Term 1 Chapter 2 | 4th Science - Matter and Materials | 4th Science : Term 1 Unit 2 : Matter and Materials
Chapter: 4th Science : Term 1 Unit 2 : Matter and Materials
Matter and Materials
Unit 2
Matter and
Materials

Learning Objectives
After learning this lesson, the students will be
able to
• classify the materials based on their properties
• conduct simple investigations related to
materials
• realize the importance of matter and materials
in daily life
• differentiate Transparent, Translucent and
Opaque objects
I. Materials
Everything in the universe is
made up of matter. We need to explore many different materials to make sense of
our world.
The matter from which a thing is
made of is called Material.
For example:
Chair is made of wood, Eraser is made of rubber, Candle is made of wax.
Try to Answer
Look at the pictures and identify the materials by
which they are made of:
(paper, clay,
glass, wood, plastic, metal rubber, wax)
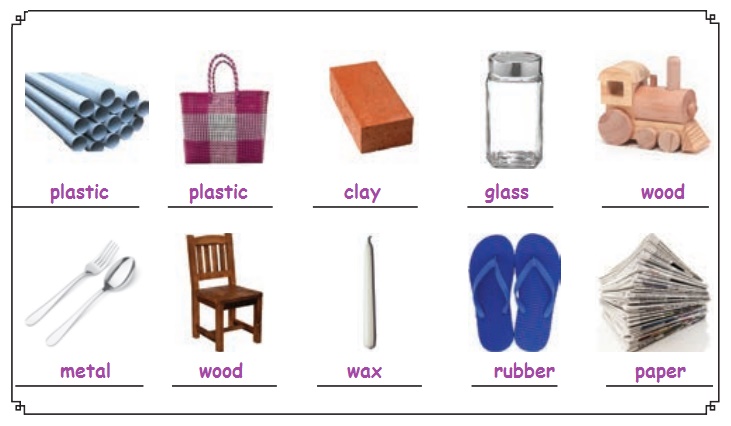
Try to
Answer
Match the objects that are made of same material.

Answer: Plastic material, Wooden material, Leather
material
II. Properties of
Materials
We can measure, see or feel the materials. Different types of material have different properties that make them useful for various purposes. Most materials have more than one property. They can be hard or soft, shiny or dull, smooth or rough and flexible or rigid.
1. Hard and Soft Materials
Materials which cannot be easily
compressed, cut, bent or scratched are called hard
materials. Example: Brick, bone and steel.

Materials which can be easily
compressed, cut, bent or scratched are called soft
materials. Example: Foam, clay and skin.

Try to Answer
Write whether the
given materials are hard or soft.
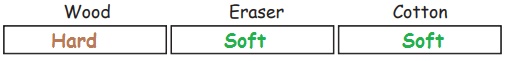
2. Shiny and Dull Materials
Materials which reflect the light
well are called shiny materials. Example: Stainless steel, gold and diamond.

Materials which do not reflect
the light well are called dull materials. Example : Candle, paper and jute bag.

Try to Answer
Collect some objects from your house and classify
them as shiny or dull materials.
3. Rough and Smooth Materials
Materials which have ups and downs
on their surface are called rough materials. Example: Brick, rock and tyre.

Materials which do not have ups
and downs on their surface are called smooth
materials. Example:
Mirror, Silk cloth and tiles.

Try to Answer
Sort the given objects as rough or smooth.
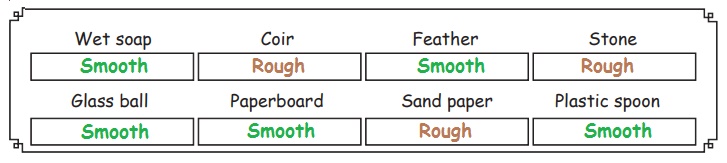
4. Flexible and Rigid Materials
Materials which can be bent or
stretched easily are known as flexible materials. Example: Rubber band, electric wire and
cycle tube.

Materials which cannot be bent or
stretched easily are known as rigid materials. Example: A stick, wooden scale and stone.

Activity
Test the flexibility.
Give one plastic scale and wooden scale to the students.
Ask them to bend. Tabulate their observation (bends, does not bend).
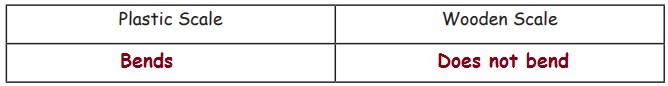
5. Waterproof Materials
Materials that do not allow water
to pass through them are called Waterproof
Materials.
Example : Raincoat and aluminium foil of tablet strip.

