Chapter: Health Management in Aquaculture: Parasitic diseases and pests
Monogenean Infestations - Fish Diseases Caused by Parasites
Monogenean Infestations
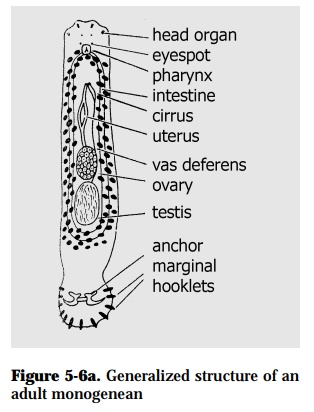
Monogeneans are ectoparasitic flatworms, <1-5 mm long, with posterior organ of attachment called haptor armed with hooks and/or suckers (Fig. 5-6a)
CAUSATIVE AGENTS:
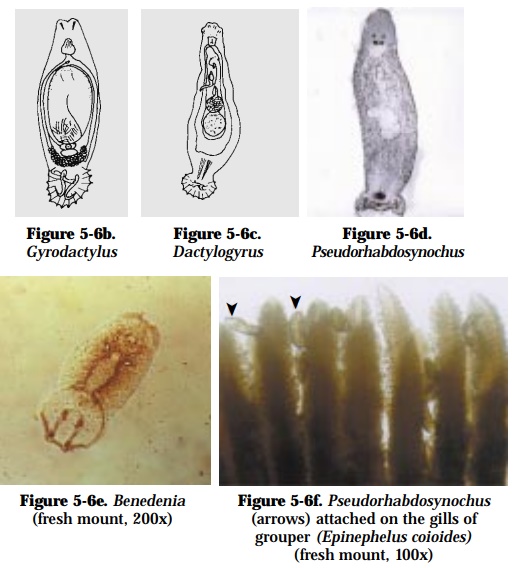
Gyrodactylus (Fig. 5-6b), Dactylogyrus (Fig. 5-6c), Pseudorhabdosynochus(Fig. 5-6d), Benedenia (Fig. 5-6e)
SPECIES AFFECTED:
Catfish, carp, tilapia, seabass, grouper, snapper
GROSS SIGNS:
Parasite attaches on gills (Fig. 5-6f), fins and body surface of fish. Affected fish have pale skin and gills with increased mucus production, frayed fins, and the cornea may become opaque.
EFFECTS ON HOST:
Heavy infestation may result to hyperplasia of the epithelial cells in the skin. Extensive damage to the gill epithelium may affect normal respiration. Heavy infestations may result in mortality. Conditions of low oxygen levels may increase mortality rates. Often associated with vibriosis.
DIAGNOSIS:
Gross and microscopic examination of gills and body surface of freshly sac-rificed fish.
PREVENTION AND CONTROL:
• Maintain optimum stocking density and adequate feeding
• 5% salt solution for 5 minutes
• Freshwater bath for 1 h for 3 days
• 100 ppm formalin for 1 h for 3 days
• 150 ppm hydrogen peroxide for 30 min
Related Topics