Chapter: Chemistry : Energy Sources
Energy Sources
ENERGY SOURCES
1 Introduction
2 Nuclear Energy
2.1 Nuclear Fission
2.2 Nuclear fusion
2.3 Nuclear chain reaction
3 Nuclear reactor
3.1 Light water Nuclear Reactor
3.2 Breeder Reactor
4 Solar Energy
4.1 Solar energy conversion
4.2 Solar cell
4.3 Application of Solar Cells
5 Wind Energy
5.1 Wind Mill
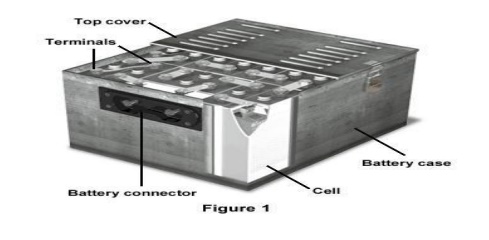
6 Batteries
6.1 Types of batteries
6.2 Alkaline Battery
6.3 Lead Storage Battery
6.4 Nickel-Cadmium Battery
6.5 Lithium Battery
7 Fuel Cells
7.1 Hydrogen Oxygen Fuel Cell
8. Glossary
1 INTRODUCTION
Sufficient
sources of energy are necessary for industrialized nations. Energy is used for
heating, cooking, transportation and manufacturing. Energy sources can be
generally classified as conventional and non-conventional. Over 85% of the
energy used in the world is from conventional sources such as fossil fuels
(coal and oil) and nuclear power.
The
convenrtional energy sources depend on coal and oil. The burnt fuels result in
the release of CO2 and other gases into the atmosphere causing environmental
damage. There are abundant renewable sources of energy such as wind, sun,
water, and biomass. These sources are pollution ofree and known as “ green
energy “.
2 Nuclear Energy :
The
enormous energy thus released during the Nuclear Fission & Fusion reaction
is known as Nuclear Energy.
2.1 N uclear fission: It is
the nuclear reaction in which heavy isotopes are split into lighter nuclei on
bombardment by neutrons. Fission reaction of U235 is given below
2.2 Nuclear fusion:
Process of combination of lighter nuclei into
heavier nucleus with simultaneous liberation of largeamount of energy. (e.g)
solar system
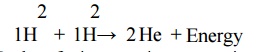
Nuclear
fusion reaction occurs in sun.
