Chapter: Chemistry : Energy Sources
Important Questions and Answers: Energy Sources
ENERGY SOURCES
1. What is nuclear energy?
The
energy released by the nuclear fission reaction is called nuclear energy.
2. What is nuclear fission
reaction?
The
process of splitting of heavy nucleus into two or smaller nuclei with
Simultaneous
liberation of large amount of energy in the form of heat is known as nuclear
fission reaction.
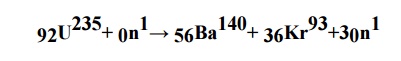
3. What is nuclear fusion
reaction? Give one example.
The
process of combination of two or more lighter nuclei into heavier nuclei, with
simultaneous liberation of large amount of energy is known as nuclear fusion
reaction.
4. Differentiate nuclear fission and fusion
reaction.

Nuclear fission
It is the
process of breaking the heavier
nucleus.
It emits
radioactive rays
Occurs at
ordinary temperature
Chain
reaction takes place
Emits
neutrons
It can be
controlled
Nuclear fusion
It is the
process of
combination
of lighter nuclei.
Does not
emit radioactive rays.
At high
temperature(>106K)
No chain
reaction.
Emits
positrons
Cannot be
controlled
5. Define nuclear chain reaction.
It is a
nuclear reaction, in which neutrons from a previous step propagate and repeat
the reaction. It takes place only nuclear fission reaction.
6.What are fissile and fertile nucleides?

7. What are
solar cells? Give one example./What is a photo galvanic cells?
It is a
device, Converting solar energy directly into electrical energy.
It
provides power supply for space satellites. Ex: solar water heater ,
photovoltaic cell
8. What is solar energy
conversion?
It is the
process of conversion of direct sunlight into more useful forms.
It undergoes mainly two types of mechanisms. 1. Thermal conversion. 2. Photo conversion
9. What are the merits of wind energy?
a)
Nonpolluting and sustainable energy source.b).The scope of wind energy is
enormous. c). It is a renewable and sustainable energy source.
d). It is
available in many offshore, onshore and remote areas.
10. What are batteries?
It is a
device, converted chemical energy into electrical energy. It is an arrangement
of electrochemical cells connected in series,and it can be used as a source of
direct electric current.
11. Define breeder reactor.
Breeder
reactor is one which converts non-fissionable material into fissionable
material.

12. What are non-conventional
energy sources? Give two examples.
Non-conventional energy sources are
those energy sources which are exposed to use from modern technological
advancements; rather than the normal use of conventional fuels as
energy sources like gas or oil.
Ex: 1. Wind energy 2. Solar energy 3.Tidal
energy 4. Hydropower energy
13. What is a fuel cell?
It is a device in which the chemical energy of the
fuel hydrogen is directly converted into electrical energy without combustion.
Fuel +
Oxygen → Oxidation products + Electricity.
14. What are
the advantages of fuel cell? Or What are the advantages of H2-O2 fuel cell?
It is
used as an auxiliary energy source in space vehicles, submarines.
Used in
military vehicles. It is a pollution free one.The product is water, so it is a
valuable source of fresh water by the astronauts.
15. What are the applications of
lithium batteries?
Used in cell phones, Digital cameras, Watches,
Remote cars, Calculators, Toys, Backup batteries in computers, etc.
16. List any two advantages of
lithium batteries.
Its cell voltage is high, 3V. Li is a light-weight metal, only 7g (1 mole) material is required
to produce 1 mole of electrons. It contains solid material so there is no
leakage from battery. This battery can be made in a variety of sizes and
shapes.
15.Define
alkaline battery.
It is
called as a dry cell.>It has the electrolyte of KOH
A zinc
cylinder is filled with an electrolyte of Zn,KOH and MnO2 A carbon rod acts as
a cathode and zinc body acts as a anode.
16.What are the general components in nuclear reactor?
The
components are fuel rods, control rods, moderators, reflectors, coolants and
pressure vessel, Turbine
PART B
1 Distinguish between Nuclear fission and Nuclear
fusion reaction.