Think and answer
Do you have a raincoat? What is its use?
Activity
Take a glass bowl. Fill three fourth of it with
water. Put an orange fruit with peel and an orange fruit without peel. Observe
which orange floats? Why?
Answer: Orange with peel floats because
it is waterproof. Orange without peel sinks because water gets into it and
makes it heavy.
III.
Transparent,Translucent and Opaque objects
Have you ever seen through
the bus window?

Some objects allow light to pass
through them. This helps us to see through them as the window of a bus. Let us
see how different objects behave with light.
1. Transparent Objects
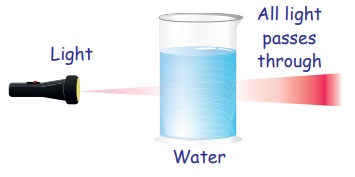
Transparent objects allow the
light to pass through them. So, we can see other objects clearly through Transparent
Objects. Examples: Air, glass and
pure water.
2. Translucent Objects
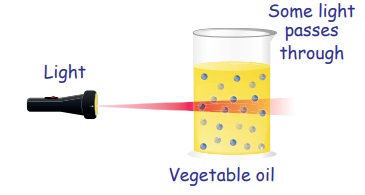
Translucent objects allow some
light to pass through them. So, we cannot see objects clearly, but we see them
as blurred images through them.
Examples: Paper soaked in oil, snow and vegetable oil.
3. Opaque objects
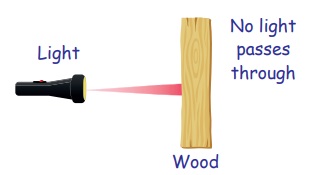
Opaque objects do not allow light
to pass through them. So, we cannot see through these objects.
Examples : Wood, stone and metals.
Think and answer
Why should we build the walls of the house with
bricks (opaque material) instead of glass (transparent material)?
Activity
Complete the Worksheet
Name : Class :
Date : Unit : 2. Matter and Materials
Complete the sentence in you own words.
1. Transparent objects allow light to pass through them.
2. Translucent objects allow some light to pass through them.
3. Opaque objects allow no light to pass through them.
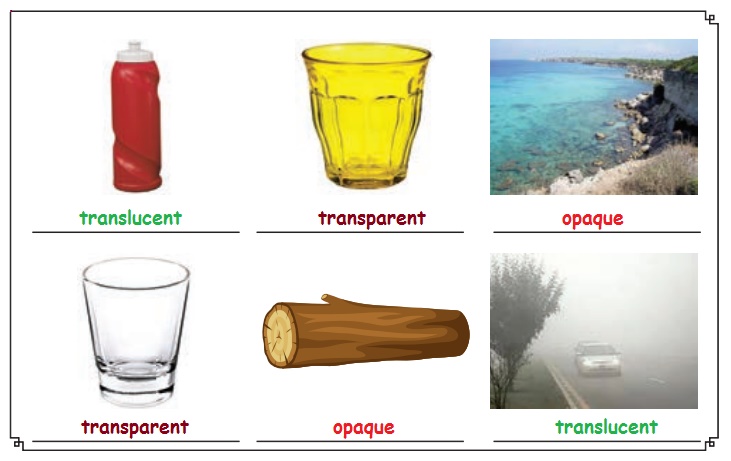
Try to Answer
Write whether the
objects are transparent, translucent or opaque.
IV. Reflection of Light

We sea the world around us with
the help of light. Where do we get
light from? Light may come either from the Sun or from other sources like an
electric lamp or a bulb. The objects that give off light are called light sources.

When light falls on a transparent
material it passes through it. However when light falls on a polished surface
of an opaque material, it does not pass through it. It bounces back. The
bouncing of light by any smooth or polished surface is called reflection.

When you look into the mirror,
you can see your own face on the mirror. What you see is a reflection of your
face in the mirror. We also see reflections of other objects that are in front
of the mirror. These reflections are formed by light and they are called images.

Try to Answer
Try to see your face on some materials like mirror,
exam pad, new stainless steel plate, table top and water in a plate. What are
the materials that show your face clearly? Do you know why?
Answer: Mirror and new stainless steel
plate show my face clearly. This is because their polished surface reflects
light.
Activity
Reflection of Light

Material
Required/Needed
A plane mirror and
a torch light
How to do?
1. Make your room
dark by closing the door and windows.
2. Ask your friend
to hold a mirror in his/her hand at one corner of the room.
3. Stand at another
corner with a torch in your hand.
4. Switch it on.
5. Direct the light
from the torch onto the mirror.
6. Answer the
following from your observation:
a) When you change
the angle of the mirror, what happens to the light?
Answer: The angle of reflection also
changes when we change the angle of the mirror.
b) Are you able to
direct the reflected light using the mirror?
Answer: Yes, I am able to direct the
reflected light using the mirror.
More to know
Mirrors can reflect sound waves too. So they were
used in the Second World War to detect sounds coming from enemy
aircraft.
Related Topics