2.3 Nuclear chain reaction:
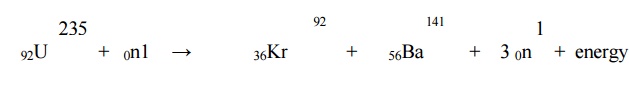
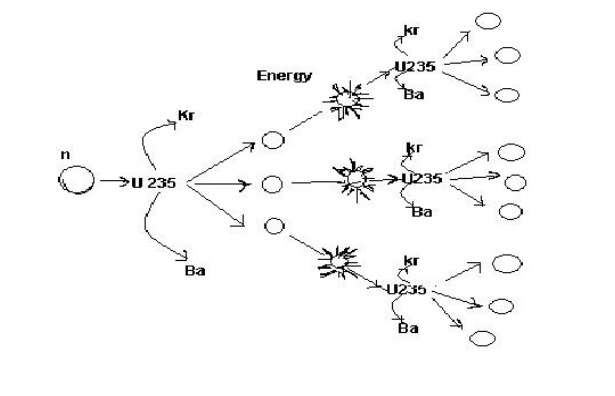
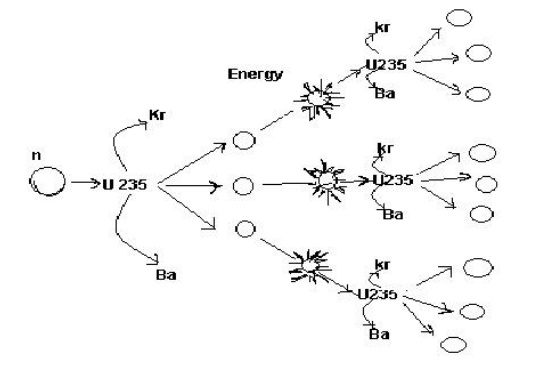
Differences between fission and
fusion reaction
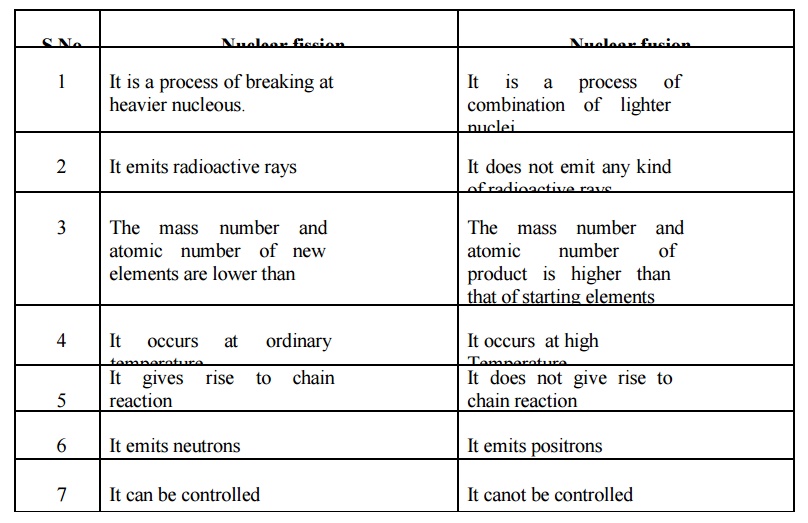
Nuclear fission
1 It is a process of breaking at heavier nucleous.
2 It emits radioactive rays
3 The mass number and atomic number of new elements are
lower than
4 It occurs at ordinary temperature
5 It gives rise to chain reaction
6 It emits neutrons
7 It can be controlled
Nuclear fusion
1. It is a process of combination of lighter nuclei.
2. It does not emit any kind of radioactive rays
3. The mass number and atomic number of product is higher
than that of starting elements
4. It occurs at high Temperature
5. It does not give rise to chain reaction
6. It emits positrons
7. It canot be controlled
3 Nuclear Reactor
3.1 Light water nuclear power
plant Definition
Light water nuclear power plant is one in which U235
feed rods are submerged in water.
Here the
water acts as coolant and moderator.
The fission reaction is controlled by inserting or
removing the control rods of B10 automatically from the spaces I
between the fuel rods.
The heat
emitted by U235 absorbed by the coolant in the fuel core is Heat is
transferred to sea water and then converted into steam. The steam then drives
the turbines, generating electricity.
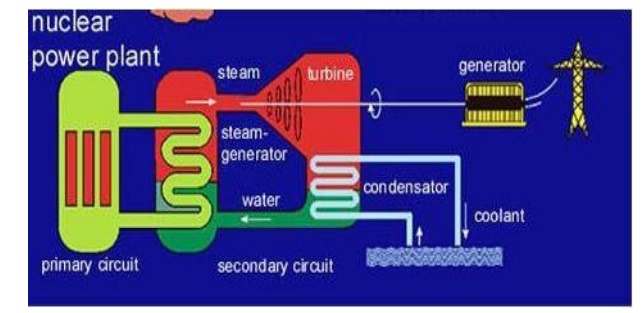
(Structure
of light water nuclear power plant)
3.2 Breeder reactor
A nuclear
reactor with conversion or multiplication factor greater than one is a breeder
reactor. A
breeder reactor generates fissionable nuclei from
fertile nuclei. E.g., the fertile material like uranium-238 is converted into
fissile 94 Pu239 by using slow neutrons. 94 Pu239
undergoes fission and produces energy.
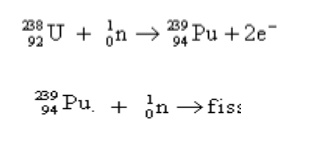
Working :
`In breeder reactor, 92U235 is used as trigger to produce sufficient
neutrons. These are used to convert 92U235 to Plutonium
undergoes fission with the production of three neutrons. One neutron is used to
propagate fission chain. The other two neutrons react with 92U238 to
fissionable 94Pu239. Thus breeder reactor produces two 239 Pu atoms for each 238 U consumed.
Thus more fissionable material is produced than consumed. Hence the reactor is
called breeder reactor.
Critical Mass:
The
minimum amount of fissile material (U235) required to continue the
nuclear chain reaction is called critical
mass.
4 Solar Energy
Solar energy
The energy that derive directly from sunlight and
can be converted into more useful forms is known as Solar energy.
4.1 Solar Energy Conversion
The energy conversion my occur
iterms of heat & current.
