Chapter: Civil : Mechanics Of Fluids : Boundary Layer
Mechanics Of Fluids- Boundary Layer
Boundary
Layers
When a fluid flows over a stationary surface, e.g. the bed of a
river, or the wall of a pipe, the fluidtouching the surface is brought to rest
by the shear stress to at the wall. The velocity increases from
thewall to a maximum in the main stream of the flow.
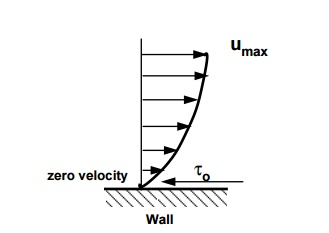
Looking at this two-dimensionally we get
the above velocity profile from the wall to the centre of the flow.
This profile doesn't just exit, it must
build up gradually from the point where the fluid starts to flow past the
surface - e.g. when it enters a pipe.
If we consider a flat plate in the
middle of a fluid, we will look at the build up of the velocity profile as the
fluid moves over the plate.
Upstream the velocity profile is
uniform, (free stream flow) a long way downstream we have the velocity profile
we have talked about above. This is the known as fully developed flow.
But how do we get to that state?
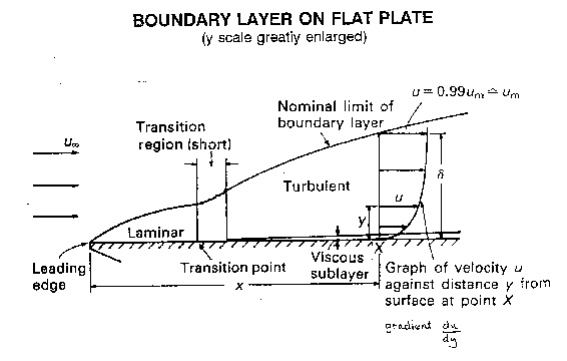
This region, where there is a velocity profile in the flow due to
the shear stress at the wall, we call the boundary layer. The
stages of the formation of the boundary layer are shown in the figure below:
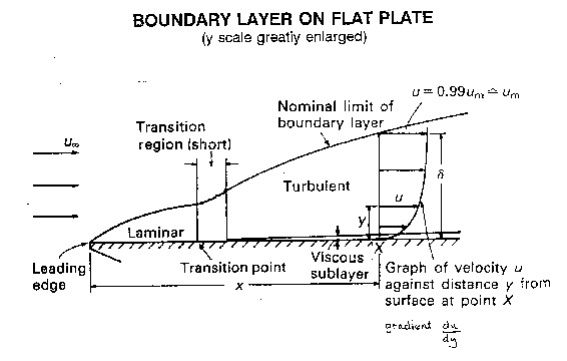
We define the thickness of this boundary
layer as the distance from the wall to the point where the velocity is 99% of
the 'free stream' velocity, the velocity in the middle of the pipe or river.
boundary layer thickness, d = distance from wall to point
where u = 0.99 umainstream
The value of d will increase with distance from the point where the fluid first
starts to pass over the boundary - the flat plate in our example. It increases
to a maximum in fully developed flow.
Correspondingly, the drag force D on the fluid due
to shear stress to at the wall increases from zero at
the start of the plate to a maximum in the fully developed flow region where it
remains constant. We can calculate the magnitude of the drag force by using the
momentum equation. But this complex and not necessary for this course.
Our interest in the boundary layer is that its
presence greatly affects the flow through or round an object. So here we will
examine some of the phenomena associated with the boundary layer and discuss
why these occur.
Related Topics