Chapter: Mechanical and Electrical : Power Plant Engineering : Diesel,Gas Tubine and Combined Cycle Power Plants
Operation Theory of Gas Turbine Power Plant
GAS TURBINE POWER PLANT
A gas
turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of internal combustion
engine. It has an upstream rotating compressor coupled to a downstream
turbine,and a combustion chamber in-between. Energy is added to the gas stream
in the combustor, where fuel is mixed with air and ignited. In the high
pressure environment of the combustor, combustion of the fuel increases the
temperature. The products of the combustion are forced into the turbine
section.
There,
the high velocity and volume of the gas flow is directed through a nozzle over
the turbine's blades, spinning the turbine which powers the compressor and, for
some turbines, drives their mechanical output. The energy given up to the
turbine comes from the reduction in the temperature and pressure of the exhaust
gas.
Theory of
operation
Gasses passing through an ideal a gas turbine
undergo three thermodynamic processes. These are isentropic compression,
isobaric (constant pressure) combustion and isentropic expansion. Together
these make up the Brayton cycle.
In a practical gas turbine,
gasses are first accelerated in either a centrifugal or radial compressor.
These gasses are then slowed using a diverging nozzle known as a diffuser,
these process increase the pressure and temperature of the flow. In an ideal
system this is isentropic. However, in practice energy is lost to heat, due to
friction and turbulence. Gasses then pass from the diffuser to a combustion
chamber, or similar device, where heat is added. In an ideal system this occurs
at constant pressure (isobaric heat addition). As there is no change in
pressure the specific volume of the gasses increases.
LAYOUT OF GAS TURBINE POWER PLANT
The gas
turbine power plants which are used in electric power industry are classified
into
two groups as per the cycle of operation.
(1) Open
cycle gas turbine.
(2) Closed
cycle gas turbine.
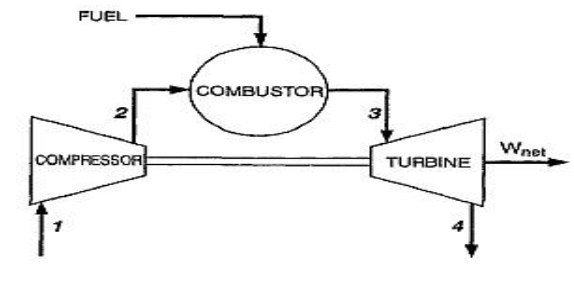
Open cycle gas turbine 1-
Atmospheric Air
2-
Compressed Atmospheric Air
3- Fuel
air mixture after compression
4- Exhaust gases.
The
heated gases coming out of combustion chamber are then passed to the turbine
where
it expands doing mechanical work. Part of the power developed
by the turbine is utilized in
driving the compressor and other accessories and remaining is
used for power generation.
Since ambient air enters into the compressor and gases coming
out of turbine are exhausted into the atmosphere, the working medium must be
replaced continuously. This type of cycle is known as open cycle gas turbine
plant and is mainly used in majority of gas turbine power plants as it has many
inherent advantages.
Closed
cycle gas turbine power plant
In this, the compressed air from
the compressor is heated in a heat exchanger (air heater) by some external
source of heat (coal or oil) at constant pressure. Then the high pressure hot
gases expand passing through the turbine and mechanical power is developed. The
exhaust gas is then cooled to its original temperature in a cooler before
passing into the compressor again.
The main difference between the
open and closed cycles is that the working fluid is continuously replaced in
open cycle whereas it is used again and again in a closed cycle. The open cycle
plant is much lighter than the closed cycle. Hence it is widely used.
1- Low Pressure Working Fluid @ Low temperature
2- High Pressure Working Fluid
3- Fuel + Working Fluid mixture @ High Pressure
and Temperature 4- Low Pressure Working Fluid @ Temperature T4 <
Temperature T3
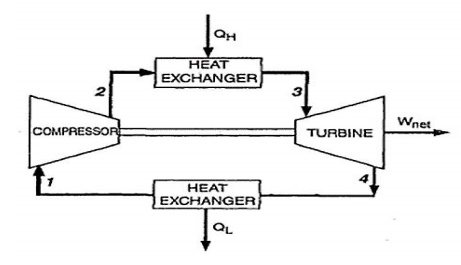
In closed cycle gas turbine
plant, the working fluid (air or any other suitable gas) coming out from
compressor is heated in a heater by an external source at constant pressure.
The high temperature and
high-pressure air coming out from the external heater is passed through the gas
turbine. The fluid coming out from the turbine is cooled to its original
temperature in the cooler using external cooling source before passing to the
compressor.The working fluid is continuously used in the system without its
change of phase and the required heat is given to the working fluid in the heat
exchanger
Related Topics