Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 18 : Heredity
Monohybrid Cross - Inheritance of One Gene
Monohybrid Cross - Inheritance of One Gene![]()
![]()
Crosses involving inheritance
of only one pair of contrasting characters are called monohybrid
crosses. For example it is a cross between two forms of a single trait like a
cross between tall and dwarf plant.
MendelŌĆÖs Explanation of
Monohybrid Cross
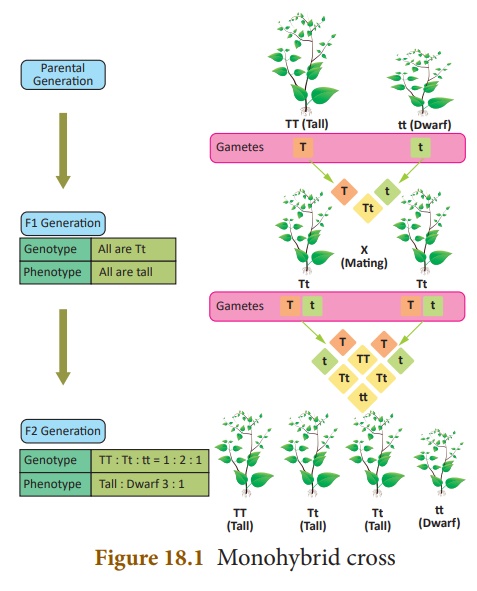
Parental generation: Pure breeding tall plant
and a pure breeding dwarf plant.
F1
generation: Plants raised from the seeds of pure breeding parental
cross in F1 generation were tall and monohybrids.
F2
generation: Selfing of the F1 monohybrids resulted in
tall and dwarf plants respectively in the ratio of 3:1. The actual number of
tall and dwarf plants obtained by Mendel was 787 tall and 277 dwarf. External
expression of a particular trait is known as phenotype. So the phenotypic ratio
is 3:1.
In the F2
generation 3 different types were obtained:
Tall Homozygous ŌĆō TT
(Pure) ŌĆō 1
Tall Heterozygous ŌĆō Tt ŌĆō
2
Dwarf Homozygous ŌĆō tt ŌĆō
1
So the genotypic
ratio 1:2:1. A genotype is the genetic expression of an organism
MendelŌĆÖs Interpretation on Monohybrid cross
Based on these
observations it was confirmed by Mendel that ŌĆśfactorsŌĆÖ are passed on from one
generation to another, now refered to as genes . Tallness and
Dwarfness are determined by a pair of contrasting factors tall
plant possess a pair of factors (represented by T- taking the first letter of
the dominant character) and a plant is dwarf because it possess factors for
dwarfness (represented as t- recessive character).
These factors occur in pairs and may be alike
as in pure breeding tall plants (TT) and dwarf plants (tt). This is referred to
as homozygous . If they are unlike (Tt) they are referred to as heterozygous.
1. Two factors making up
a pair of contrasting characters are called alleles or allelomorphs.
One member of each pair is contributed by one parent.
2. When two factors for
alternative expression of a trait are brought together by fertilization only
one expresses itself, (tallness) masking the expression of the other
(dwarfness). The character which expresses itself is called
dominant condition and that which is masked is called recessive
condition.
3. The
factors are always pure and when gametes are formed, the unit factors segregate
so that each gamete gets one of the two alternative factors. It means that
factors for tallness(T) and dwarfness(t) are separate entities and in a gamete
either T or t is present. When F1 hybrids are self crossed the two
entities separate and then unite independently, forming tall and dwarf plants.
Related Topics