Chapter: Pathology: Skin Pathology
Malignant Tumors
MALIGNANT TUMORS
Squamous
cell carcinoma (SCC) has peak incidence at age 60. Risk factors
includechronic sun exposure (ultraviolet UVB); fair complexion; chronic skin
ulcers or sinus tracts; long-term exposure to hydrocarbons, arsenic, burns, and
radiation; immunosuppression; and xeroderma pigmentosum. Common mutations
include TP53 and HRAS.
·
Precursors include actinic keratosis
(a sun-induced dysplasia of the keratino-cytes that causes rough, red papules
on the face, arms, and hands) and Bowen disease (squamous cell carcinoma in situ).
·
Squamous cell carcinoma occurs on
sun-exposed areas (face and hands) and causes a tan nodular mass which commonly
ulcerates. Microscopic examina-tion shows nests of atypical keratinocytes that
invade the dermis, (oftentimes) formation of keratin pearls, and intercellular
bridges (desmosomes) between tumor cells. Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
rarely metastasizes and complete excision is usually curative.
·
A variant is keratoacanthoma (well differentiated Squamous cell carcinoma),
which causes rapidly growing, dome-shaped nodules with a central keratin-filled
crater; these are often self-limited and may regress spontaneously.
Basal
cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common tumor in adults in the
Westernworld; it is most common in middle-aged or elderly individuals and
arises from the basal cells of hair follicles. Risk factors include chronic sun
exposure, fair complexion, immunosuppression, and xeroderma pigmentosum.
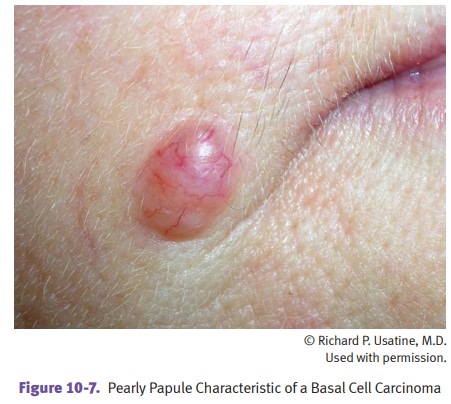
BCC
occurs on sun-exposed, hair-bearing areas (face), and may form pearly pap-ules;
nodules with heaped-up, translucent borders, telangiectasia, or ulcers (rodent
ulcer). Microscopically, BCCs show invasive nests of basaloid cells with a
palisading growth pattern.
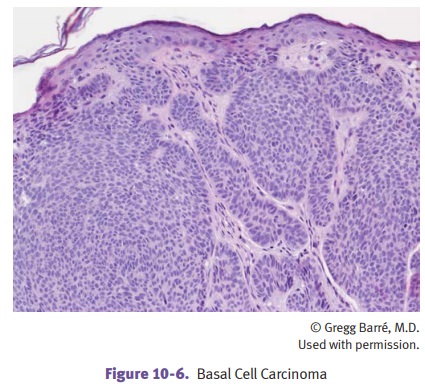
BCC
grows slowly and rarely metastasizes, but it may be locally aggressive. Shave
biopsies have a 50% recurrence rate, but complete excision is usually curative.
Muta-tions affecting the Hedgehog pathway are seen in sporadic and familial
cases.