Chapter: Microbiology and Immunology: Bacteriology: Actinomycetes
Laboratory Diagnosis - Nocardia Infections
Laboratory Diagnosis
Laboratory diagnosis of nocardiosis depends on the demon-stration of Nocardia by microscopy and isolation by culture.
◗ Specimens
Nature of the clinical specimens depends on clinical presen-tation of nocardiosis. Sputum is a frequently used specimen. Other specimens include respiratory secretions, skin biopsies, or pus from the abscesses.
◗ Microscopy
Diagnosis is made by demonstration of branching actinomy-cotic filaments in pus or in multiple sputum specimens by microscopy. Smears from the specimen are stained by Gram or Ziehl–Neelsen method.
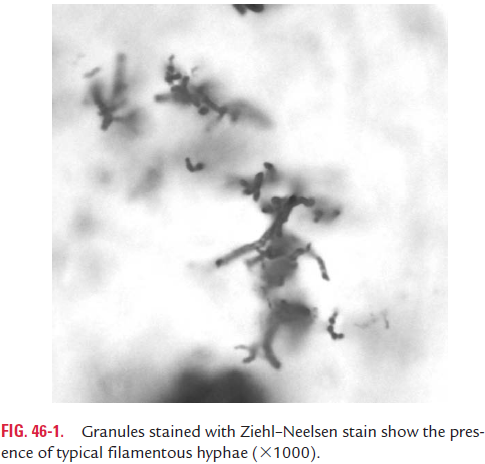
◗ Culture
Pus, sputum, and granules are cultured on nutrient agar, BHI agar, and Sabouraud’s agar and are incubated at 36°C for up to 3 weeks. Colonies on these media may appear as early as 7 days.
◗ Identification of bacteria
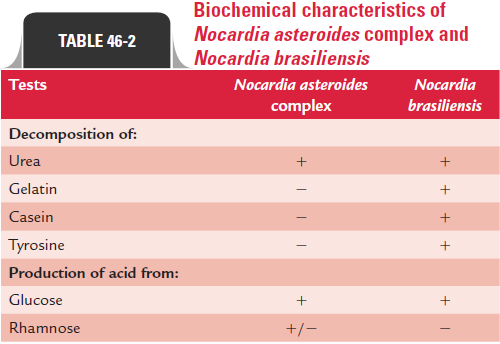
The colonies are identified on the basis of Gram-positive and weekly acid-fast positive filamentous bacilli and with other biochemical properties. All the species of the genus Nocardia(N. asteroides com-plex, N. brasiliensis, and N. otitidiscaviarum, N. asteroides complex including N. asteroides, N. farcinica, and N. nova) are identified by using a battery of biochemical tests (Table 46-2).
Related Topics