Heredity - Dihybrid Cross-Inheritance Two Genes and Law of Independent Assortment | 10th Science : Chapter 18 : Heredity
Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 18 : Heredity
Dihybrid Cross-Inheritance Two Genes and Law of Independent Assortment
Dihybrid
Cross-Inheritance Two Genes and Law of Independent Assortment
Dihybrid cross involves
the inheritance of two pairs of contrasting characteristics (or
contrasting traits) at the same time. The two pairs of contrasting
characteristics chosen by Mendel were shape and colour of seeds: round-yellow
seeds and wrinkled-green seeds.
1. Mendel crossed pea
plants having round-yellow seeds with pea plants having wrinkled-green seeds.
Mendel made the following observations: Mendel first crossed pure breeding pea
plants having round-yellow seeds with pure breeding pea plants having
wrinkled-green seeds and found that only round-yellow seeds were produced in
the first generation (F1). No wrinkled-green seeds were obtained in
the F1 generation. From this it was concluded that round shape
and yellow colour of the seeds were dominant traits over the wrinkled
shape and green color of the seeds.
2. When the hybrids of F1 generation pea plants having round-yellow seeds were cross-bred by self pollination, then four types of seeds having different combinations of shape and color were obtained in second generation or F2 generation. They were round yellow, round-green, wrinkled yellow and wrinkled-green seeds.
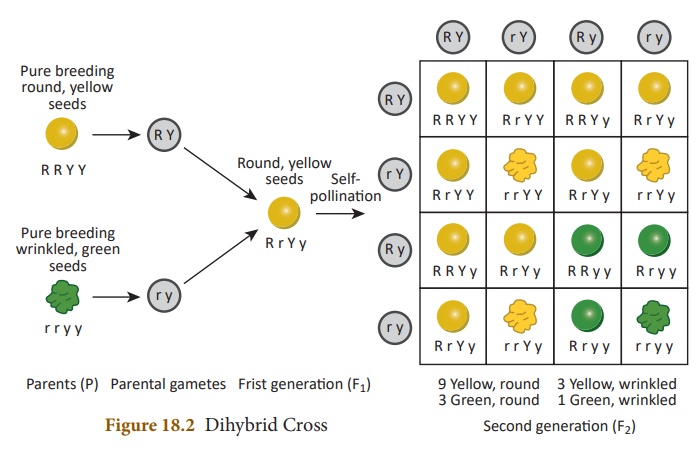
The ratio of each
phenotype (or appearance) of seeds in the F2 generation is
9:3:3:1. This is known as the Dihybrid ratio.
From the above results
it can be concluded that the factors for each character or trait remain
independent and maintain their identity in the gametes. The factors are
independent to each other and pass to the offsprings (through gametes).
Results of a Dihybrid Cross:
Mendel got the following
results from his dihybrid cross
1. Four Types of Plants:
A dihybrid cross produced
four types of F2 offsprings in the ratio of 9 with two dominant traits,
3 with one dominant trait and one recessive trait, 3 with another dominant
trait and another recessive trait and 1 with two recessive traits.
2. New Combination: Two new combinations of
traits with round green and wrinkled yellow had appeared in the dihybrid cross
(F2 generation).
Related Topics