Geography - Minerals and its Types in India | 10th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 4 : India - Resources and Industries
Chapter: 10th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 4 : India - Resources and Industries
Minerals and its Types in India
Minerals
Mineral is a natural substance of organic or
inorganic origin with definite chemical and physical properties. The process of
extracting mineral from the earth is known as mining. The mines near the earth
crust are known as open pit mines while the deep mines are known as shaft
mines.
The organisations associated
with minerals in India are
1. The Geological
Survey of India Headquarter is at Calcutta
2. Indian Bureau of
Mines Headquarter at Nagpur
3. Non-Ferrous
Material Technology Development Centre NFTDC, Hyderabad.
4. The Ministry of
Mines is responsible for the administration of all mines and minerals
(Development and Regulation Act, 1957).
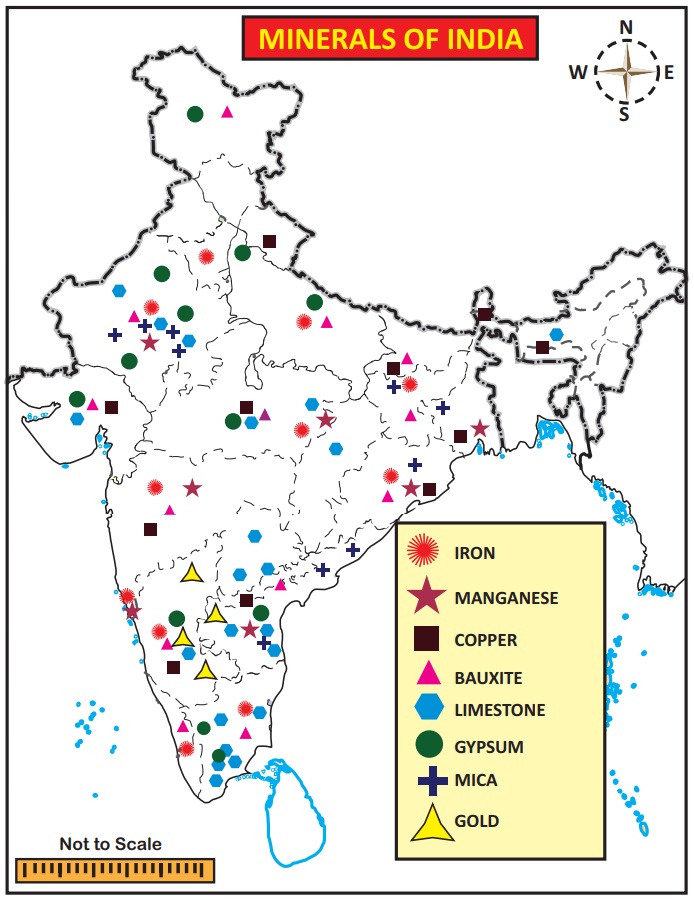
Types of Minerals
On the basis of chemical and physical properties,
minerals are broadly grouped under two categories. They are metallic and
non-metallic minerals.
A) Metallic Minerals
Metallic minerals are the minerals which contain one or more metallic elements in them. Metallic minerals occur in rare, naturally formed concentrations known as mineral deposits. These deposits consist of a variety of valuable metals such as iron, manganese, copper, bauxite, nickel, zinc, lead, gold etc.
The iron is usually found in
following form.
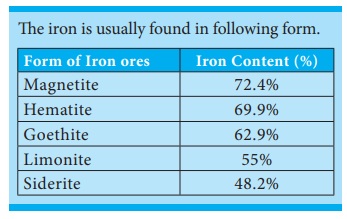
Form of Iron ores: Iron Content (%)
Magnetite: 72.4%
Hematite: 69.9%
Goethite: 62.9%
Limonite: 55%
Siderite: 48.2%
1. Iron ore
Iron ore
is the most widely distributed elements of the earth crust, rarely occurs in a
free state. It enters into the composition of many rocks and minerals
especially from igneous and metamorphic rocks. The total recoverable reserves
of iron ore in India are haematite and magnetite
Jharkhand is the leading producer of iron ore with
25% the country’s production. Singhbhum, Hazaribagh, Dhanbad and Ranchi
districts are its major producers. Odisha with 21% production ranks second.
Sundargarh, Mayurbhanj, Sambalpur and Keonjhar districts are its major
producers. The magnetite production of Chhattisgarh is 18% (Rajgarh and
Bilaspur are its leading districts) and the Karnataka is 20% (Chikmangalur,
Chitradurga, Shimoga and Dharwad districts are its major producers). Andhrapradesh
and Tamil Nadu produce about 5% each. Kurnool, Guntur, Cuddapah and Anantapur
districts in Andhra Pradesh and Salem, Namakkal, Tiruvannamalai,
Tiruchirappalli, Coimbatore, Madurai and Tirunelveli districts in Tamil Nadu
are notable for the production of iron ore.
SAIL (Steel Authority of India
Limited): The Ministry of Steel is responsible for planning and development of
iron and steel industry in India.

