Chapter: Microbiology and Immunology: Bacteriology: Pseudomonas, Burkholderia, and Moraxell
Pathogenesis and Immunity - Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Pathogenesis and Immunity
P. aeruginosa is an invasive pathogen.
◗ Virulence factors
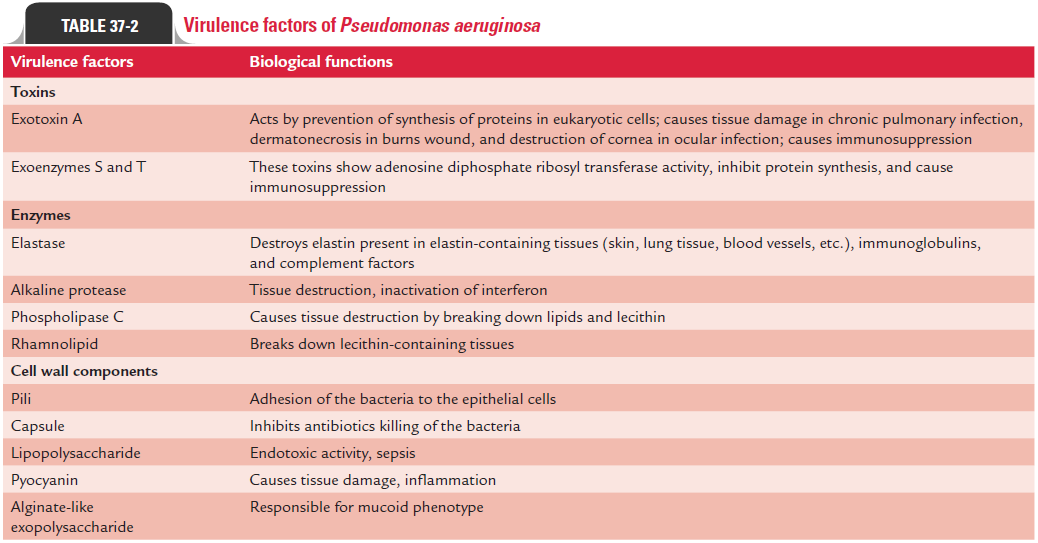
P. aeruginosa invasion is mediated by many virulence fac-tors including toxins, enzymes, and structure of the cell wall (Table 37-2) as follows:
1. Toxins:These include exotoxin A, and exotoxins S and T.
2. Enzymes: Elastase, alkaline protease, phospholipase C,and rhamnolipid.
3. Cell wall components: Pili, loose slime layer, LPS, andpyocyanin.
Toxins
Exotoxin A : Exotoxin A is one of the most important virulencefactor produced by P. aeruginosa. The toxin like that of the diphtheria toxin acts by preventing synthesis of proteins in eukaryotic cells. Exotoxin A, however, differs from exotoxin ofCorynebacterium diphtheriae immunologically and structurally.Exotoxin A is less potent than diphtheria toxin. Exotoxin A is responsible for causing tissue damage in chronic pulmonary infection, dermatonecrosis in burns wound, and destruction of cornea in ocular infection. The toxin also causes suppression of immunity in the infected host.
Exotoxins S and T : Exotoxins S and T are the toxins producedby P. aeruginosa. These toxins show adenosine diphosphate ribosyl transferase activity. These toxins are believed to facilitate spread of bacteria and invasion of tissues followed by necrosis by causing damage in the epithelial cells.
Enzymes
Elastase: The enzyme elastase is of two types: serine protease(LasA) and zinc metalloprotease (LasB). These two enzymes act in combination to destroy elastin present in elastin-containing tissues. These enzymes cause damage in parenchymal tissues of the lung and produce hemorrhagic lesions associated with spreading P. aeruginosa infections. These enzymes also facilitate spread of infection and damage of tissues in acute infections by degrading several components of the complement and also by inhibiting chemotaxis activities of neutrophils. Chronic P. aeruginosa infection is associated with development ofantibodies to both the enzymes, LasA and LasB, and deposition of immune complexes in the infected tissues.
Alkaline protease: Alkaline protease is also responsiblefor destruction of tissue and dissemination of P. aeruginosa infection. The enzyme also interferes with immune response of the host.
Phospholipase C: Phospholipase C is a heat-labile hemolysin.It contributes to tissue destruction by breaking down lipids and lecithin.
Rhamnolipid: Rhamnolipid is a heat-stable hemolysin. It alsocontributes to breaking down of lecithin-containing tissues.
Cell wall
These include pili, loose slime layer, LPS, and pyocyanin as described earlier (Table 37-2).
Related Topics