Achieving Equality | Term 1 Unit 2 | Civics | 6th Social Science - Inequality and Discrimination | 6th Social Science : Civics : Term 1 Unit 2 : Achieving Equality
Chapter: 6th Social Science : Civics : Term 1 Unit 2 : Achieving Equality
Inequality and Discrimination
Inequality and Discrimination
Inequality means difference in treatment.
The different forms of inequalities such as caste inequality, religious inequality,
race inequality or gender inequality give rise to discrimination.
Discrimination can be
defined as negative actions towards people. Discrimination can happen on the basis
of colour, class, religion, gender etc. Treating
dark-skinned people differently from fair-skinned
people, giving more importance to people of higher than to those of lower caste
and thinking boys are smarter than girls are all thoughts of discrimination.
Article 15(1) of the
Constitution states that the State shall
not to discriminate against any citizen on grounds only of religion, race, caste,
sex, place of birth or any of them.
End of Apartheid
After 27 years in
prison, South African President, Nelson Mandela, was freed in 1990 and succesfully
achieved the end of apartheid in South Africa, bringing peace to a racially
divided country and leading the fight for human rights around the world.

Dr. Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar
* He is
popularly known as Baba Saheb.
* He was an Indian
jurist, economist, politician and social reformer.
* He earned
his M.A. in 1915 and then obtained a D.Sc at the London School of Economics before
being awarded Ph.D by Columbia University in 1927.
* He served
as the chairman of drafting committee of the constituent assembly and hence regarded
as the father of Indian Constitution.
* He was
independent India’s first Law Minister.
* He was
posthumously awarded the Bharat Ratna in 1990.

1. Caste Discrimination
Caste system is the
most dominant reason for inequality and discrimination in India. In the beginning,
the society was divided into different groups on the basis of occupation, known
as Varnas.
Many people in India
have fought against caste oppression. The most prominent among them was Dr. B.R.
Ambedkar. He belonged to a such depressed family and suffered discrimination throughout
his childhood. He fought actively for equality among the citizens of India.
2. Gender Discrimination
Gender discrimination
refers to health, education, economic and political inequalities between men and
women in India. For example, A girl is not allowed to go to college after finishing
her schooling. Similarly, most of the girls are not allowed to select a career of
their choice rather they are forced into marriage. In some families, girls are not
allowed to wear modern dresses while boys in such families often wear modern dresses.
3. Religious Discrimination
Religious discrimination
is unequal treatment of an individual or group based on their beliefs. Religious
discrimination has been around for a long time. There have been problems between
people of different religions for thousands of years. Some people are not allowed
to enter in public places; especially the places of worship because they belong
to another religion. Some religious people often end up in conflict with each other
because of their rituals and way of life.
4. Socio-Economic Inequality
In the socio-economic
field, the benefits of growth have not been spread evenly. However, the income inequality
is much higher than the inequality in human development. The low income districts
are associated with low industrial development, low agricultural productivity and
low human development.
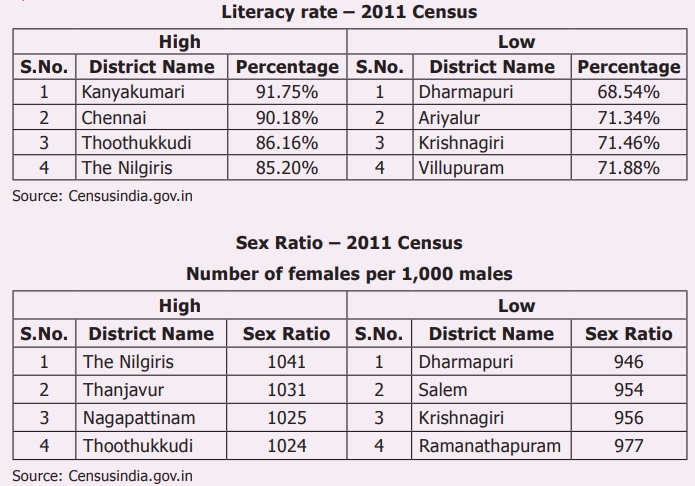
Similarly, the Districts
with literacy rate are found to be with lower sex ratio.
5. Remedial Measures for Abolishing Inequality and Discrimination
The remedial measures for abolishing
inequality and discrimination in Indian society are as follows.
1. Wider access to quality
basic services like healthcare and education for all.
2. Be aware of current
gender bias.
3. Make women more visible
in public life and institution to eradicate gender disparity.
4. Be open to learning about other
religions.
5. Promoting community dining in
the classroom may help the students to sit together without any bias of caste, religion
or gender.
6. Socialise with people of all
types outside home.
7. Effective implementation of laws.
6. Constitution of India andEquality
A Constitution is a set of rules
and regulations guiding the administration of a country. Article 14 of the constitution
of India provides equality before the law
or equal protection within the territory of India and prohibits the
unreasonable discrimination between persons.

Our Constitution says ours is a
land of diversity; therefore, equality has to be ensured for all. Two
significant parameters to ensure equality in society are respecting diversity
and ensuring freedom. The different kinds of freedom are freedom to follow
their religion, speak their language, celebrate their festivals and express
their views freely.
The Constitution is a legal
framework of rules and regulations by which a nation would function. Equality
is where untouchability is seen as a crime. In India, as per the Article 17 of
the Indian Constitution, untouchability is totally abolished and it's any form
is forbidden.
Even today, different types of
discrimination are reported across the country. Women, peasants, tribes and
people from lower social classes are still striving for equality in India.
Related Topics