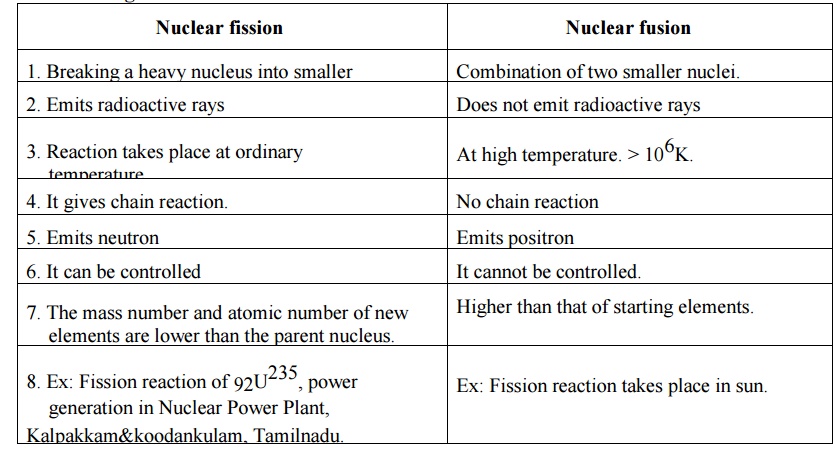
Nuclear
fission
1. Breaking a heavy nucleus into smaller
2. Emits radioactive rays
3. Reaction takes place at ordinary
temperature
4. It gives chain reaction.
5. Emits neutron
6. It can be controlled
7. The mass number and atomic number of new
elements are lower than the parent nucleus.
8. Ex: Fission reaction of 92U235, power
generation in Nuclear Power Plant, Kalpakkam&koodankulam, Tamilnadu.
Nuclear
fusion
1.
Combination of two smaller nuclei.
2. Does
not emit radioactive rays
3. At
high temperature. > 106K.
4. No
chain reaction
5. Emits
positron
6. It
cannot be controlled.
7. Higher
than that of starting elements.
8. Ex:
Fission reaction takes place in sun.
2. Define Nuclear fission reaction. Explain with
one example in detail.


03. Explain Nuclear Reactor-Power
Generator with neat diagram./ Light Water Reactor
Nuclear
Reactor: A device used for power generation, in which a nuclear chain reaction
is initiated, maintained and controlled to produce the heat energy is known as
nuclear reactor.
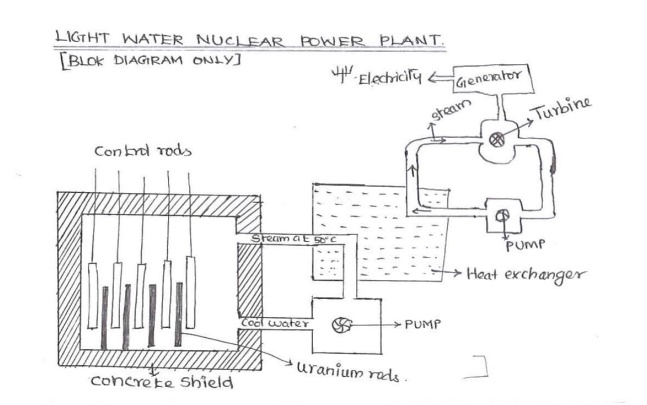
Components:
1) Fuel Rods: It produces heat energy and neutrons.
Ex: Natural Uranium
(99.28% U238 and 0.714 % U235) and Pu239
2)
Control Rods: To keep power production at
a steady state.
Ex: Boron and
Cadmium rods.
3) Moderators: Function to reduce the kinetic energy of fast fission
neutrons to slow
neutron and this is
done in a small fraction of a second.
Ex: Graphite, Be,
Ordinary water and Heavy water.
4) Coolants: To
remove the intense heat produced in the reactor and to bring it out for
utilization. Ex:
Ordinary water, Heavy water, liquid metals and gases.
5) Reflector: It
placed around the core to reflect back some of the neutrons that leak out
from the surface of
the core.
6) Pressure vessel: It enclosed the core and
reflector. It also provides the entrance and exit passages for coolant.
(Pressure 200 kg/cm2)
7) Shielding: To
attentiate the Gama rays and other radiations coming out from the reactor. 2
Types. (i). Thermal shield (ii).
Biological shield.
8) Turbine: The
steam at high pressure, generated in the heat exchanger is used to operate a
steam turbine, which derives a generator to produce electricity.
04. Explain Breeder reactor with
reactions.


Solar
cell = Photogalvanic cell : It is a device used for converting solar energy
into electricity. It is made by interconnecting a large number of photovoltaic
cells.
Solar
Energy Conversion: It is the process of conversion of direct sunlight
into more useful forms. Conversion may be in two forms. 1. Thermal Conversion.
