Measurement | Chapter 1 | 8th Science - International System of Units | 8th Science : Chapter 1 : Measurement
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 1 : Measurement
International System of Units
International
System of Units
In
earlier days, scientists performed their experiments and recorded their results
in their own system. Due to lack of communication, they couldn’t organise
experimental results of others. So, they planned to follow a uniform system for
taking the measurements.
As
you studied in the lower classes, in 1960, in the 11th General Conference on
Weights and Measures at Paris in France, scientists recognised the need of
using standard units for physical quantities. That was called as ‘International
System of Units’ and is popularly known as SI System (abbreviated from the
French name ‘Systeme International’). Scientists, chose seven physical
quantities as ‘Base Quantities’ and defined a ‘Standard Unit’ to measure each
one. They are known as Base Units or Fundamental Units (Table 1. 1)
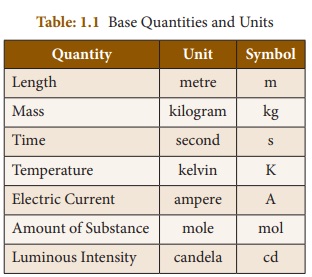
You have already studied about
length, mass and time in your lower classes. Now you are going to study about
the other base quantities such as temperature, current, amount of substance and
luminous intensity.
In December, 1998, the National Aeronautics and Space
Administration (NASA) USA, launched the Mars Climate Orbiter to collect data
about the Martian climate. Nine months later, on September 23, 1999, the
Orbiter disappeared while approaching Mars at an unexpectedly low altitude. An
investigation revealed that the orbital calculations were incorrect due to an
error in the transfer of information between the spacecraft’s team in Colorado
and the mission navigation team in California. One team was using the English
FPS system of units for calculation, while the other team was using the MKS
system of units. This misunderstanding caused a loss of 125 million dollars
approximately.
1. Temperature
Identify, which of the following objects are hot and which of them
are cold?

We see a number of objects in our
daily life. Some of them are cold and some of them are hot. Some times we may
say that two objects are equally hot or cold. But, there will be some
difference in their hotness or coldness. How do you decide, which is hotter and
which is colder? You need a reliable quantity to decide the degree of hotness
or coldness of an object. That quantity is ‘temperature’.
Temperature is a physical quantity
that expresses the degree of hotness or coldness of a substance. Heat energy
given to a substance will increase its temperature. Heat energy removed from a
substance will lower its temperature.
Temperature is defined as a measure
of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a system. The SI unit of
temperature is kelvin. Thermometers are used to measure the temperature
directly. Usually, thermometers are calibrated with some standard scales.
Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin are the most commonly used scales to measure
temperature.
ACTIVITY
Measure
the room temperature inside the class room and outside the class room by using
a thermometer and tabulate it with different time intervals for a week. Do you
find any differences in these values? Discuss your observations.
Answer:
Aim : To measure the room temperature inside the class room and
outside the class room at different time intervals for a week.
Materials
required : Thermometer.
Procedure
:
(i) With the help of a thermometer, note down the room
temperature inside and outside the class room at different time intervals of a
day.
(ii) Repeat the process for 5 days.
(iii) Note down the temperature in the tabular column.
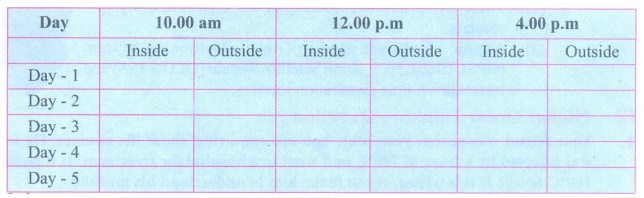
Inference:
(i) Temperature varies at different time intervals.
(ii) It varies from place to place.
Activity 2
From the news paper or television, collect the highest and
lowest temperature experienced in your nearest town or city for a week and
record the values in a tabular column. Does this data remain same throughout
the year?
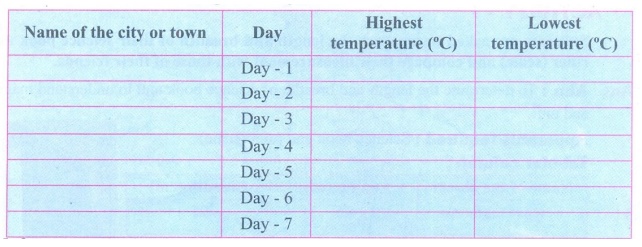
Inference: The data (temperature) does not remain same throughout the week.
2. Electric
Current (I)
Flow of electric charges, in a particular direction is known as
‘electric current’. The magnitude of electric current is the amount of electric
charges flowing through a conductor in one second.
Electric current = Amount of electric charge / time
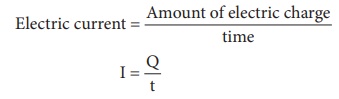
I = Q / t
Electric charge is measured in coulumb. The SI unit of electric
current is ampere and it is denoted as A.
If one coulomb of charge is flowing through a conductor in one
second, then, the amount of current flowing is said to be one ampere. Ammeter
is the device used to measure ‘electric current’ (Fig 1. 2)

