Chapter: Microbiology and Immunology: Mycology, Fungi: Introduction to Mycology
Introduction to Mycology
Introduction to Mycology
Introduction
Mycology is the study of fungi. The name “fungi” is derived from “mykos” meaning mushroom. The fungi are eukaryotic organisms and they differ from the bacteria, which are prokaryotic organisms, in many ways (Table 71-1). The fungi possess rigid cell walls, which possess two characteristic cell structures: chitin and ergosterol.
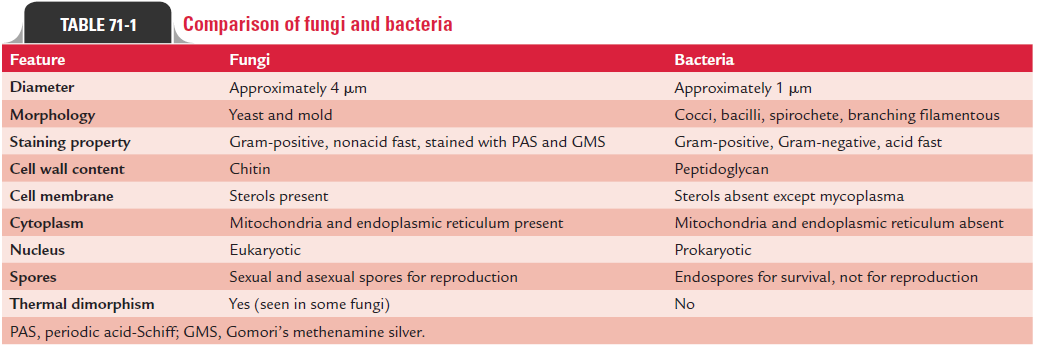
Chitin: The fungi consist primarily of chitin, unlike pepti-doglycan present in cell wall of bacteria. Hence, fungi are not sensitive to action of penicillin and other antibiotics that inhibit peptidoglycan synthesis. Chitin is a polysaccharide consisting of long chains of N-acetylglucosamine. In addition to chitin, the fungal cell wall also contains mannan and other polysac-charides. Of these, beta-glucan is most important, because it is the target of antifungal drug caspofungin.
Ergosterol: The cell membrane of fungus contains ergosterol,unlike human cell membrane which contains cholesterol. The antifungal agents, such as amphotericin B, fluconazole, and ketoconazole have selective action on the fungi due to this basic difference in membrane sterols.
Related Topics