Chapter: Mobile Networks : Routing
On Demand Multicast Routing Protocol (ODMR): Algorithm, Illustration, Advantages, Disadvantages
ON DEMAND MULTICAST ROUTING PROTOCOL (ODMR)
1. On- Demand Multicast routing protocol is a mesh
architecture protocol, i.e, it has multiple paths from the sender to the receivers
and uses a forwarding group concept.
2. It applies on-demand procedures to dynamically
build route and maintain multicast group membership.
3. By maintaining a mesh instead of a tree, the
drawbacks of multicast trees in ad hoc networks like frequent tree reconfiguration
and non-shortest path in a shared tree are avoided.
4. In ODMRP, group membership and multicast routes
are established by the source on demand when a multicast source has packets to
send, but no route to the multicast group, it broadcasts a Join-Query control
packets to the entire network.
5. This control packet is periodically broadcast
to refresh the membership information and
updates routes.
6. When the Join-Query packet reaches a multicast
receiver, it creates and broadcasts Join- Reply
to its neighbours. When it has been received by the node, it checks if the next
hop own id.
7. If it is does, the node realizes that it is on
the path to the source and becomes the part of the forwarding group by setting
the FG_FLAG (Forwarding Group flag).
8. When receiving a multicast data
packet, a node forwards it only
when it is not a duplicate, hence minimizing traffic
overhead. Because the nodes maintain soft state, finding the optimal flooding
interval is critical to ODMRP performance.
9. ODMRP uses location and movement information to
predict the duration of time that routes will remain valid. With the predicted
time of route disconnection, a ―join data‖ packet is flooded when route breaks
of ongoing data sessions are imminent.
10. It reveals that ODMRP is better suited for ad
hoc networks in terms of bandwidth utilization
Example
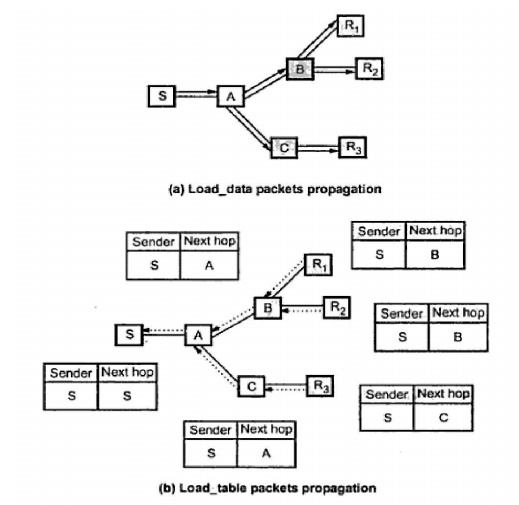
Consider the source node ‗S‘. It will flood the
JOIN_DATA packets to all other nodes in the network. When a host node receives
first JOIN_DATA packet it will rebroadcast it to form a reverse path with the
previous host. Each host in the network acts as multicast receiver. It receives
JOIN_DATA packet and replies in turn with a JOIN_TABLE packet to the upstream
to establish reverse paths.
The process repeats until source host ‗S‘ is reached.
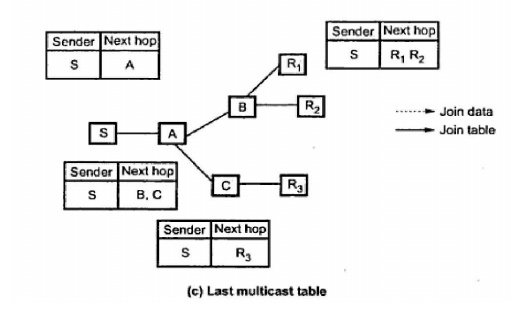
The method of packet forwarding is for Figure (a) is shown in Figure (b). As
the JOIN_TABLE is received a host has to build a multicast table so as to
facilitate future packet forwarding. For example the host B receives the R1‘s
JOIN_TABLE which is shown in the diagram.
It will add R1 as its next hop step. Assume B
receives R2 ‘s JOIN_TABLE. Now it will add R2 as its next hop step. A simple
final multicast table for each host is shown in the Figure (c) in propagation
of data packets.
Advantages
1. Low channel and storage overhead
3. Usage of
up-to-date shortest routes
4. Robustness
to host mobility
5. Maintenance
and exploitation of multiple redundant paths
6. Exploitation
of the broadcast nature of the wireless environment
7. Unicast
routing capability
Disadvantages
0 The main
disadvantage of ODMRP is its excessive overhead, because broadcasting of the
reply packets to many nodes.
1 It has a
complex topology.
Related Topics