Chapter: Object Oriented Programming(OOP) : Advanced Programming
Inheritance - C++
INHERITANCE
Introduction
•
Inheritance
– Single Inheritance
•
Class inherits from one base class
– Multiple Inheritance
•
Class inherits from multiple base classes
– Three types of inheritance:
• public: Derived objects are accessible by the base class objects (focus of this chapter)
•
private: Derived objects are inaccessible by the
base class
•
protected:
Derived classes and friends can access protected members of
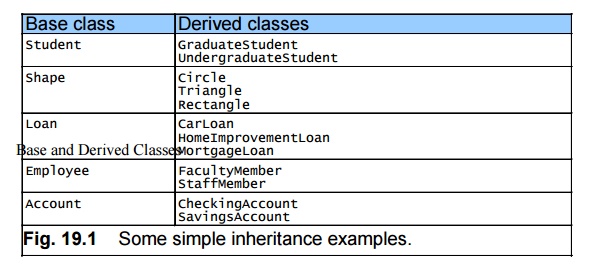
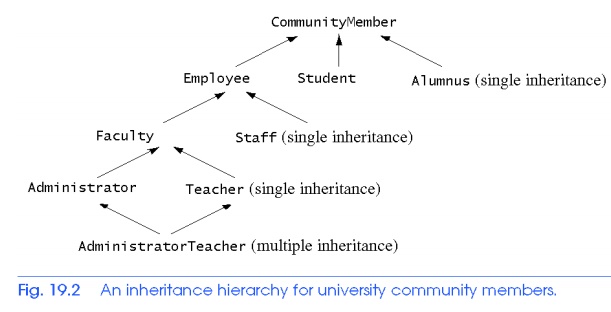
the base class Base and Derived Classes
1. public inheritance
•
Implementation of public inheritance
Class CommissionWorker : public Employee
{
...
};
Class
CommissionWorker inherits from class Employee
– friend functions not inherited
– private members of base class not accessible
from derived class
Protected
Members
§ protected
inheritance
– Intermediate level of protection between
public and private inheritance
– Derived-class members can refer to public and
protected members of the base class simply by using the member names
– Note that protected data “breaks”
encapsulation
Example:
Base Class
class base {
int x;
public:
void setx(int n) { x = n; }
void showx() { cout << x << ‘\n’ }
};
Example:
Derived Class
//
Inherit as public
class
derived : public base {
int y;
public:
void
sety(int n) { y = n; }
void
showy() { cout << y << ‘\n’;}
};
Access
Specifier: public
z The
keyword public tells the compiler that base will be inherited such that:
y all
public members of the base class will also be public members of derived.
However, all private elements of base will remain private to it and are not
directly accessible by derived.
Example:
main()
int
main() {
derived
ob;
ob.setx(10);
ob.sety(20);
ob.showx();
ob.showy();
}
2. Types
Single
Level Inheritance
Multiple
Inheritance
Hierarchical
inheritance
Multilevel
Inheritance
Hybrid
Inheritance.
Single
Level Inheritance
#include
<iostream.h>
Class B
{
int a;
public: int b;
void
get_ab();
int
get_a();
void
show_a();
};
Class D:
public B
{
int c;
public:
void mul();
void
display();
};
Void B ::
get_ab()
{
a=5;b=10; } Int B :: get_a() { return a;}
Void B ::
show_a()
{
count<< “a=”<<a<< “
\
n” ;
}
Void D ::
mul() { c=b*
get_a();}
Void D ::
display()
{
Count<<
“a=”<<get_a()
Count<<
“b=”<<b
Count<<
“c=”<<c
}
int
main()
{
D d;
d.get_ab();
d.mul();
d.show_a();
d.display();
d.b=20;
d.mul();
d.display();
return 0
Multiple
Inheritance
#include
<iostream.h>
Class M
{
Protected:
Int m; Public :
Void
get_m(int); };
Class N
{
Protected:
Int n; Public :
Void
get_n(int); };
Class P
:public M,public N
{
Public :
Void
display(); };
Void M ::
get_m(int x)
{
M=x;
}
Void
N::get_n(int y)
{
N=y;
}
Void P::
dis play()
{
Count<<”m=”<<m<<”
\
n”;
Count<<”n=”<<n<<”
\
n”;
Count<<”m*n=”<<m*n<<”
\
n”;
}
int
main()
{
P p1;
P1.get_m(10); P1.get_n(20); P1.display(); Return 0
Hierarchical
inheritance
class
first
{
int x=10,y=20;
void
display()
{
System.out.println("This
is the method in class one");
System.out.println("Value
of X= "+x); System.out.println("Value of Y= "+y);
}
}
class two
extends first
{
void
add()
{
System.out.println("This
is the method in class two"); System.out.println("X+Y= "+(x+y))
;
}
}
class
three extends first
{
void
mul()
{
System.out.println("This
is the method in class three");
System.out.println("X*Y=
"+(x*y));
}
}
class
Hier
{
public
static void main(String args[])
{
two
t1=new
two();
three
t2=new three(); t1.display(); t1.add();
t2.mul();
Multilevel
Inheritance
class A
{
A()
{
System.out.println("Constructor
of Class A has been called");
}
}
class B
extends A
{
B()
{
super();
System.out.println("Constructor
of Class B has been called");
}
}
class C
extends B
{
C()
{
super();
System.out.println("Constructor
of Class C has been called");
}
}
class
Constructor_Call
{
public
static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("
------
Welcome
to Constructor call Demo
------
")
C objc =
new C();
Hybrid
Inheritance
class
stud
{
Protected:
int rno;
Public:
Void
getno(int n)
{
Rno=n;
}
Void
display_rno()
{
Cout<<“Roll_no=”<<rno<<”
\n”;
}
};
Class
test: Public stud
{
Protected:
Int
sub1,sub2;
Public:
Void
get_mark(int m1,int m2)
{
Sub1=m1;
Sub2=m2;
}
Void
display_mark()
{
Cout<<”sub1”<<sub1<<”
\n”;
Cout<<”sub2”<< sub2<<”\n”;
}
};
Class
sports
{
Protected:
Float score; Public :
Void
get_score(float s) {
Score=s;
}
Void
put_score()
{
Cout<<”Sort
:”<<score<<”
\n”;
}
};
Class
result: public test ,public sports
{
Float
total; Public:
Void
display(); };
Void
result::display()
{
Total=sub1+sub2+score;
display_rno(); display_mark(); put_score();
cout<<”
total score:”<<total<<”
\n”;
}
int
main()
{ Result
s r1;
r1.
getno(123);
r1. get_mark(60,80)
r1.get_score(6); r1.display()
Related Topics