2. Photo Conversion.
01. Thermal Conversion:
It involves absorption of thermal energy in the
form of IR radiation. Temperature below 100oC, is useful for heating
purpose of water and refrigeration.
Methods: (i).Solar heat collectors. (ii).Solar water heater.
(i). Solar heat collectors: It
consists of natural materials like stones, bricks which can absorb heat during
the day time and release it slowly at night.
Uses: It
is used for houses in cold condition.
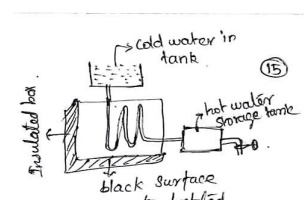
(ii).
Solar Water Heater:
It
consists of an insulated box inside of which is painted with black paint. There
is a provision for sun light absorption using a glass lid and store solar heat.
Inside the black painted, copper coil and cold water is flow in and gets heated
and storage in a tank.
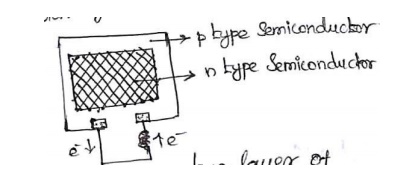
02. Photo Conversion:
It
involves conversion of light energy directly into electrical energy.
Methods:
Solar Cell.
Solar
Cell: Ex: Solar light, solar pump, solar battery.
It is a
device, converting solar energy directly into electrical energy.
Principle:
When solar rays fall on a two layer of
semi-conductor
devices, a potential difference between the two layers is produced. This
potential difference causes flow of electrons and produces electricity.
Working:
When the solar ray falls on the top layer and the e-s promoted to the
conduction into n-type semiconductor. The potential difference occurs; it
should lead current increasing (i.e) flow e-s. They are connected with an
external circuit, and current is generated.
Applications of Solar Energy :(i). Used in calculators,Watches,
etc. (ii). Used to drive Vehicles.
(iii).
Used in boilers to produce hot water for domestic and Industrial uses.
(iv).
Used for lighting purposes. (v). Used as a source power in space crafts and
satellites. (vi). Used for producing hydrogen by hydrolysis of H2O.
Demerits of Solar Energy: (i). Huge
capital cost.
(ii). Not
available during night and cloudy days. (iii). Storage of energy is not
possible
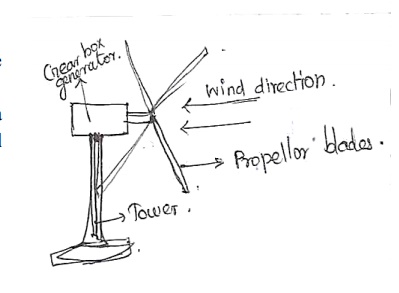
06. Write a short note on Wind
Energy.
Moving
energy is called Wind.Energy recovered from the force of the wind is called
wind energy. The wind energy is harnessed by making use of wind mills.
01.Wind
Mills:
The
strikes of blowing wind on blades of the wind mill make it rotating
continuously.
The
rotational motion of the blade drives a number of machines like water pump,
flour mills and electric generators.
Wind
mills are capable of generating about 100 kw electricity.
02. Wind
Farms.
It is
known as the large number of joining wind mills called wind farm. It produces a
large amount of electricity.The minimum speed required for working of a wind
generator is 15 km/hr
03. Other
methods: (i). Sky Sail (ii). Ladder
mill.
Advantages/ Merits of Wind energy:
i. It
does not cause any Air pollution. ii. It is very cheap and economic.
iii. It is renewable.
Disadvantages
of Wind energy:
i. It produces noise.
ii. It produces unwanted sound.
Affects bird‟s life.
Affected to the radio signals.
7. Define Battery. Explain with its types.
Battery:
It is a device, converted chemical energy into
electrical energy. It contains several anodes and cathodes.
It is an
arrangement of several electrochemical cells connected in series and it can be
used as a source of direct electric current. (D.C).
TYPES OF
BATTERIES:
01.
PRIMARY BATTERY
i. It is
known as Non-Reversible battery.
ii. Electrode and electrode reactions cannot be
reversed by passing an external current. iii. Reactions take place only once
and after use they become dead.
iv. They are
not chargeable.
Ex: Dry Cell, Mercury Cell, Leclanche‟s cell.
SECONDARY BATTERY
It is known as Reversible battery.
ii. Electrode and electrode reactions are
reversiblewhen an external current is passing iii. It can be recharged again
and again.
iv. Also called as Storage cells or Accumulators.
v. Ex: Lead-Acid Battery, Ni-Cd.
