topics