Chapter: Programming and Data structures : Object Oriented Programming Fundamentals
Objects
OBJECTS:
Objects
are the variables of user defined data type called class. Once a Class has been
created we can declare any number of variables belongs to that class. In the
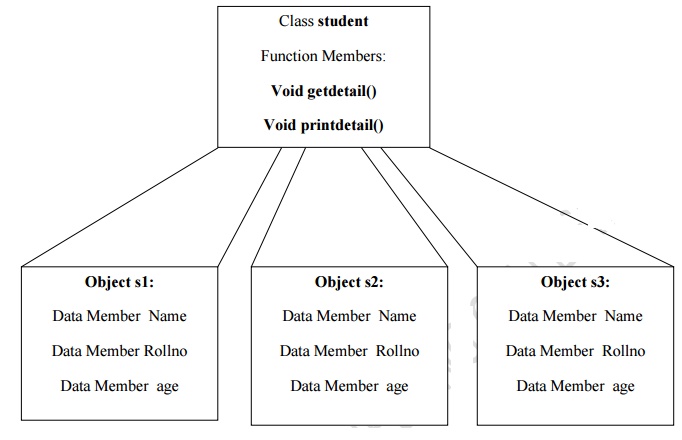
above example class student we can declare any number of variables of class
student in the main function.
Using
objects we can access any public members of a class using Dot Operator.
For accessing Data Members and assigning value:
object_name.data_member=value;
For accessing Function Members:
Object_name.function_name();
Syntax:
Class_Name
object1, object2, object3…….object n;
void main
()
{
class
Name
student
s1, s2,s3; -- -- > s1,s2,s3 are objects(variables) of class
Student
s1.rollno=28;
-- -- > Object s1 assigns the value for the data
member rollno=28
s1.getdetail
(); Object s1 access (call) the function member getdetail () of student class
s1.printdetail
();; -- -- > Object
s1 access (call) the function member
printdetail
() of student class
}
Memory Requirement for Objects and Class:
Once the
object is created memory is allocated for the data members of a class and not
for its function Members‟ .So each object holds the total memory size of the
data members. For example in the class student the object s1 holds the memory
size of 5 bytes. Char I byte, int 2 bytes.
Once the
class is created only single copy of function member is maintained which is
common for all the objects.
Related Topics