03.
FLOW BATTERY
In these cells, the reactants, products and
electrolytes and continuously passing through the cell. Here chemical energy is
converted to electrical energy.
Ex: H2-O2 fuel cell.
08. Explain Alkaline Battery with
neat diagram and cell reactions.
Anode :
Zinc body
Cathode :
Carbon rod / Graphite rod
Electrolyte
: Powdered KOH, MnO2 in the form of
paste.
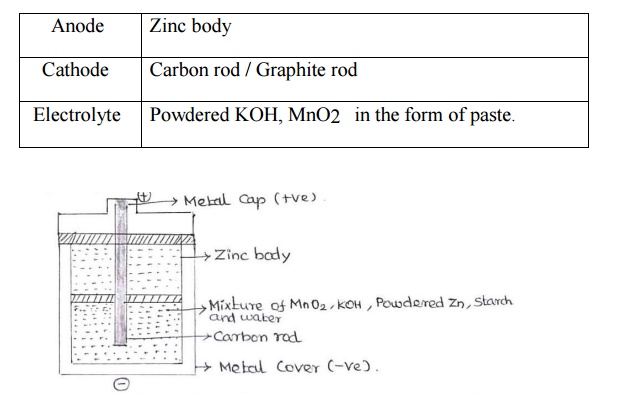
Alkaline battery consists of electrolyte KOH and a
Zinc cylinder filled with powdered Zn, KOH and MnO2 in the form of paste using
starch and water. A carbon rod [Graphite] acts as a cathode and it is immersed
in the electrolyte in the centre of the cell. The outside cylindrical
zinc body
acts as an anode.
Advantages:
Zinc
doesn‟t dissolve in a basic medium.
ii. Its life is longer than dry battery because
there is no corrosion on Zn. iii. It maintains its voltage, when the current is
drawn from it.
Uses:
It is
used in calculators and watches.
09. Explain Lead acid storage
battery.
Cell
Representation: Pb/Pb(SO)4//H2(SO)4(aq)/PbO2/Pb
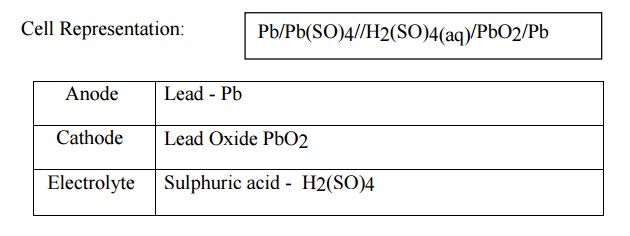
Anode :
Lead - Pb
Cathode :
Lead Oxide PbO2
Electrolyte
: Sulphuric acid - H2(SO)4
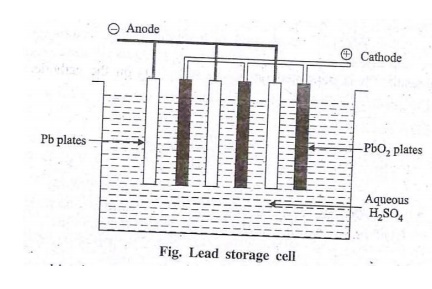
This is also a rechargeable battery.It consists of
number of voltaic cells. In each cell, anode is Pb plate and cathode is PbO2
A known number of lead plates are connected with
parallel and a number of PbO2 plates and also connected in parallel. Various
plates are separated by insulators like glass fibre. The total anodes and
cathodes are immersed in dil.H2(SO)4 Solution.
Cell
reactions: Discharging
Advantages:
(i). It is made easily. (ii). It produces very high current.
(iii). Effective one at low temperature. (iv). Self- discharging rate is low.
Uses:
(i). Used
in automobiles like Car, Bus, Van, Lorry, Bike etc.
(ii).
Used in Hospitals, Power stations, Telephone exchanges etc.
10. Explain Nickel – Cadmium
battery with cell reactions.
Cell
Representation: Cd/Cd(OH)2//KOH(aq)/NiO2/Ni
Anode :
Cadmium (Cd)
Cathode :
A metal grid containing a paste of NiO2
Electrolyte
: KOH
This is
also a rechargeable battery.
It
consists of Cd anode and a metal grid containing a paste of NiO2 acts as a
cathode. The electrolyte is KOH.
