Chapter: Civil : Prefabricated Structures : Design Principles
Prefabricated Structures: Disuniting of structures
Disuniting of structures
The solution of problems
connected with the transportation and placing of structures demands as a rule,
their disuniting in to smaller members.
Construction of roof and floor slabs:-
Roofing members:-
Roofing members can be divided
into two groups. short span and long span roofing members. The short span
members rest on purlins. While long span one are directly supported by the main
girders.
The short span roofing members
the reinforced planks mode of porus hollow tiles, light weight concrete,
roofing material and small reinforced concrete roofing members will be dealt
with here.
Among the long span roofing
members the reinforced concrete members are discussed.
(a) Reinforced planks mode of porous hollow tiles:-
These roofing members consist of
porous tiles having longtidutional circular holes. The thickness placed in to
these graces. Which are subsequently fined with cement mortar. In this way
reinforced porous tile planks having a length of 2.3m, a thickness of 6-10 cm
and a width of 20cm can be produced of these tiles, two kinds exist.
The first kind is heat insulating
and has a unit weight of 750kg/m3, the second kind is load bearing,
its unit weight is 1100kg/m3, this is used for production of reinforced
planks.
The
disadvantage of using the porous hollow tiles in question for roof covering is
that the material of the latter is highly moisture absorbing, and therefore not
frast resistant. Thus the roof cover should protected from moisture and hence
it should be rough rendered with lime cement mortar.
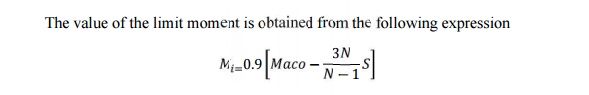
![]() Where,
Where,
Mi = limit moment
Maco= arithmetic mean of the ultimate moment
mi = Value of the ultimate moments belonging to the
individual planks, where (i=1.............N)
N= Number
of loading tests.
C=
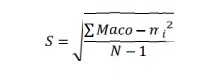
An 8cm
thik plank of porous hollow tiles and its reinforcement.
(b) Light weight concrete roofing members:-
Light weight concrete roofing
members play a role. In additional to space brodering and load bearing. In heat
insulating and so the application of a separate heat insulating layer is not
necessary.
Light weight concrete roofing
members can only be applied if there is a possibility of their reinforcement.
It requires a bond between the steel and the light weight concrete for ensuring
the transmission of the tensile force acting in steel bars to the concrete with
the steel bars sliding, hence it is necessary to protect the reinforcement
against corrosion.
From the view point of strength
light weight concrete of the quality Lc 70 or Lc 1000 are
quite suitable on the production of roofing members with a rectangular c/s and
a thickness of in 25cm of 7.5=25cm and a length of 1.75-6.00m
Prefab roofing members can be
produced of concrete mode in the usual way, using light weight materials on
gravel and sand for aggregates. In the case of prefab structures the steel
wires must be embedded in to a concrete the availity of which is at least C300.
b) Small
Reinforced - concrete roofing members.
The small reinforced-concrete
roofing member is essentially a pre cast simply supported, ribbed
reinforced-concrete slab. The width of the member is 50-120 cm
The large reinforced-concrete
roofing members resting directly on the main girders of structures represents a
more advanced kind of pre cast roofing structure. These members are
manufactured in a length corresponding to the spacing of the frames (6-10m)
their width is 1.30-1.80m. They are directly supported by the main girders so
that purlins are not required.
A large roofing member consist of
two longitudinal edge ribs, cross, ribs and a slab having thickness of 2.5 -3.0
cm, and the two way reinforcement. These members connected to each other and to
the frame girders form a unified continuous roofing structure.
Flooring members:-
In industrial buildings the us of
prefab members, for floor consist of precast joints and flooring member.
The
flooring member is designed for a span of 9m and for the bearing of a live load
of 1000 kg/m2. After the members are placed in final positions a
longitudinal load bearing reinforcement and stirrups are placed in the trough
formed between the longitudinal ribs of the adjacent member. A continuous mgh
reinforcement is placed on the top of these members, there after a 5cm thick
insist concrete layer is cast on the top of the members and the troughs between
the longitudinal ribs are also filled u[p with concrete. In this way the slab
is transformed in to a span of 6.0m & live load of 500kg/m2
& a wt of 1450kg are widely used.
Flooring members to be used for
smaller loads similarly to roofing members can also be made of lightweight
concrete. These members are used chiefly in houses and public buildings.
The
flooring members rest in general joists i.e. their cantilever like part.
The weight of flooring members
should not exceed 5 tons otherwise the storage and transportation as well as
the placing of these members using the presents available equipment would be
difficult.
Flooring member spanning = 6.00m
P= 80-500 kg/M G=1450kg
1-Transverse rib at a spacing of 1.50m2, -pre
stressed reinforcement 12-20mm dia.
Shear walls:
Shear walls are the walls
transmit then through the column of the frame work to the foundations their
main load bearing direction is therefore horizontal as contrasted with
vertically load-bearing wall panels for their reason these infilling wall
panels or slabs are usually disposed horizontally (i.e) extending from column
to column.
They arise from the basic
conception that the overall stability of the supporting from work of a building
can be ensured without additional bracing by means of components that are
necessary any way thus the large roof panels serve as bracing for the roof,
& the wall panels similarly provide the rigidity of the external walls.
Industrial buildings not exceeding about 6m in height will not require such
bracing at all since the horizontal force is in the longitudinal direction the more
so as these forces may be distributed over a member of columns wall panels also
as wind bracing is that it is necessary to provide flexurally rigid connections
between the columns and these panels and such connections are difficult to
establish without giring rise to cold bridges in the thermal insulation.
Shear walls in shed type industrial buildings:-
In the construction of shed type
buildings for industrial purpose the horizontally placed panels are arranged
are above the other. They span from column to column. They may contain. The
widows, alternatively, the latter are accommodated in special panels. The
cross-sectional shapes adopted for the wall, panels are generally similar to
those of vertical load bearing wall panels except that now the direction of
structural action. The direction of load transmission is different. The bracing
panels or slabs are
a. ribbed
slabs
b. hollow
slabs
c. solid
light weight concrete slabs.
are
designed according to the same principles as are applied to [Load bearing wall]
units of similarity type. Depending on the roof beam spacing the slabs may be
up to 12m in length and may be as much as 4m wide transported in the upright
position, however as a rule they seldom exceed 3m in width.
up to
length of 6m light right concrete panels of the kinds also used for roof
construction can suitably be employed (eg) siperex x tong Leca, aerated
concrete etc, as they possess ladequate strength) to perform the function of
bracing in important rule is to secure each panel individually.
Related Topics