4.2 Photo galvanic cell or Solar
cell
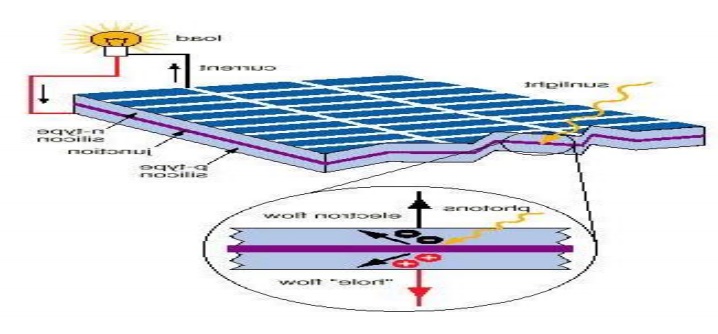
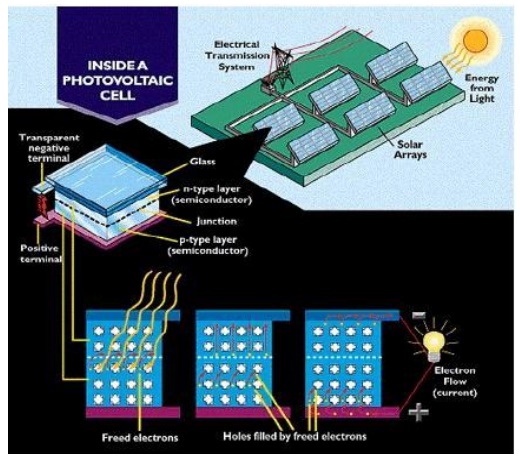
PRINCIPLE:
The principle of Solar cell is based on
photovoltaic effect. When light radiation falls on the p-n junction semi
conductor device, charge separation takes place and a potential difference is
setup. This causes flow of electrons and produces electricity.
Working:
When sun rays all on the top layer of p- type
semiconductor, electrons from valence band are promoted to conductance band and
cross the p-n junction into the n-type semiconductor. A potential difference is
set up between the two layers. This causes flow of electrons and produces
electricity. When the „p‟ and „n‟ layers are connected to an
external circuit, electrons flow from „n‟ layer to „p‟ layer
and current is generated.
4.3 Application of Solar Cell
1. Lighting purpose
Now a
days electrical street lights are substituted by solar street lights.

2. Solar pumps are run by solar battery
A large
number of solar cells are connected in series to form a solar battery. Solar
battery produces enough electricity to run water pump, etc., They are also used
in remote areas where conventional electricity is not available.
SOLAR
BATTERY
Solar cells are used in calculators, electronic
watches etc.
Solar
cells are superior to other type of cells, because they are non-polluting and
eco-friendly.
Solar cells are used to drive vehicles.
Silicon solar cells are used as a source of
electricity in space crafts and satellites.
Advantages of Solar cells
Solar cells are used in remote areas, forests and
hilly regions.
Maintenance cost is minimum.
Solar cells are pollution free.
They have long life.
Disadvantages
Solar
cells are costly.
Storage
of energy is not possible with solar cells.
5 WIND ENERGY
Moving
air is called wind. Energy recovered from the forces of wind is called wind
energy.
5.1 Generation of electricity
from wind mill
Wind energy is used to generate electricity with
the help of wind mills. The crank of the wind mill is connected to a dynamo.
When the blades of wind mill rotate, they turn the coil of the dynamo and
produce electricity. Usually a number of wind mills are erected side-by-side.
The outputs from the wind mills are coupled to generate electricity for
commercial purpose. This type of system is wind energy farms.
Condition: Wind
speed should be more than 15km/hr.
Advantages of wind energy
(i) It is
cheap and economical. (ii) It is renewable
(iii) It
does not cause pollution.
Disadvantages
They produce noise.
Wind
farms erected on the migratory routes of birds create problems. (iii) Wind
turbines interfere with electromagnetic signals.
6
BATTERIES (or) ENERGY STORAGE DEVICES
Battery:
It is an arrangement of several electrochemical
cells connected in series that can be used as a source of direct electric
current.
6.1 TYPES
OF BATTERIES
Secondary
battery or secondary cells
In these
cells, the electrode reactions can be reversed by passing an external energy.
They can
be recharged by passing electric current.
They are
called storage cells or accumulators.
Ex: Lead acid
storage cell, Nickel- cadmium cell.
