Drawbacks, Identifying different types, Harmful effects of plastics - Plastics - Catenated long chain carbon compounds | 9th Science : Carbon and its Compounds
Chapter: 9th Science : Carbon and its Compounds
Plastics - Catenated long chain carbon compounds
Plastics
- Catenated long chain carbon compounds
Plastics are a major
class of catenated organic carbon compounds. They are made from long chain
organic compounds called ‘polymer resins’ with chemical additives that give
them different properties. Different kinds of polymers are used to make
different types of plastics. Plastics are everywhere.
They are convenient,
cheap and are used in our everyday life. Plastics have changed the way we live.
They have helped improve health care, transport and food safety. Plastics have
allowed many breakthroughs in technology such as smartphones, computers and the
internet. It is clear that plastic has given our society many benefits. But
these benefits have come at a cost.
1. Drawbacks of plastics
·
Plastics take a very long time to fully break down in nature.
·
The microbes that break down plastic are too few in nature to deal
with the quantity of plastics we produce.
·
A lot of plastic does not get recycled and ends up polluting the
environment.
·
Some types of plastics contain harmful chemical additives that are
not good for human health.
·
Burning of plastics releases toxic gases that are harmful to our
health and contribute to climate change.
·
One-time use and throwaway plastics end up littering and polluting
the environment.
In order to know which
plastics are harmful, you will need to learn the secret ‘language’ of plastics
(resin codes).
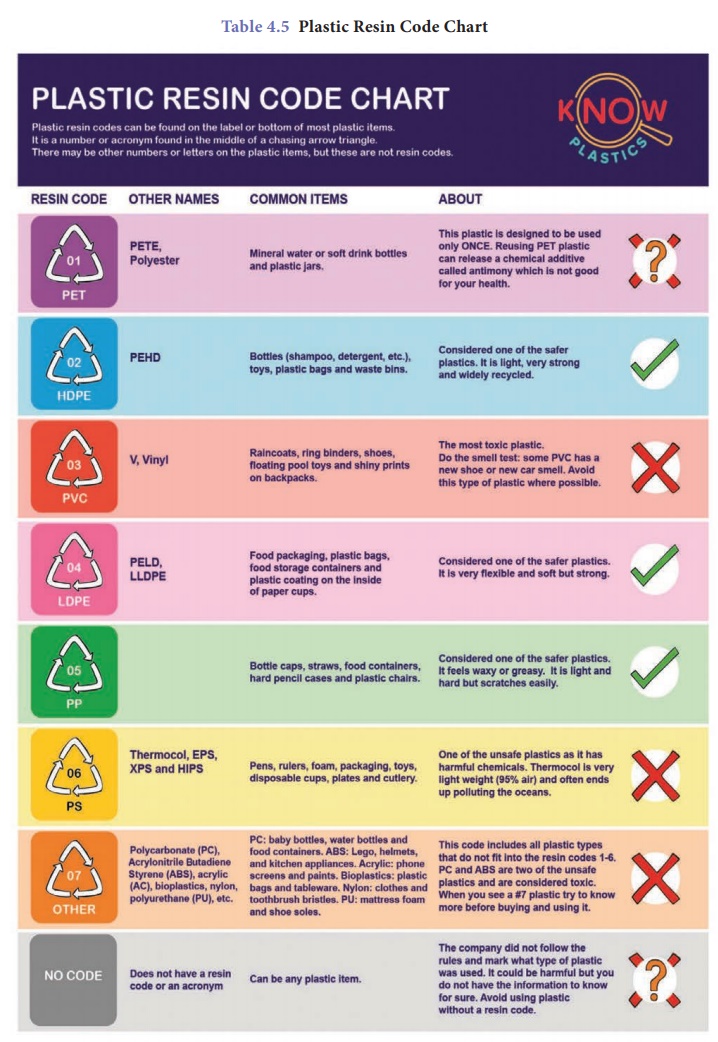
2. Identifying different types of plastics
(a) The resin codes
Look at the following
pictures.

