IPv4, IPv6 Address - IP Address | 12th Computer Applications : Chapter 12 : DNS (Domain Name System)
Chapter: 12th Computer Applications : Chapter 12 : DNS (Domain Name System)
IP Address
IP
Address
Internet Protocol (IP) address is simply the
logical address in the network layer. Like how the door number/flat number is
used to differentiate individual house from others in the same apartment, IP
address is also used to find the host system in the whole network. Due to
increase in the number of system in a network there is a need of more addresses
which lead to two addressing methods i.e., IPv4 and IPv6.
IPv4 Address
IPv4 address is a 32-bit unique address given to a
computer system. No two systems can have same IP address. If the network has p
connections then ‘ p’ addresses should be there. An address space is the total
number of addresses that can be made by that protocol. It is determined by the
number of bits that the protocol use. If the protocol uses ‘n’ bits then the
address space of that protocol would be ‘2n’ addresses. So, the number of
addresses that can be formed in IPv4 is 232. There are two ways to represent
the IP address
● Binary
notation
● Dotted-decimal
notation
In binary notation the address is expressed as
32-bit binary values.
For E.g. 00111001 10001001 00111000 00000111
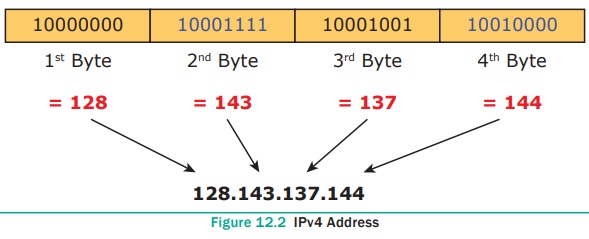
In dotted -decimal notation the address is written
in decimal format separated by dots(.). Refer Figure 12.2
For e.g. 128.143.137.144
IPv6 Address
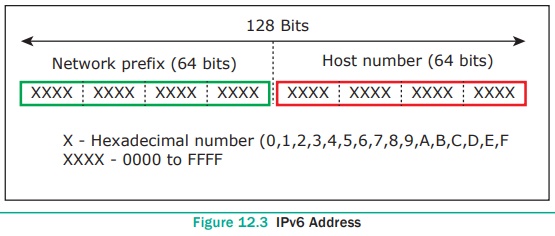
IPv6 address is a 128-bit unique address given to a
computer system. The number of addresses that can be formed in IPv6 is 2128. In
IPv6 address, the 128 bits are divided into eight 16-bits blocks. Each block is
then changed into 4-digit Hexadecimal numbers separated by colon symbols. E.g.
2001:0000:32313:DFE1:0063:0000:0000:FEFB. Refer Figure 12.3
Related Topics