2. Manganese
Manganese is a silvery grey element. It is very
hard and brittle in nature. It is always available in combination with iron,
laterite and other minerals. It is an important mineral used for making iron
and steel and serves as basic raw material for alloying. It is the most
important mineral for making iron and steel. Nearly 10 kg manganese is required
for manufacturing one ton of steel. It is also used in the manufacturing of
bleaching powder, insecticides, paints and batteries.
MOIL- Manganese Ore
India Limited state-owned manganese ore mining company headquartered in Nagpur. With a
market share of 50%. It was the largest producer of manganese ore in India.

Manganese
deposits occur mainly as metamorphosed bedded sedimentary deposits. The largest
deposits of manganese is found in Odisha followed by Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh,
Maharashtra, Goa, Andhra Pradesh, Jharkhand, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Telengana and
West Bengal together constitute about 2% of the India’s manganese resource.
India is the fifth largest producer of manganese in the world.
3. Copper
Copper is
the first metal that prehistoric man has started using for many purposes. Being
flexible, it can be made into utensils of any shape. Brass and Bronze are
obtained when the copper alloys with zinc and tin respectively. Copper has been
commonly used for making cooking utensils and other objects of common utility.
In modern days, it is extensively used in vast variety of electrical machinery,
wires and cables
Largest
reserves of copper ore is in the state of Rajasthan followed by Jharkhand and
Madhya Pradesh. The states of Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Haryana, Karnataka,
Maharashtra, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Odisha, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, Telangana,
Uttarakhand and West Bengal account for 7.9% of the total copper reserves of
India.
Hindustan Copper Ltd
is a Government-owned-corporation
in the central public Enterprise under the Ministry of minies, India.

4. Bauxite
Bauxite
is an important ore from which aluminium is extracted. It is found in the rock
consisting mainly of hydrated aluminium oxides. Bauxite is widely distributed
as surface deposits in the areas of laterite soil. Being light in weight and
tough, aluminium is used in the manufacture of aircraft s and automobile
engines. Bauxite is also used in the manufacture of cement and chemicals.
Bauxite is an oxide of aluminium; the name has been derived
after the French word Le Baux.
The main
bauxite deposits occur in Odisha, Gujarat (Junagadh, Amreli and Bhavnagar
districts), Jharkhand (Ranchi and Gumila districts), Maharashtra (Sindhu durg
and Ratnagiri), Chhattisgarh (Ballarpur and Durg districts), and Tamil nadu.
National Aluminium
Company Limited, abbreviated as NALCO, (incorporated
1981) has units in Odisha at places like Angul and Damanjodi. It was
incorporated as a public sector enterprise of the Ministry of Mines, Government
of India in 1981.

B) Non-Metallic Minerals
These
minerals do not contain metal in them. Mica, limestone, gypsum, nitrate,
potash, dolomite, coal, petroleum etc are the non-metallic minerals.
Mica
In
ancient time, Mica was used in ayurvedic medicine. Mica became very popular
with the development of electrical industry. Abhrak is a good quality mica. It
is translucent, easily splitable into thin sheets, flat, colourless, elastic and
incompressible. Mica is used in making of insulating properties, as it
withstands high voltage and has low power loss factor. Since it is a non
conductor of electricity, it is exclusively used in electrical goods. It is
also used in making of lubricants, medicines, paints and varnishes.
The major
deposits of mica are found in Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan, Odisha and Jharkhand.
Lime Stone
Limestone
is associated with rocks composed of either calcium carbonate or the double
carbonate of calcium and magnesium or mixture of both. Limestone also contains
small quantities of silica, alumina, iron oxides, phosphorous and sulphur.
Limestone
is used in the industries of chemicals for soda ash, caustic soda, bleaching
powder, paper, cement, iron and steel, glass and fertilizers. The major
producing areas: Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Rajasthan, Madhya
Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Meghalaya, Gujarat and Chhattisgarh
Gypsum
Gypsum is
a hydrated sulphate of calcium which occurs as white, opaque or transparent
minerals in beds of sedimentary rocks such as limestone, sandstone and shale.
Gypsum is used in the manufacture of cement, fertilizers, wall board, plaster
of paris and in soil conditioning. Rajasthan, Tamil nadu, Gujarat, Himachal
Pradesh, Karnataka, Uttarakhand, Andhra Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh are the
major producers.
Related Topics