Chapter: Essential Anesthesia From Science to Practice : Clinical management : The anesthesia machine
Multi-valve system with gas storage - The anesthesia machine
Multi-valve system with gas
storage
A
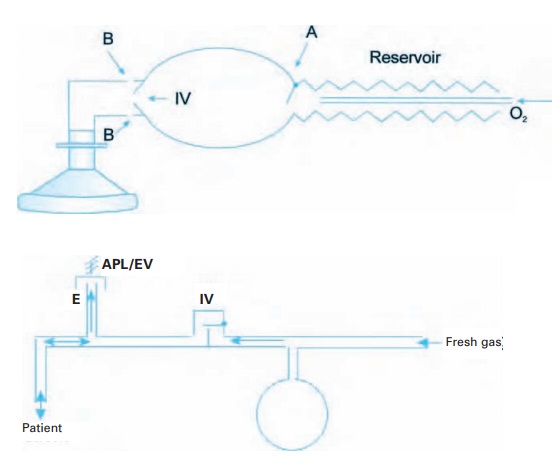
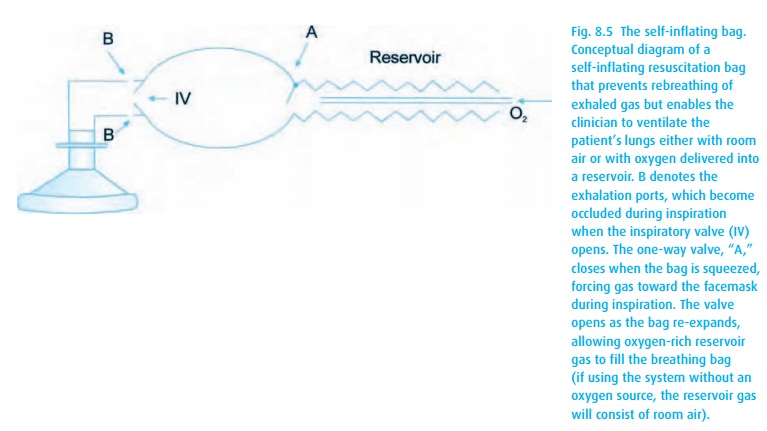
self-inflating bag provides an alternative that enables the resuscitator to
venti-late the patient’s lungs with room air or, if oxygen is available, with
air enriched with oxygen. For the latter to succeed, the self-inflating bag
must have a reservoir in which oxygen can accumulate during inspiration (see
Fig. 8.5).
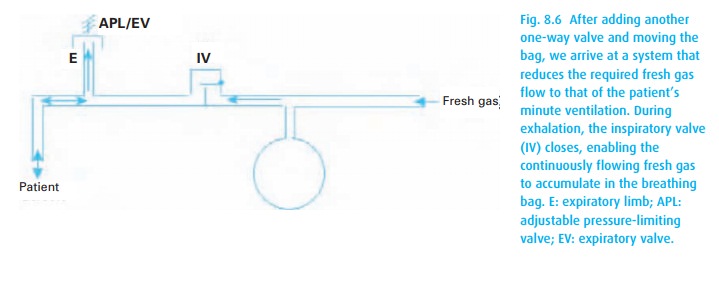
Without
a self-inflating bag, gas has to be admitted to the breathing system under
pressure. Figure 8.6shows a simple
arrangement. We incorporate a bag and two valves. Now the fresh gas accumulates
in the bag during exhalation when the inspiratory valve closes and the
expiratory valve opens (venting CO2-laden gas to the atmosphere).
During inspiration the valves swap roles: the inspiratory valve opens and the
expiratory one closes. Such valves have little resistance, perhaps 1 or 2 cm H2O,
and thus will easily open during the respiratory cycle. This works for a
patient breathing spontaneously. Again, an adjustable pressure-limiting valve
on top of the expiratory limb enables us to ventilate the patient’s lungs.
Related Topics