One is a plastic sachet
in which milk is distributed to consumers and the other is a plastic food
container. Observe the code shown on it (circled). Do you know what this code
means? It is called a ‘resin code’. The resin code represents the type
of polymer used to make the plastic.
(b) Need for resin codes
Plastics should be
recycled or disposed of safely. Certain types of plastics should be avoided so
that they do not end up polluting the environment or harming our health. Each
plastic is composed of a different polymer or set of molecules. Different
molecules do not mix when plastics are recycled, it is like
trying to recycle paper and glass together. For this reason, they need to be
separated. The resin codes of plastics were designed in 1988 and are a uniform
way of classifying the different types of plastic which help recyclers in the
sorting process.

(c) How to find the resin code on plastic items
The secret resin codes
are shown as three
chasing arrows in a triangle. There is a number in the middle or letters under the
triangle (an acronym of that plastic type). This is usually difficult to
find. It can be found on the label or bottom of a plastic item.

The resin codes are
numbered from 1 to 7. Resin codes #1 to #6 each identify a certain type of
plastic that is often used in products. Resin code #7 is a category which is
used for every other plastic (since 1988) that does not fit into the categories
#1 to #6. The resin codes look very similar to the recycling symbol, but this
does not mean all plastics with a code can be recycled. The Table 4.5 shows
information of various resin codes.
(d) Where will the resin code be shown on plastic items?
Flip a plastic item to
find the resin code on the bottom.

Sometimes the bottom of
plastic item will only have an acronym or the full name of that plastic type.

If you do not find it on
the bottom, search for the code on the label.

Some plastics do not
have a code. The company did not follow the rules and you do not know if it is
safe to use.

3. Harmful effects of plastics
Plastics in our everyday
life can be harmful for two reasons. The first reason is that some types of
plastic contain chemicals that are harmful to our health. The second reason is
that a lot of plastics are designed to be used just one time. This use and
throwaway plastic causes pollution to our environment.
(a) Harmful plastics
There are three types of
plastic that use toxic and harmful chemicals. These chemicals are added to
plastics to give them certain qualities such as flexibility, strength, colour
or fire and UV resistance. The three unsafe plastics are PVC (resin code #3),
PS (resin code #6 also commonly called Thermocol) and PC/ABS (resin code #7).
PVC – Polyvinyl Chloride plastics
·
Heavy metals (cadmium & lead) are added to PVC.
·
Phthalates (chemical additive) copy our hormones.

·
Burning PVC releases dioxins (one of the most toxic chemicals
known to humans).
PS – Polystyrene plastics
·
Styrene is a building block of this plastic and may cause cancer.
·
It takes very long time to break-down (100- 1 million years).
·
Higher amounts of toxic styrene leak into our food and drinks when
they are hot or oily.

PC – Polycarbonate plastics
·
PC plastic contains Bisphenol A (BPA).
·
BPA leaks out of PC products used for food and drinks.
·
BPA increases or decreases certain hormones and changes the way
our bodies work.
ABS – Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
·
Styrene causes problems for our eyes, skin, digestive system and
lungs.
·
Brominated Flame
·
Retardants (BFRs) are often added.
·
Studies show toxic chemicals leak from this plastic.

(b) One-time use plastic
Use and throwaway
plastics cause short and long-term environmental damage. Half of all the
plastic made today is used for throwaway plastic items. These block drains and
pollute water bodies. One-time use plastic causes health problems for humans,
plants and animals. Some examples are plastic carry bags, cups, plates, straws,
water pouches, cutlery and plastic sheets used for food wrapping.

These items take a few
seconds to be made in a factory. You will use them for a very short time. Once
you throw them away, they can stay in our environment for over a 1,000 years
causing plastic pollution for future generations.
We need rules and laws
to protect people and the environment from plastic pollution.
Related Topics