Chapter: Maternal and Child Health Nursing : Obstetric Interventions
Induction of Labour
Induction of Labour
Definition:
Induction is the initiation of uterine contractions by artificial means after
28 weeks of gestation before the onset of labour with purpose of effecting a
birth of the baby.
Indication
Induction
of labour should be done if the health and wellbeing of the mother or the fetus
would be affected if the pregnancy should continue.
Indications
Prolonged
pregnancy, Diabetes mellitus – Big baby , Pre-eclampsia and Essential
Hypertension , Diminished fetal well being , Placental insufficiency , Rubella
in current pregnancy, Early rupture of membranes – Draining of liquor aft er
12hrs, Cardiac conditions , APH types 1 & II anterior – Ab ruptio Placneta
, Acute hepatitis , Previsous precipitate labour, Chronic Nephritis , Fetal
conditions – Big baby, in trauterine growth retardation, Anencephaly, Fetal
Death in utero – previous still birth , unstable lies , Polyhydramnios , Bad Obstetric
history – elderly Primigravida, Social re asons, Rhesus incompalibility .
Types
1.
Surgical Induction
2.
Medical Induction
It is
always good to combine the two.
Methods
Surgical Induction includes
1. Stimulation of the cervix – stripping
of the membranes. It isenough to commence labour – PG E 2 is rapidly
produced as fetal membranes are the detached from the deciduas.
a. It can
lead to removal of operculum
b. It can
lead to infection if labour does not start 2-3 days.
2. Artificial
Rupture of membranes – (ARM) Amniotomy.
i. Forewater
Rupture of membranes – using Amniotomy forceps or Amnihoook, kocher’s forceps
Danger – Cor d prolapse, Infection.
ii. Hindwater
Rupture of membranes – using Drew symthe catheter.
iii. Danger
– Placenta separation, can puncture chorion , Infection, cord prolaps may
occur.
Medical Induction
1. Oil,
Bath, Enema – OBE Oil – castol oil
Bath –
Hot Bath
Enema –
Hot, High and a lot.
This
enough can stimulate uterine contraction if pregnancy is term and ready.
2. The use
of Oxytocin:
Intravenous
infusion of syntocinon or pitocin can be used.
Technique
of Administration: the lie, presentation, fetal heart rate are checked, CPD
excluded.
·
Enema is given.
·
Assess the condition of the cervix – dilatation and
consistency using the Bishops score 5-10
·
Membranes are ruptured.
Preparation
Preparation
of the Patient
1.
Explain the procedure to the woman .
2.
Patient’s health must be ascertained.
3.
Shave the vulva and wash, ensure the woman empties
her bladder
4.
ARM is done in the morning of the procedure
5.
Inform specialists – paediatrician, haematologist
Role of midwife
1.
Label the bottle – unit, time of starting
2.
Monitor the drops
3.
Monitor the strength, consistency and frequency of
contractions and vital signs quarter hourly.
4.
Monitor the progress of labour and fetal condition
5.
Intake and output chart is kept
6.
Give Psychological support
7. Make patient aware of progress of labour.
8.
Notify Dr. Early and stop drip in case of any
complications.
9.
Relief pains as necessary.
Indication for stopping the drip
1.
Over stimulation of the uterus
2.
Strong contractions
3.
Tonic uterine contractions
4.
Deterioration in the woman’s condition – e.g. incr
eased B/P, maternal or fetal distress, pre-eclampsia if due to over stimulation
or tonic contraction give 2 puffs of ventolin inhaler before Doctor’s arrival.
Bucal Pitocin
It is
given inform of tablet. It brings out erratic absorption and contraction is
uncontrollable. It can cause uterine spasm and fetal anorexia. Dosage 10 unit
in each bucal and another ½ hourly 2, 50, 50, 100, 100 units. If there is fetal
distress or hypertonic uterine action the tablets are removed.
Prostaglandin
This is a
hormone in the prostate gland but present in females. It causes contraction of
the uterine muscles. It is useful in ripening of the cervix prior to induction
by oxytocin or Amniotomy.
It may be
used in form of passaries, tablets ,
or gel .
Favourable Factors
·
Ensure fetal maturity
·
Consider the gestational age, it is better when
pregnancy is at term above 38 weeks.
·
Ripening of the cervix – Bishops score: A score of
6 and above is favourable with level of presenting part at 3/5 or less above
the brim. (good prognosis). Must ascertain the lie, is longitudinal
presentation ,cephalic, Fetal Heart Rate are checked. Exclude CPD – obtain
consent from the husb and or the woman.
·
5 Features are considered, each is awarded 0-3. A
score of 6 above is favourable and of good prognosis – Referred to a s “Ripe
cervix”.
Bishop’s Score
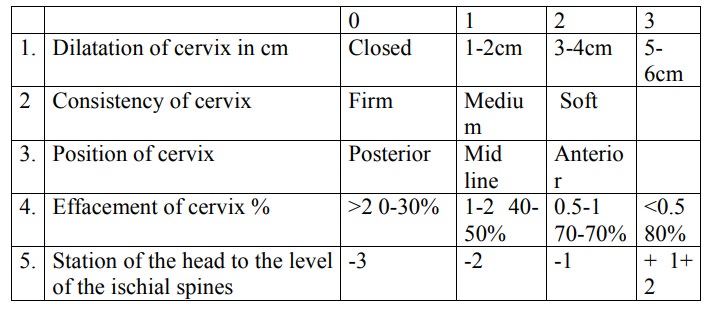
Favourable
score 6-10
Unfavourable
0 – 5 score
Related Topics