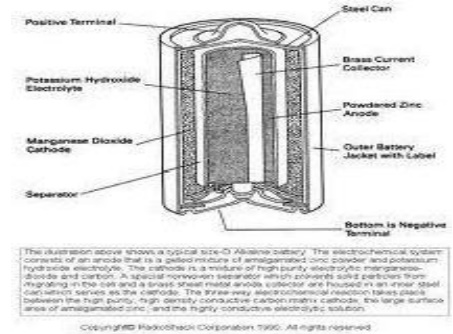
6.2 Alkaline Battery
Here the
powdered zinc is mixed with KOH and MnO2 to get a gel. A Carbon rod acts as
cathode. IT is immersed in KOH The outside cylindrical body is made up of zinc.
Cell reactions
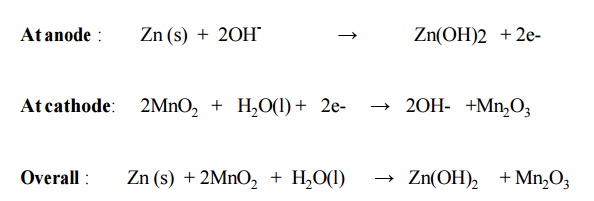
6.3 Lead storage cell Description:
It consists of number of voltaic cells connected in
series Pb is anode and PbO2 is cathode
Number of
Pb plates and PbO2 plates are connected in parallel.
Plates are separated from adjacent ones by
insulators like rubber or glass fiber.
This
arrangement is immersed in dil. H2SO4
Cell reactions
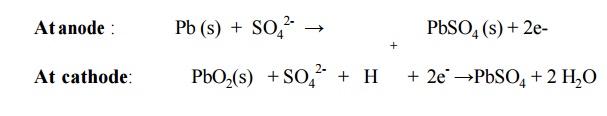
Overall reaction:
Pb (s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4
→ PbSO4 + H2O +
energy
Uses:
It is
used to supply current mainly in automobiles such as cars. Buses, trucks, etc.,
* It is
also used in gas engine ignition, telephone exchanges, hospitals, power
stations.
6.4 Nickel – Cadmium Battery
Description
It
consists of a cadmium anode. A metal grid containing a paste of NiO2 acting as
a cathode. KOH is electrolyte
Ni-Cd
battery
Cell reactions
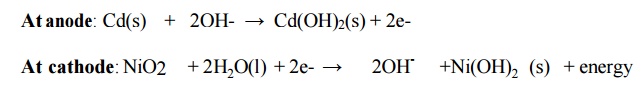
Overall reaction:
Cd(s) + NiO2 + 2H2O(l) →
Cd(OH)2(s) + Ni(OH)2 (s) + energy
Uses: It is used in calculators.
Electronic flash units, transistors and cordless appliances.
6.5 Lithium Battery
Description
It
consists of a lithium anode and a TiS2 cathode.
A solid electrolyte generally a polymer is packed
in between the electrodes.
The
electrolyte permits the passage of ions but not electrons.
Cell reactions
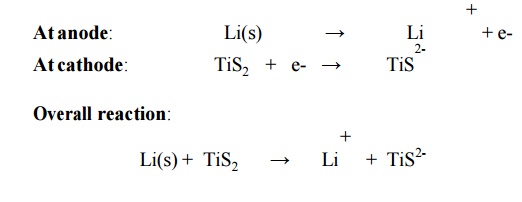
Other types of secondary lithium
batteries
Li/ MnO2
Li/V2O5
Li/MoO2
Li/Cr3O8
Advantages of Li battery
It is the
cell future. Why?
Its cell
voltage is high, 3.0VSince Li is a light weight metal, only 7kg material
required to produce 1mole of electrons.Since all the constituents of the
battery are solids, there is no risk of leakage from the battery. This battery
can be made in a variety of shapes and sizes.
Disadvantages of Li battery
Li
battery is more expensive than other batteries
Uses
Button
sized batteries are used in calculators, watches, cameras, mobile phones,
laptop computers.
Lithium Battery
It is a
solid state battery. Solid electrolyte is used.
Construction
It has a lithium anode and a TiS2 cathode. A solid
electrolyte, a polymer, is packed in between the electrodes. The polymer
electrolyte permits the passage of ions but not that of electrons.
Working (Discharging)
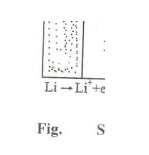
The anode
is connected to cathode through the polymer electrolyte. Lithium ions and
electrons are produced at the anode . The cathode receives the lithium ions and
electrons.
