Chapter: Programming and Data structures : Object Oriented Programming Fundamentals
Pointers
POINTERS:
Every
storage location of memory has an associated address. The address is a number
that grows sequentially. For every program placed in memory, each variable or
function in the program has an associated address.
The address of operator:
The
address of operator or Reference operator is denoted by the notation &.
When the user wants to get the address of a variable, then the reference
operator & can be used. The operator & is used to find the address
associated with a variable.
The
syntax of the reference operator is as follows:
&variablename - This
means that the address of the variable name is achieved.
For Example
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void
main()
{
int
exf=200;
int
test=300;
cout
<< endl << &exf << endl << &test;
}
The
output of the above program could be one of the following, and at each run it
differs slightly:
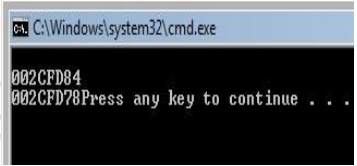
The
&exf has the address associated with the integer variable exf and the
&test has the address associated with the integer variable test which are
displayed using the cout statement.
Using the
understanding of address of operators, the discussion turns to the concept of pointers.
exforsys
= 100;
test =
exforsys;
x =
&exforsys;
Using the
above information, the assignment takes place as below:

exforsys
is an integer variable having the value of 100 stored in memory address
location 3501.
When the variable exforsys is assigned to the variable test in the
second statement: test = exforsys;
The value
of the variable exforsys 100 is copied to the variable test.
In the
third statement, the address of the variable exforsys is denoted by reference
operator &exforsys is assigned to the variable x as:
x =
&exforsys;
The
address of the variable 3501 and not the contents of the variable exforsys is
copied into the variable x. The pointers concept fits in this statement.
Pointers are the variables that store the reference to another variable.
Pointers are variables that store the address of the variable that it is
pointed by. Variable x is referred to as the pointer in the above example.
The
programmer must note that the address operator placed before a variable is not
the same as operator & placed after the variable. For example, &x is
not same as x&. Variable &x refers to address operator whereas x&
refer to reference operator&. Pointer is a variable that holds the address,
also called pointer variable.
Defining Pointer Variables or Pointer:
To define
pointer variable is as follows:
datatype_of_ variable_pointedto*
pointer_varaible;
For example:
char* ch;
This defines that ch is a pointer variable which
points to char data type. int* i;
This defines that i is a pointer variable which
points to int data type. float* f;
This
defines that f is a pointer variable which points to float data type.
Related Topics