Chapter: Discrete Time Systems and Signal Processing : Discrete Time System Analysis
Pole-Zero Plot
POLE –ZERO PLOT
1. X(z) is a
rational function, that is a ratio of two polynomials in z-1 or z.
The roots
of the denominator or the value of z for which X(z) becomes infinite, defines
locations of the poles. The roots of the numerator or the value of z for which
X(z) becomes zero, defines locations of the zeros.
2. ROC dos
not contain any poles of X(z). This is because x(z) becomes infinite at the
locations of the poles. Only poles affect the causality and stability of the
system.
3. CASUALTY CRITERIA FOR LSI SYSTEM
LSI system is causal if and only if the ROC the system function is exterior to the circle. i. e |z| > r. This is the condition for causality of the LSI system in terms of z transform.
(The
condition for LSI system to be causal is h(n) = 0 ….. n<0 )
4. STABILITY CRITERIA FOR LSI SYSTEM
Bounded
input x(n) produces bounded output y(n) in the LSI system only if
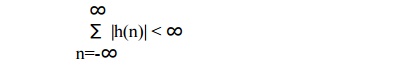
With this
condition satisfied, the system will be stable. The above equation states that
the LSI system is stable if its unit sample response is absolutely summable.
This is necessary and sufficient condition for the stability of LSI system.

Taking
magnitude of both the sides

Magnitudes
of overall sum is less than the sum of magnitudes of individual sums.
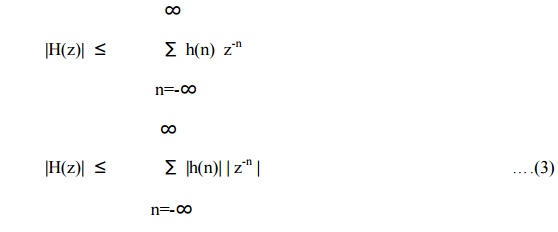
5. If H(z)
is evaluated on the unit circle | z-n|=|z|=1.
Hence LSI
system is stable if and only if the ROC the system function includes the unit
circle. i.e r < 1. This is the condition for stability of the LSI system in
terms of z transform. Thus
For
stable system |z| < 1
For
unstable system |z| > 1
Marginally
stable system |z| = 1
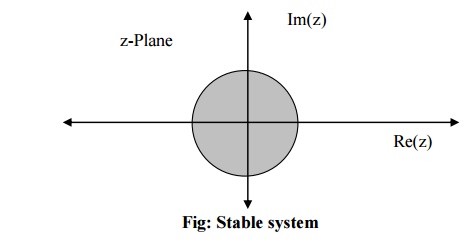
Poles
inside unit circle gives stable system.Poles outside unit circle gives unstable
system. Poles on unit circle give marginally stable system.
6. A causal
and stable system must have a system function that converges for |z| > r
< 1.
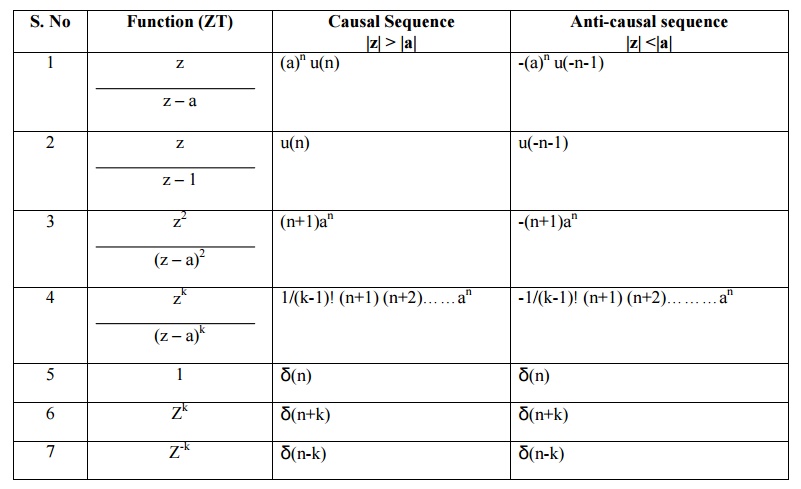
STANDARD INVERSE Z TRANSORMS
Related Topics