Accountancy - Items peculiar to notÔÇôforÔÇôprofit organisations | 12th Accountancy : Chapter 2 : Accounts of-Not-For Profit Organisation
Chapter: 12th Accountancy : Chapter 2 : Accounts of-Not-For Profit Organisation
Items peculiar to notÔÇôforÔÇôprofit organisations
Items
peculiar to notÔÇôforÔÇôprofit organisations
Distinction between
revenue and capital items will be helpful while preparing the final accounts of
notÔÇôforÔÇôprofit organisations. Revenue items will be recorded in income and
expenditure account while capital items will be recorded in the balance sheet.
Items peculiar to notÔÇôforÔÇô profit organisations and their accounting treatment
in that context is given below:
(i) Subscription
NotÔÇôforÔÇôprofit
organisations usually collect subscriptions periodically from their members.
These may be collected monthly, quarterly, half-yearly or yearly. In addition,
some special subscriptions, for example, subscription for tennis, billiards,
etc., are collected from the concerned members playing tennis or billiards as
the case may be. All these subscriptions are revenue receipts.
(ii) Interest on investment
For investments made,
the organisation may receive interest. It is a revenue receipt.
(iii) Sale of old sports materials
The sale proceeds of old
sports materials like balls, bats, etc. are revenue receipts.
(iv) Sale of old newspapers
The sale proceeds of old
newspapers are revenue receipts.
(v) Life membership fee
Amount received towards
life membership fee from members is a capital receipt as it is non-recurring in
nature.
(vi) Legacy
A gift made to a notÔÇôforÔÇôprofit
organisation by a will, is called legacy. It is a capital receipt.
(vii) Admission fee or Entrance fee
It is a fee collected
from every member only once at the time of his or her admission into the
organisation. It may be treated as a revenue receipt as it is a recurring
income from new members admitted every year and may be used to meet the
expenses at the time of admission. It may also be treated as a capital receipt.
(viii) Grants from government and other organisations
NotÔÇôforÔÇôprofit organisations
may receive different forms of grant from government and other organisations.
Grants received towards
construction of buildings, acquisition of assets, etc., are treated as capital
receipts as they are non-recurring in nature.
Grants received towards
maintenance of assets, payment of salaries, etc., are treated as revenue
receipts as they are recurring in nature.
(ix) Donations
These are the amounts
received by notÔÇôforÔÇôprofit organisations as a gift. It may be general donation
or specific donation.
General donation: If the
donation is received without any specific condition, then it is a general
donation. It is a revenue receipt.
Specific donation: If
the donation is received with a specific condition for a particular purpose
like donations for sports fund, prize fund etc., it is known as specific
donation. It is a capital receipt.
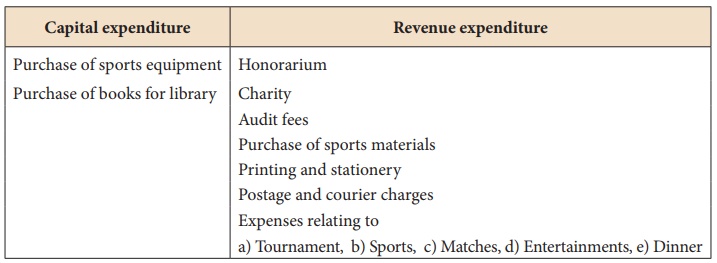
(x) Honorarium
It is the remuneration
paid to a person who is not a regular employee of the organisation. It is a
revenue expenditure.
(xi) Purchase of sports materials
Sports materials such as
balls, bats, nets, etc. are consumable items. Amount of consumed sports
materials are taken as revenue expenditure and value of unconsumed sports
materials (stock) are shown as asset in the balance sheet.
(xii) Purchase of sports equipment
It is a capital
expenditure. Examples: Purchase of Table tennis table, Billiards table, etc.
(xiii) Purchase of books for library
Books purchased for
library is a capital expenditure.
Few examples of capital
and revenue items peculiar to notÔÇôforÔÇôprofit organisations are given below:
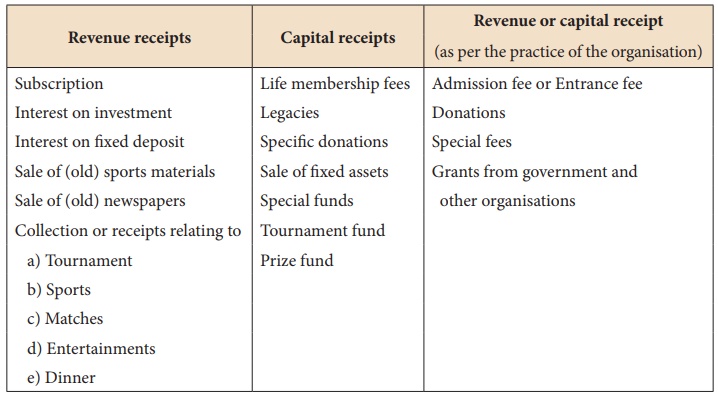
Note: In this unit, entrance
fees or admission fees, donations, special fees and grants from government
and other organisations have been treated as revenue receipts eventhough these
may also be treated as capital receipts.
Related Topics