Structure, Types | Heredity - Chromosomes, DNA and Genes | 10th Science : Chapter 18 : Heredity
Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 18 : Heredity
Chromosomes, DNA and Genes
Chromosomes,
DNA and Genes
The human body is made
up of million cells. The nucleus of each cell contains thin thread like
structures called chromosomes. The term ŌĆśchromosomesŌĆÖ was first coined
by Waldeyer in 1888. The chromosomes are the carrier of genetic
material which contain the heredity information.
The chromosomes are
highly condensed coiled chromatin fibres packed with the DNA (Deoxyribonucleic
acid) that forms the genetic material. Genes are segments of DNA,
which are responsible for the inheritance of a particular phenotypic character.
Each gene is present at a specific position on a chromosome called its locus.
During cell division, the genetic information present in the genes are passed
from one generation to another.
1. Structure of a Chromosome
The chromosomes are
thin, long and thread like structures consisting of two identical strands
called sister chromatids. They are held together by the centromere. Each chromatid
is made up of spirally coiled thin structure called chromonema. The
chromonema has number of bead-like structures along its length which are
called chromomeres. The chromosomes are made up of DNA,RNA, chromosomal
proteins (histones and non-histones) and certain metallic ions. These proteins
provide structural support to the chromosome .
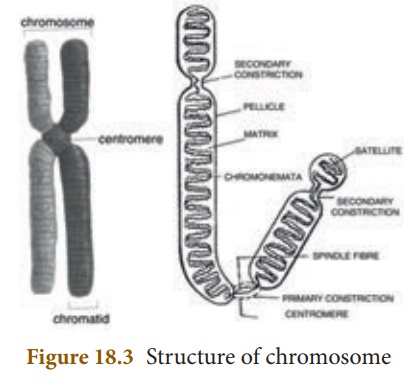
A chromosome consists of
the following regions
Primary constriction: The two arms of a chromosome
meet at a point called primary constriction or centromere.
The centromere is the region where spindle fibres attach to the
chromosomes during cell division.
Secondary constriction: Some chromosomes possess
secondary constriction at any point of the chromosome. They are known as
the nuclear zone or nucleolar organizer (formation of nucleolus in the
nucleus).
Telomere: The end of the
chromosome is called telomere. Each extremity of the chromosome has
a polarity and prevents it from joining the adjacent chromosome. It maintains
and provides stability to the chromosomes.
Satellite: Some of the chromosomes
have an elongated knob-like appendage at one end of the
chromosome known as satellite. The chromosomes with satellites are called as
the sat-chromosomes.
2. Types of Chromosomes based on the position of Centromere
Based on the position of
centromere, the chromosomes are classified as Telocentric, Acrocentric,
Submetacentric and Metacentric
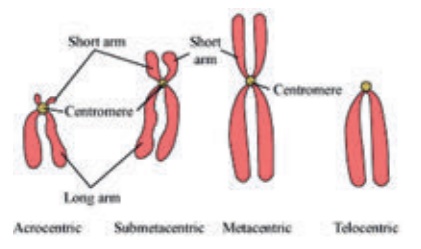
a)
TelocentricŌĆō The centromere is found on the proximal end. They are rod
shaped chromosomes.
b)
Acrocentric ŌĆō The centromere is found at the one end with a short arm
and a long arm. They are also rod-shaped chromosomes.
c)
Submetacentric ŌĆō The centromere is found near the centre
of the chromosome. Thus forming two unequal arms. They are J shaped or L shaped
chromosomes.
d)
Metacentric ŌĆō The centromere occurs in the centre of the chromosome and
form two equal arms. They are V shaped chromosomes
3. Types of Chromosomes based on function
The eukaryotic
chromosomes are classified into autosomes and allosomes.
Autosomes contain genes
that determine the somatic (body) characters. Male and female have equal
number of autosomes.
Allosomes are chromosomes
which are responsible for determining the sex of an individual. They are also
called as sex chromosomes or hetero-chromosomes. There are
two types of sex chromosomes, X and Y- chromosomes. Human male have one X
chromosome and one Y chromosome and human female have two X chromosomes.![]()
![]()
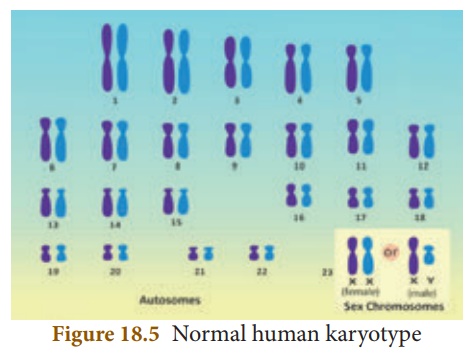
4. Karyotype
The number of
chromosomes in any living organism (animal or plant) is constant. In human,
each cell normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes. Out of which 22
pairs are autosomes and the 23rd pair is the allosome or sex chromosome.
In the body cells of
sexually reproducing organisms, the chromosomes generally occur in pairs. This
condition is called diploid (2n). The gametes produced by the organisms
contain a single set of chromosomes. Hence, the gametes are said to be haploid
(n).
Karyotype is the number,
size and shape of chromosomes in the cell nucleus of an organism.
Idiogram is the diagrammatic representation of karyotype of a species.
It consists of all the metaphasic chromosomes arranged in homologous pairs
according to decreasing length, thickness, position of centromere, shape etc.,
with the sex chromosomes placed at the end.
Related Topics