Operations Research - Meaning of Decision Theory | 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 10 : Operations Research
Chapter: 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 10 : Operations Research
Meaning of Decision Theory
Meaning
The decision maker: The decision maker
refers to individual or a group of individual responsible for making the
choice of an appropriate course of action amongst the available courses of
action.
Acts (or courses of
action):
Decision making problems deals with the selection of a single act from a
set of alternative acts. If two or more alternative courses of action occur in
a problem, then decision making is necessary to select only one course of
action. Let the acts or action be a1, a2, a3,ŌĆ”
then the totality of all these actions is known as action space denoted by A.
For three actions a1, a2 a3; A = action space
= (a1, a2, a3) or A = (A1, A2,
A3). Acts may be also represented in the following matrix form.

Events (or States of
nature): The
events identify the occurrences, which are outside of the decision
makerŌĆÖ s control and which determine the level of success for a given act.
These events are often called ŌĆś States of natureŌĆÖ or outcomes. An example of an
event or states of nature is the level of market demand for a particular item
during a stipulated time period.
A set of states of
nature may be represented in any one of the following ways:
S = {S1, S2,
ŌĆ”,Sn} or E = {E1, E2, ŌĆ”,En} or ╬® =
{╬Ė1, ╬Ė2, ╬Ė3}
For example, if a
washing powder is marketed, it may be highly liked by outcomes (outcome ╬Ė1) or
it may not appeal at all (outcome ╬Ė2) or it may satisfy only a small fraction,
say 25% (outcome ╬Ė3)
╬® = {╬Ė1 , ╬Ė2,
╬Ė3}
In a tree diagram the
places are next to acts. We may also get another act on the happening of events
as follows:
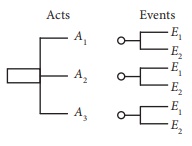
In a matrix form, they
may be represented as either of the two ways.
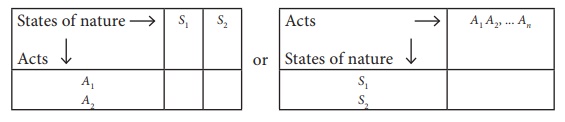
Pay-off: The result of
combinations of an act with each of the states of nature is the outcome
and monetary gain or loss of each such outcome is the pay-off. This means that
the expression pay-off should be in quantitative form.
Pay -off may be also in
terms of cost saving or time saving. In general, if there are k alternatives
and n states of nature, there will be k ├Ś n outcomes or pay-offs.
These k ├Ś n payoffs can be very conveniently represented in the form of a k
├Ś n pay -off table.
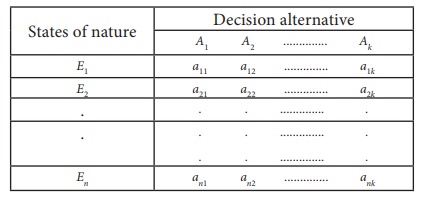
Where aij
= conditional outcome (pay-off) of the i th event when j
th alternative is chosen. The above pay-off table is called pay-off
matrix.
Related Topics