Geography - Industries in India | 10th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 4 : India - Resources and Industries
Chapter: 10th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 4 : India - Resources and Industries
Industries in India
Industries
It refers
to the activities which converts the raw materials into finished products. This
sector is called as the value addition sector. On the basis of the source of
raw materials, Industries are classified into the Agro based industries, Forest
based industries and Mineral based industries.
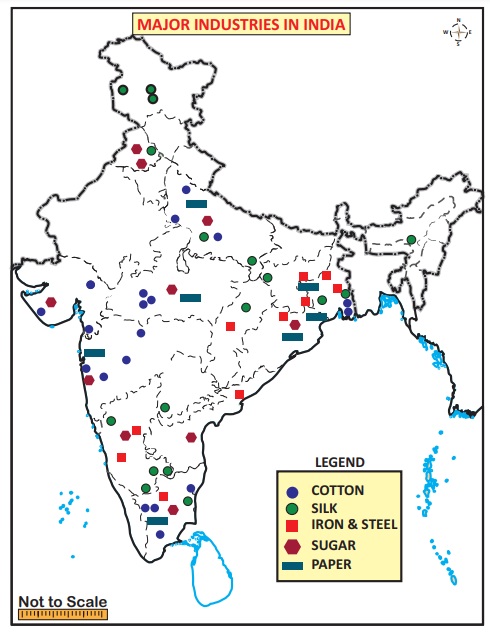
Agro based industries
These industries draw their raw materials from agricultural sector. The following part discusses the agro based industries in India.
a) Cotton Textile Industry
Textile
is a broad term which includes cotton, jute, wool, silk and synthetic fibre
textiles. This sector in India is the second largest in the world.
The first cotton textile mill was established at Fort Gloster
near Kolkata in 1818.
Traditional
sectors like hand loom, handicrafts and small power-loom units are the biggest
source of employment for millions of people in rural and semi urban areas.

Currently,
India is the third largest producer of cotton and has the largest loom arc and
ring spindles in the world. At present, cotton textile industry is the largest
organized modern industry of India.
Ginning is the process of separating cotton seed from cotton.
The higher concentration of textile mills in and around Mumbai, makes it as “Manchester of India”. Presence of black cotton soil in Maharastra, humid climate, presence of Mumbai port, availability of hydro power, good market and well developed transport facility favour the cotton textile industries in Mumbai.
The major cotton textile industries are concentrated in the states of Maharashtra, Gujarat, West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh and Tamil nadu. Coimbatore is the most important centre in Tamil nadu with 200 mills out of its 435 and called as “Manchester of South India”. Erode, Tirupur, Karur, Chennai, Thirunelveli, Madurai, Thoothukudi, Salem and Virudhunagar are the other major cotton textiles centres in the state.
b) Jute Textiles
Jute is a
low priced fibre used mainly for making package materials like gunny bags.
Today jute is blended with cotton and wool to produce textiles. This is the
second important textile industry in India after cotton textiles. Jute is the
golden fibre which meets all the standards of goods packing with its natural,
renewable, bio degradable and eco-friendly products.
The first
jute mill in India was established at Rishra near, Kolkata in 1854 by the
English man George Auckland. India tops in the production of raw jute and jute
goods and second in the export of jute goods next to Bangladesh. Jute
production includes gunny bags, canvas, pack sheets, jute web, carpets,
cordage, hessians and twines. Now jute is also being used in plastic furniture
and insulation bleached fibres to blend with wool. It is also mixed with cotton
to make carpet and blankets. The major jute producing areas are in West Bengal
and concentrated along the Hooghly river within the radius of six kilometre of
Kolkata. Titagarh, Jagatdat, Budge-Budge, Haora and Bhadreshwar are the chief
centres of jute industry. Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Assam,
Chhattisgarh and Odisha are the other jute goods producing areas.
National jute board is headquarter at Kolkata.