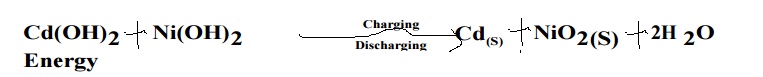
Discharging: When
Ni-Cd battery operates, Cd gets oxidation and forms Cd2+ and
insoluble Cd(OH)2 is formed. Its emf value is 1.4 V.
Cell Reaction:
Recharging:
When an current is passed opposite direction, the cell reaction is reversed. As
a result, Cd gets deposited on anode and NiO2 on cathode.
Advantages:
(i). It
is smaller and lighter.
(ii). It
has longer life than lead storage cell.
Uses:
(i). It is used in calculators, Electronic devices.
(ii). Used in transistors, cordless appliances.
11. Explain Lithium batteries in
detail.
It is
known as solid state battery because the electrolyte is used here at solid
state.
Anode :
Lithium (Li)
Cathode :
TiS2
Electrolyte
: Polymer
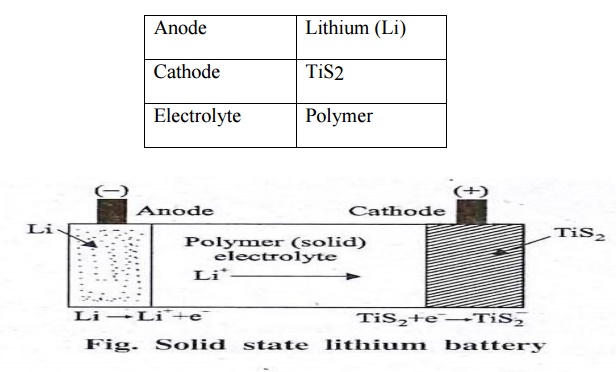
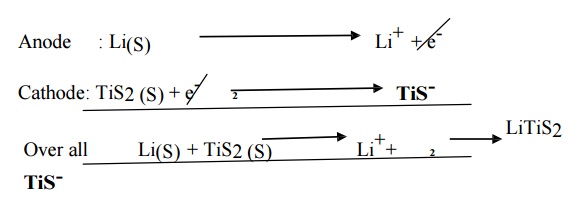
Discharging:
When the anode is connected to cathode, Li+ ions
move from anode to cathode. Anode is Li and cathode is TiS2 and the electrolyte
is solid polymer. The cathode is a material capable of receiving the Lithium
ions and electrons.
Recharging:
LiTiS2 -- -- >
Li+ + TiS2-
It is
recharged by applying an external current. Emf of Li cells = 3.0V.
Advantages: (i). Itsemf is high 3.0V.
(ii). It
is a light weight material only 7g required for produce 1 mole of e-s.
12. Explain Hydrogen- Oxygen Fuel
cell / [H2 – O2] Fuel cell.
Fuel
Cell: It is a
device in which the chemical energy of the fuel hydrogen is directly converted into electricity without combustion.
Anode :
Hydrogen
Cathode :
Oxygen ( oxidizer)
Electrolyte
: 25% KOH or NaOH
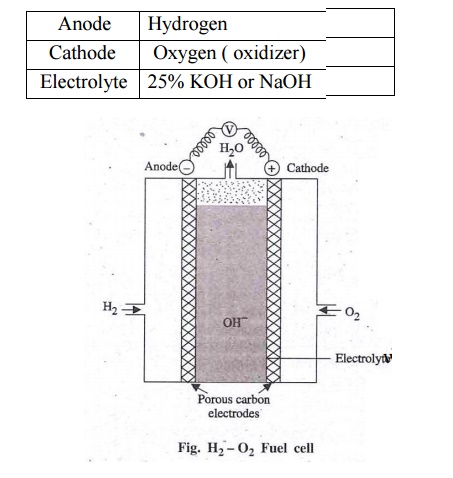
Two
porous electrodes – Made of compressed carbon containing a catalyst like pt /
pd.
It
consists of two porous electrodes anode and cathode. In between two electrodes
an electrolytic solution 25% KOH or NaOH filled.
When H2
is bubbled through the anode compartment, where it is oxidized. The O2
is bubbled at the cathode compartment where it is reduced.
The emf
of the cell = 0.8 to 1.0 V. Merits:
High
efficiency.
ii. No unwanted noise and less maintenance. iii. No
pollution
No need to change electrode often. Uses:
Used in military vehicles and space vehicles.
H2 – O2 fuel cell, the product is water, so no need of fuel because fuel is water