Chapter: Organic Chemistry: Acid–base reactions
Lewis acids and bases
LEWIS ACIDS AND BASES
Key Notes
Lewis acids
Lewis
acids are electron deficient molecules which are termed acidic because they
will accept a pair of electrons (in the form of a bond) from an electron-rich
species in order to fill up their valence shell. BF3, AlCl3,
TiCl4, and SnCl4 are examples of Lewis acids.
Lewis bases
Lewis
bases are ions or neutral molecules containing an atom with a lone pair of
electrons. Lewis bases use a lone pair of electrons to form a bond to a Lewis
acid.
Lewis acids
Lewis acids are ions or electron deficient
molecules with an unfilled valence shell. They are classed as acids because
they can accept a lone pair of electrons from another molecule to fill their
valence shell. Lewis acids include all the Brønsted–Lowry acids we have already
discussed, as well as ions (e.g. H+ , Mg2+ ), and neutral
species such as BF3 and AlCl3.
Both Al and B are in Group 3A of the periodic
table and have three valence elec-trons in their outer shell. This means that
these elements can form three bonds. However, there is still room for a fourth
bond. For example in BF3, boron is sur-rounded by six electrons
(three bonds containing two electrons each). However, boron’s valence shell can
accommodate eight electrons and so a fourth bond is pos-sible if the fourth
group can provide both electrons for the new bond. Since both boron and aluminum
are in Group 3A of the periodic table, they are electropositive and will react
with electron-rich molecules in order to obtain this fourth bond. Many
transition metal compounds can also act as Lewis acids (e.g.TiCl4
and SnCl4).
Lewis bases
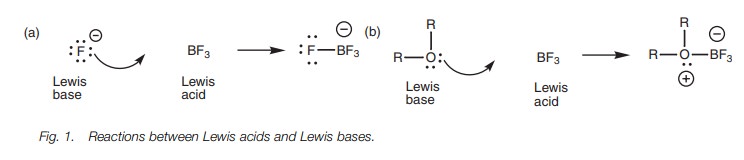
A Lewis base is a molecule which can provide a
lone pair of electrons to fill the valence shell of a Lewis acid (Fig. 1). The base can be a negatively
charged group such as a halide, or a neutral molecule such as water, an amine,
or an ether, as long as there is an atom present with a lone pair of electrons
(i.e. O, N, or a halogen).
All the Brønsted–Lowry bases discussed earlier
can also be defined as Lewis bases. The crucial feature is the presence of a
lone pair of electrons which is avail-able for bonding. Therefore, all
negatively charged ions and all functional groups containing a nitrogen,
oxygen, or halogen atom can act as Lewis bases.
Related Topics