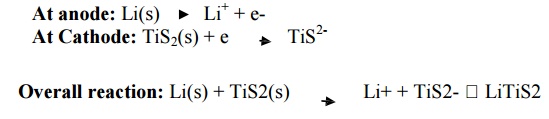
Overall reaction: Li(s) +
TiS2(s) -- --- > Li+ + TiS2- LiTiS
Recharging
The battery is recharged by passing an external
current, which drives the lithium ions back to the anode. The overall reaction
is
LiTiS2 Li+
+ TiS2
![]()
This cell
has a voltage of 3.oV.
Uses:
It possesses very small size and high energy
density. So it is used in calcutors, electronic flash units, computers,
transistors head phones etc.
Advantages
The cell has a voltage of 3.0V.
Li is a
light-weight metal. Just 7g (1 mole) of Li is required to produce 1 mole of
electrons.
Li has the most negative Eo value. So it gives a
higher voltage than other cells. (iv)
It is a
total solid state battery. There is no risk of current leakage from the
battery. (v) It is manufactured in a variety of sizes and shapes.
Disadvantages
It is
more expensive than other batteries.
7 FUEL CELLS:
Definition
Fuel cell is a voltaic cell. It converts chemical
energy of the fuels directly into electricity without combustion. In these
cells, the reactants and electrolytes are continuously
supplied
to the cell.
Fuel +
Oxygen -- -- > Oxidation products + Electricity.
Examples : Hydrogen
- oxygen fuel cell.
7.1 Hydrogen - oxygen fuel cell
It is the simplest and most successful fuel cell.
The fuel-hydrogen and the oxidiser-oxygen and the liquid electrolyte are
continuously supplied to the cell.
Description
The cell
has two porous electrodes, anode and cathode. The electrodes are made of
compressed carbon containing a small amount of catalyst (Pt, Pd, Ag). Between
the two electrodes an electrolytic solution, 25% KOH is filled
Working
Hydrogen passes through the anode compartment, where it is oxidised. Oxygen passes through the cathode compar tment, where it is reduced.


Advantages of Fuel Cells
They are efficient and instant in operation.
They are pollution free.
They produce electric current directly from the
reaction of a fuel and an oxidiser.
They are light in weight
Disadvantages
Fuel cells cannot store electric energy.
Electrodes are expensive and short lived.
H2 should be pure.
Applications
H2 - O2 fuel cells are used in space crafts,
submarines to get electricity
In H2 - O2 fuel cell, the produt water is a
valuable source of fresh water for astronauts
8 Glossary
Nuclear fission
The
process of splitting of heavier nucleus into two or more smaller nuclei with
simultaneous liberation of large amount of energy is called Nuclear Fission.
Nuclear Fusion
The
process of combination of lighter nuclei into heavier nuclei, with simultaneous
liberation of large amount of energy is called Nuclear Fusion.
Nuclear Chain Reaction
A fission
reaction, where the neutrons from the previous step continues to propagate and
repeat the reaction is called Nuclear
Chain Reaction.
Breeder reactor
Breeder reactor is the one which converts
non-fissionable material ( U238, Th232) into fissionable material ( U235,
Pu239 ). Thus the reactor produces or breeds more fissionable
material than it consumes.
Fissionable nucleides (or ) Fissile nucleides
The nucleides
like U235, Pu239 which undergo fission reaction is known
as Fissle nucleides.
Non- fissionable nucleides (or) Fertile nucleides
The
nucleides like U238, Th232 which do not undergo fission reaction is
known as
Fertile nucleides.
Critical Mass:
The minimum amount of fissile material (U235)
required to continue the nuclear chain reaction is called critical mass.
Solar energy
The
energy that derive directly from sunlight and can be converted into more useful
forms is known as Solar energy.
Photogalvanic cell
Photogalvanic cell is
one, which converts the solar energy (energy obtained from the sun ) directly into electrical energy.
Wind energy
Moving
air is called wind. The energy possessed by wind is because of its high speed.
The wind energy is harnessed by
making use of wind mills, sky sail, ladder mill, kite ship etc.
Fuel cell
Fuel cell is a voltaic cell which converts
the chemical energy directly into electricity without combustion. In these cells, the reactants, products and
the electrolytes pass through the cell.
Battery
Battery is an arrangement of several
electrochemical cells connected in series that can be used as a sources of direct electric current.
Electrolytic Cell
Electrolytic Cell converts
electrical energy into chemical energy. Eg. Decomposition of water into hydrogen and hydroxide ion.
Electrochemical Cell
Electrochemical Cell converts
chemical energy into electrical energy. Eg. Galvanic (or) Voltaic cell.