CSTRI is the only research institute in the country dedicated to
the Research
Developmental activities related to
silk technology. CSTRI was established in the year 1983 by the Central Silk
Board, Ministry of Textiles, Govt. of India having head quarter at Bengaluru

c) Silk Industry
India has been well known for the production of
silk since the ancient times. India is the second largest producer of raw silk
next only to China.
Karnataka is the largest producer of silk. Other
major producers of silk are West Bengal, Jammu Kashmir, Bihar, Jharkhand,
Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Assam and Tamil nadu states.
Office of the Development Commissioner for Handlooms was set up as an attached non-participating office on 20th November, 1975 under the Ministry of Commerce. At present it is functioning under the Ministry of Textiles, headquarters at Udyog Bhawan, New Delhi.

d) Sugar Industry
Sugar can
be produced from sugar cane, sugar-beets or any other crop which have sugar
content. In India, sugar cane is the main source of sugar. At present this is
the second largest agro based industry of India after cotton textiles. India is
the world’s second largest producer of sugar cane after Brazil. Sugar industry
is decentralized and located near the sugarcane growing areas as they are
weight loosing and bulky to transport.
Uttar Pradesh is the largest producer of sugar,
producing about 50% of the country’s total. Other major producers are
Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil nadu, Bihar,
Punjab, Gujarat, Haryana and Madhya Pradesh states. These states account for
more than 90% of the sugar mills and sugar production.
Forest based industries
Forest provide us with different types of material which are used as raw material for certain industries like paper, lac, sports goods, plywood etc.
a) Paper industry
Paper Industry produces numerous types of papers
that comes in various use such as sheet paper,paperboxes,tissues,paperbags,stationery,
envelopes and printed-paper products such as books, periodicals, and
newspapers. In India the Soft wood is the principal raw material used for
making paper especially newsprint and high class printing papers. Paper is the
pre-requisite for education and literacy and its use is an index of advancement
in these two fields as well as the overall well being of the society.