Activity 3
Connect a battery, an ammeter and a lamp in series as shown in
the figure. Note the ammeter reading. It is the amount of current flowing in
the circuit.
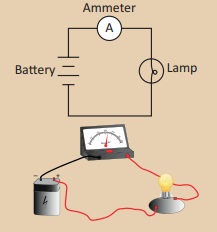
Answer:
Aim: To measure the current in an electric circuit.
Components
required: Battery, Ammeter and Lamp (Bulb).
Procedure
:
(i) Connect the battery, ammeter and the lamp in series as shown
in the figure.
(ii) Note the ammeter reading.
(iii) It is the current in the circuit.
Inference: Current is measured by using ammeter in an electric circuit.
Problem 1
If 2 coulomb of charge
flows through a circuit for 10 seconds, calculate the current.
Solution
Charge (Q) = 2 C; Time
(t) = 10 s
I = Q/t = 2/10 = 0.2 A
3. Amount of Substance
Amount of substance is a measure of the number of entities
(particles) present in a substance. The entity may be an atom, molecule, ion,
electron or proton etc.
Generally, the amount of substance
is directly proportional to the number of atoms or molecules.
Can you count the number of copper
coins in the picture? We can count them easily. But, can you count the number
of copper atoms in a coin? It is very difficult to count the number of atoms
because they are not visible. The number of atoms or molecules in a substance
is measured in mole. It is a SI uinit.

Mole is defined as the amount of substance, which contains 6.023 ×
1023 entities. It is denoted as ‘mol’.
More to Know: The number 6.023 × 1023 is also known as Avogadro
Number.
4. Luminous Intensity

Have you seen these scenes on the
television? What is the umpire doing? He is checking the intensity of light by
using an instrument. The measure of the power of the emitted light, by a light
source in a particular direction, per unit solid angle is called as luminous
intensity. The SI unit of luminous intensity is candela and is denoted as ‘cd’.
The light emitted from a common wax
candle is approximately equal to one candela. Luminous intensity is measured by
‘photometer’ (Luminous Intensity Meter) which gives the luminous intensity in
terms of candela directly.

Info bits
Luminous flux or
Luminous power is the measure of the perceived power of light. Its SI unit is
‘lumen’.One lumen is defined as the luminous flux of the light produced by the
light source that emits one candela of luminous intensity over a solid angle of
one steradian.
Apart
from the seven fundamental units, we have two more units known as derived
units, we will study about them now.
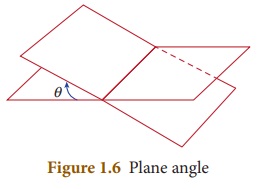
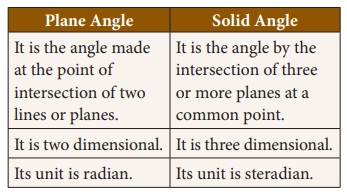
5. Plane
angle
Plane
angle is the angle made at the intersection of two straight lines or
intersection of two planes. The SI unit of plane angle is ‘radian’ and is
denoted as ‘rad’
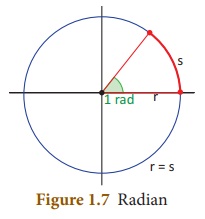
Radian is the angle subtended at the
centre of a circle by an arc whose length is equal to the radius of the circle
(Fig 1. 7).
π radian = 180°
1 radian = 180°/π
Problem 2
Convert 60° into
radian.
Solution
We know that,
1° = π/180
60° = π/180 × 60 = π/3
radian
Problem 3
Convert 4π into
degrees.
Solution
We know that,
π radian = 180°
π/4 radian = 180/4 =
45°
6. Solid angle
Solid angle is the angle formed by
three or more planes intersecting at a common point. It can also be defined as
‘angle formed at the vertex of the cone’. The SI unit of solid angle is
‘steradian’ and is denoted as ‘sr’.
Steradian is the solid angle at the
centre of a sphere subtended by a portion whose surface area is equal to the
square of the radius of the sphere.
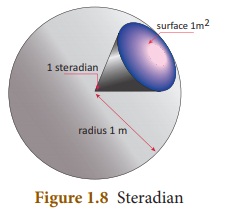
Until 1995, plane
angle and solid angle were classified under supplementary quantities. In 1995,
they were shifted to derived quantities.
Related Topics