Chapter: Introduction to Botany: Introduction
Plants, Botany, and Kingdoms
Plants, Botany, and Kingdoms
Botany
is the scientific study of plants and plant-like
organisms. It helps us un-derstand why plants are so vitally important to the
world. Plants start the major-ity of food and energy chains, they provide us
with oxygen, food and medicine.
Plants can be divided into two groups: plants1 and plants2. Plants1
contain all photosynthetic organisms which
use light, H2O, and CO2to make organiccompounds and O2.
Plants1 are defined ecologically
(based on their role in nature).
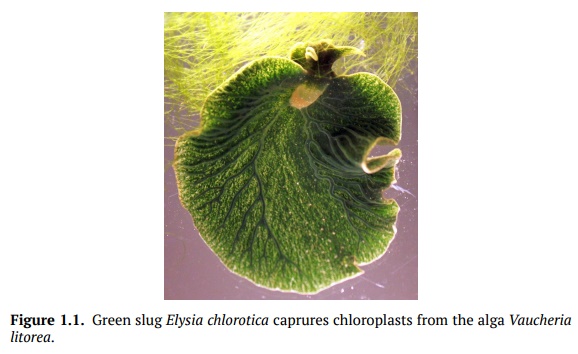
Some plants1 can be bacteria or even animals! One example of this a green slug, Elysia chlorotica (Fig. 1.1). Green slugs collect chloroplasts from algae anduse them for their entire life as food producers. Therefore, green slugs are both animals and plants1.
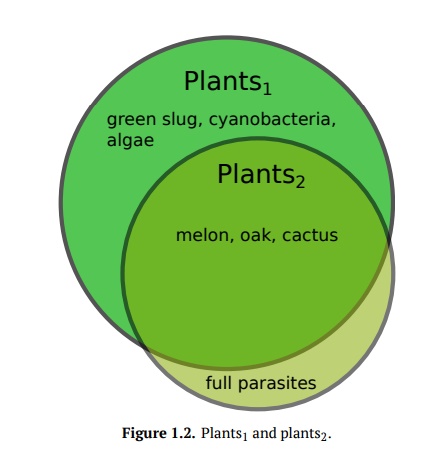
Plants2 are all organisms from Vegetabilia kingdom. Normally, plants2
are green organisms with a stem and leaves. We can define them also as multi-tissued, terrestrial, and primarily
photosynthetic eukaryotes. This defini-tion is taxonomical (based on evolution).
It is possible for the organism to be plant2 but not plant1 (Fig. 1.2). Those who fall into that category, are fully parasitic plants (mycoparasites like Pterospora,root parasites like Hydnora, stem parasites like Cuscuta, and internal parasites like Pilostyles) which do not practice photosynthesis but have tissues, terrestrial lifestyle and originated from photosynthetic ancestors.
Plants may be understood on several levels of
organization: (from top to bottom)
(a) ecosystems or taxa, (b) populations, (c)
organisms, (d) organs, (e) tissues, (f) cells, (g) organelles, and (h)
molecules (Fig. 1.3).
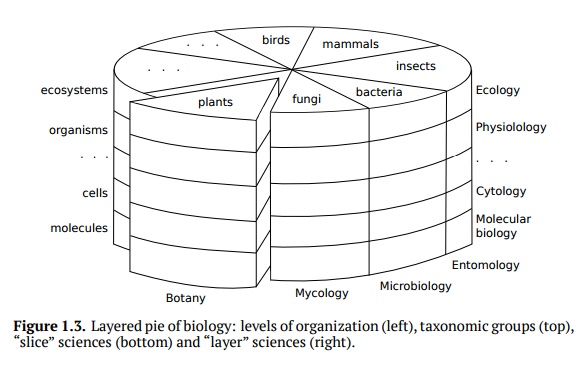
Botany is considered to be a “slice science”
because it covers multiple levels of organization.
Related Topics