The first paper mill of India was
started in 1812 at Serampore in West Bengal.
The first successful effort was made in 1867 with
the setting up of the Royal Bengal paper mills at Ballyganj near Kolkata. The
raw materials for paper industry includes wood pulp, bamboo, salai and sabai
grasses, waste paper and bagasse. West Bengal is the largest producer of paper
in the country followed by Madhya Pradesh, Odisha and Tamil nadu.
National Newsprint and Paper Mills
(NEPA) is at Nepanagar in Burhanpur District of Madhya Pradesh.
Mineral based industries
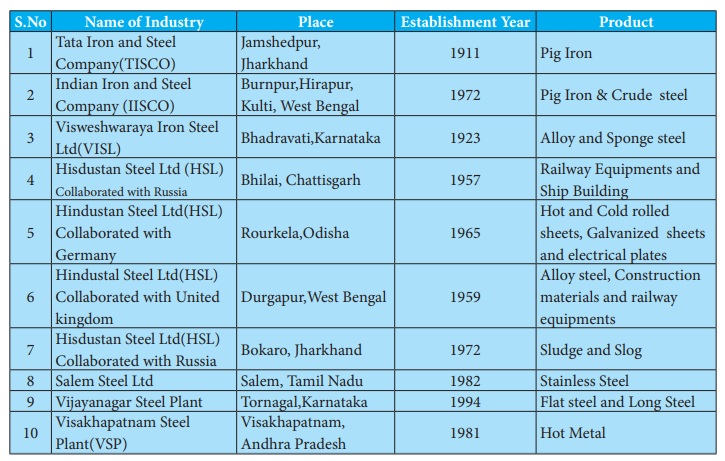
Mineral based industries use both metallic & non metallic minerals as raw materials. The major mineral based industry of country is the iron steel industry
a) Iron and steel industries
Iron and steel industry is called a basic
metallurgical industry as its finished product is used as raw material by host
of other industries. Several industries like engineering, heavy machines and
machine tools, automobile, locomotives and railway equipment industries use
iron and steel as their primary raw material. Due to this, the steel producing
capacity of a country is generally taken as an indicator of its level of
industrial development.
The first attempt to produce iron and
steel unit was set up at Porto Novo in Tamil nadu in 1830.
The
modernization of the industry was started in 1907 with the establishment of
Tata Iron and Steel Company at Sakchi, now called Jamshedpur. Iron and steel
industry of India is mainly concentrated in the states of Jharkhand, West
Bengal and Odisha. Proximity to the coal fields of Jharia, Raniganj, Bokaro and
Karanpura and the iron ore mines of Mayurbhanj, Keonjar and Brona are
responsible for this. This area also has sufficient deposits of limestone,
dolomite, manganese and silicon which are required for the industry.
Automobile Industry
India is
set to emerge not only as a large domestic market for automobile manufacturers,
but also as a crucial link in the global automotive chain. It is one of the
most dynamic industrial groups in India.
The first automobile industry of India was started
in 1947. The industry is the Premier Automobiles Ltd located at Kurla (Mumbai).
It was followed by the Hindustan Motors Ltd at Uttarpara (Kolkata) in 1948. At
present, India is the 7th largest producer of automobile manufacturers which
include two wheelers, commercial vehicles, passenger car, jeep, scooty,
scooters, motor cycles, mopeds and three wheelers. Major centres are at Mumbai,
Chennai, Jamshedpur, Jabalpur, Kolkata, Pune, New Delhi, Kanpur, Bengaluru,
Sadara, Lucknow and Mysuru.
Chennai is nicknamed as the “Detroit
of Asia” due to the presence of major automobile manufacturing units and allied
industries around the city.
Tata Motors, Maruti Suzuki, Mahindra & Mahindra
and Hindustan Motors are the largest passenger car manufacturers of Indian
companies in the country. Presence of foreign car companies such as Mercedes
Benz, Fiat, General Motors, Toyota and the recent entry of passenger car
manufacturers BMW, Audi, Volkswagen and Volvo makes the Indian automobile
sector a special one. Tata Motors, Ashok Leyland, Eicher Motors, Mahindra &
Mahindra and Ford Motors are the major Indian companies which manfacture
commercial vehicles. MAN, ITEC, Mercedes-Benz, Scania and Hyundai are the
foreign companies engage in the manfacture of commercial vehicles. Two-wheeler
manufacturing is dominated by Indian companies like Hero, Bajaj Auto and TVS.
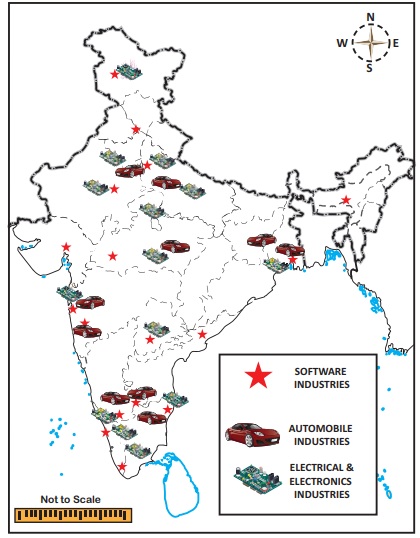
Electrical and Electronic Industries
Heavy
electrical industries manufacture equipment used for power generation,
transmission and utilization. Turbines for steam and hydro power plants, boilers
for thermal power plants, generators, transformers, switch gears etc. are the
chief products of this industry. The most important company in the field of
heavy electrical is Bharat Heavy Electricals Ltd (BHEL). It has its plants at
Hardwar, Bhopal, Hyderabad, Jammu, Bengaluru, Jhansi and Tiruchirappalli. This
Industry covers a wide range of products including television sets, transistor
sets, telephone exchanges, cellular telegram, computers and varied equipments
for post and railway, defence and meteorological department.
Bengaluru is the largest producer of electronic
goods in India, hence it is called as the “Electronic Capital of India”. The
other major producers of electronic goods centers are Hyderabad, Delhi, Mumbai,
Chennai, Kolkata, Kanpur, Pune, Lucknow, Jaipur and Coimbatore.
Make in India program was launched in
2014 to put India on the world map as a major hub for global design and
manufacturing.
Software Industry
India is
home to some of the finest software companies in the world. The software
companies in India are reputed across the globe for their efficient IT and
business related solutions. The Indian Software Industry has brought about a
tremendous success for the emerging economy.
In India, software industry began in 1970 with the
entry of Tata Consultancy Services (TCS). Along with this, L & T, Infotech,
i-Flex, Accenture, Cognizant, GalexE Solutions India Pvt Ltd and ITC Infotech
are the major software industries in the country. At present, there are more
than 500 software companies all over India. It exports software service to
nearly 95 countries in the world.
The main
centres of IT parks are located in Chennai, Coimbatore, Thiruvananthapuram, Bengaluru,
Mysuru, Hyderabad, Visakhapatnam, Mumbai, Pune, Indore, Gandhi Nagar, Jaipur,
Noida, Mohali and Srinagar.
Major challenges of Indian Industries
Industries
in India face many problems.
Some
major problems are listed below.
• Shortage and fluctuation in Power Supply.
• Non- availability of large blocks of land.
• Poor access to credit.
• High rate of interest for borrowed loan.
• Non- availability of cheap labourers.
• Lack of technical and vocational training for
employees.
• Inappropriate living conditions nearby industrial
estates.
Related Topics