Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Management of Patients With Immunodeficiency
Nursing Management for Patients With Immunodeficiencies
Nursing Management for Patients With
Immunodeficiencies
Nursing management includes assessment,
patient teaching, and supportive care. Assessment of the patient for infection
and for response to treatment is important if it is to be effective. Nursing
care of patients with primary and secondary immunodeficiencies depends on the
underlying cause of the immunodeficiency, the type of immunodeficiency, and its
severity. Because immuno-deficiencies result in a compromised immune system and
high risk for infection, careful assessment of the patient’s immune status is
essential. The assessment focuses on history of past infec-tions, particularly
the type and frequency of infection; signs and symptoms of any current skin,
respiratory, gastrointestinal, or genitourinary infection; and measures that
prevent infection. The nurse monitors the patient for signs and symptoms of
infection: fever; chills; cough with or without sputum; shortness of breath;
difficulty breathing; difficulty swallowing; white patches in the oral cavity;
swollen lymph nodes; nausea; vomiting; persistent diarrhea; frequency, urgency,
or pain on urination; redness, swelling, or drainage from skin wounds; lesions
on the face, lips, or perianal area; persistent vaginal discharge with or
without perianal itching; and persistent abdominal pain.
Because the inflammatory response may be blunted, the pa-tient is monitored for subtle and unusual signs and changes in physical status. Vital signs and the development of pain, neuro-logic signs, cough, and skin lesions are monitored and reported. Pulse rate and respiratory rate should be counted for a full minute, as even subtle changes can signal deterioration in the patient’s clin-ical status. Thorough auscultation and assessment of the breath sounds are also key in detecting changes in respiratory status. Any unusual response to treatment and any significant change in the patient’s clinical condition are promptly reported to the physician.
The nurse also monitors laboratory values
(ie, white blood cell count and differential cell count) for changes indicating
infection. Culture and sensitivity reports from wound drainage, lesions,
spu-tum, stool, urine, and blood are monitored to identify pathogenic organisms
and appropriate antimicrobial therapy. Changes in laboratory results and subtle
changes in clinical status must be re-ported to the physician because the
immunocompromised pa-tient may not develop typical signs and symptoms of
infection.
Assessment also focuses on nutritional
status; stress level and coping skills; use of alcohol, drugs, or tobacco; and
general hy-giene, all of which may affect immune function. Strategies the
pa-tient has used to reduce risk for infection are identified.
Other aspects of nursing care are directed
toward reducing the patient’s risk for infection, assisting with medical
measures aimed at improving immune status and treating infection, improving the
nutritional status, and maintaining bowel and bladder func-tion. These include
careful hand hygiene, encouraging the patient to cough and perform
deep-breathing exercises at regular inter-vals, and protecting the integrity of
the skin and mucous mem-branes. All health care personnel must use strict
aseptic technique when performing invasive procedures, such as dressing
changes, venipunctures, and bladder catheterizations.
Other
aspects of nursing care include assisting the patient in managing stress and in
adopting a lifestyle that enhances immune system function.
If the patient is a candidate for any of the
newer or experi-mental therapies (gene therapy, bone marrow transplantation,
immunomodulators such as interferon gamma), the patient or parents (if the
patient is a child) must be informed about the po-tential risks and benefits of
the treatment regimen. A major role of the nurse is to assist the patient and
family to understand the treatment options and to cope with the uncertainties
of treatment outcomes.
PROMOTING HOME AND COMMUNITY-BASED CARE
Teaching Patients Self-Care.
The patient and the caregivers areinstructed about the signs and
symptoms that indicate infection. The nurse explains that the immunosuppressed
patient may also have atypical symptoms secondary to underlying
immunosup-pression. Patients should be advised that they know themselves best;
therefore, whenever they experience a symptom that is not typical for them,
they should contact their health care provider. The health care provider will
then determine and initiate indi-cated therapy. The patient and caregiver need
instruction about any prophylactic medication regimen, including dosage,
indica-tions, times, actions, and side effects. The patient is instructed about
the importance of avoiding others with infections and avoiding crowds. The
patient and family also need to learn about other ways to prevent infection
(Chart 51-3).
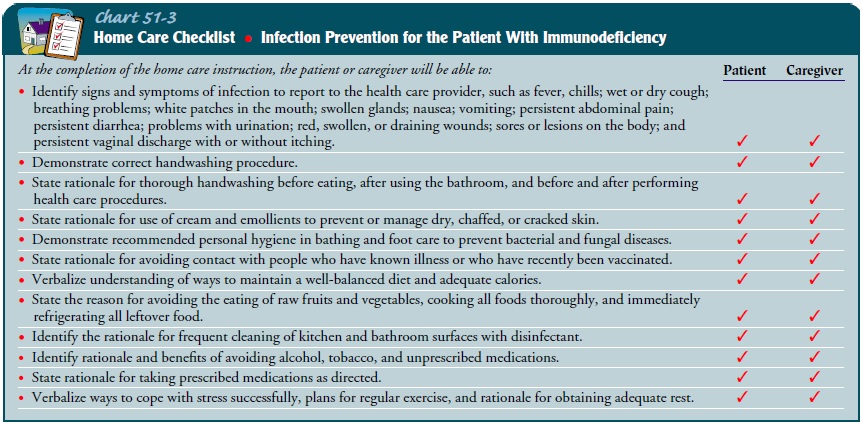
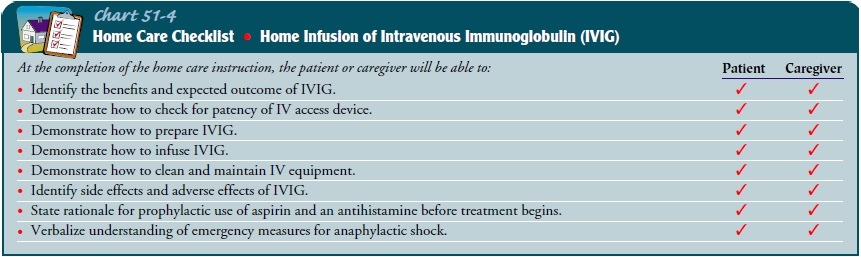
The patient who is to receive IVIG at home will need infor-mation about the expected benefits and outcomes of the treat-ment as well as expected adverse reactions and their management (Chart 51-4). Patients who can perform self-infusion at home are instructed in sterile technique, medication dosages, administra-tion rate, and detection and management of adverse reactions.
The
patient and family must be instructed to monitor for sub-tle changes in
physical status and must be informed of the im-portance of seeking immediate
health care if changes occur. Patients and their families are also instructed
about the impor-tance of continuing the treatment regimen and assisted in
incor-porating it into their lives.
Continuing Care.
The
importance of follow-up appointments isemphasized to the patient and family.
They are urged to notify the primary health care provider about early signs and
symptoms of infection, including any subtle changes. The importance of
continuing disease-prevention strategies is stressed because these strategies
need to be followed lifelong. The patient should be en-couraged to have
recommended health screening because of the increased susceptibility for cancer
secondary to the immune suppression.
If the
patient’s treatment includes IVIG and the patient or family cannot administer
it, a referral for home care or an infu-sion service may be warranted.
Related Topics