Chapter: 10th English: UNIT 4 : Prose: The Attic
Grammar (Conjunctions, Phrases and Clauses)
Grammar

Conjunctions And Their Functions
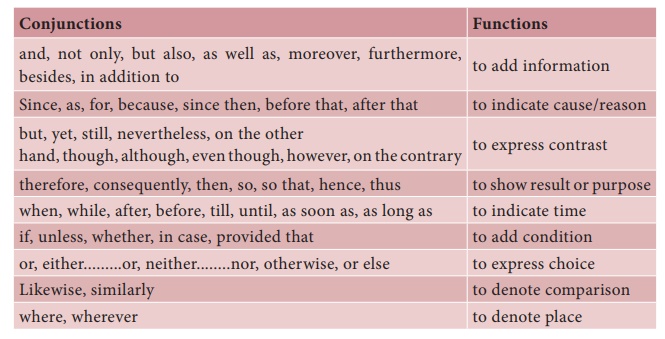
Now, let us see various types of Conjunctions and practise how to use them in sentences.
I. Coordinating Conjunctions:
1. I rang up but he didn’t speak to me.
2. Slow and steady wins the race.
3. Finish your work or you will not be sent home.
4. The child was ill so he was admitted in the hospital.
5. He is rich for he is hard-working.

II. Subordinating Conjunctions:
1. Unless you work hard, you cannot secure good marks.
2. Wait till I return.
3. He is honest, though he is poor.
4. As John is very weak, he is not able to walk fast.
5. I will return home after sunset.
6. My uncle entered my house, while I was doing my homework.

III. Correlative Conjunctions:
1. Sheeba is both a singer and a dancer.
2. Neither Jane nor Ram has attended the function.
3. No sooner did the teacher enter the class than the boys stood up.
4. Scarcely had they gone out when it started raining.
5. The car is not only economical but also feels good to drive.

EXERCISE:
A. Complete the sentences given below choosing the right connectors given in brackets.
1. Call me in case you need money. (so that, in order that, in case)
2. I forgot that I had to meet the Principal. (whether, that, if)
3. Though he is ninety years old, he is in the pink of health. (when, since, though)
4. It is raining. Take an umbrella or else you will get drenched. (or else, and, but)
5. They faced many hardships nevertheless they are always cheerful. (although, nevertheless, otherwise)
B. Fill in the blanks with the connector that goes with the underlined words.
1. Both the minister and the officers visited the affected areas.
2. Jaya teaches not only English but also Science.
3. Either Raghu or Bala will have to buy vegetables from the market.
4. No sooner did I enter the house than it started drizzling.
C. Combine the pairs of sentences using appropriate connectors.
1. We came late. We did not miss the train.
-Though we came late, we did not miss the train.
2. They checked the packet twice. Then they sealed it.
They checked the packet twice and then they sealed it.
3. Sita saw a snake. At once she ran away.
As soon as Sita saw a snake, she ran away, (or)
Sita saw a snake and at once she
ran away.
4. Robert completed the project. He submitted it to the teacher.
Robert completed the project and
submitted it to the teacher.
5. Yusuf was running high temperature. He could not take part in the competition.
As Yusuf was running high temperature, he could not take part in the competition,
(or) Yusuf was running high temperature and so he could not take
part in the competition.
D. Tick the correct linker.
1. Though he was honest, he was punished.
though,but
2. Walk carefully otherwise you will fall down.
unless, otherwise
3. My mother called me while I was playing football.
or, while
4. My salary is low nevertheless I find the work interesting.
Nevertheless, similarly
5. The passengers rushed to board the bus as soon as it arrived.
as soon as,as long as
E. Supply suitable linkers.
1. “When I was alive and had a human heart, ” answered the statue, “I did not know what tears were, for I lived in the palace where sorrow was not allowed to enter. My courtiers called me the Happy Prince and Happy Indeed I was. So I lived and so I died.
2. Many writers make incorrect sentences when they try to put sentences together. They may make grammatical errors and leave out important punctuation marks. Making such mistakes is quite common while preparing the first draft . So he must carefully edit his final draft.
3. In most large cities and towns of our country, there are special schools for girls. Moreover / And also, there are many co-educational schools where girls and boys study together. Most parents allow their daughters to attend these schools, but there are some parents who are against such schools for girls after the age of 14 or 15.
F. Rearrange the words in the correct order to make meaningful sentences.
1. as / I / healthy / are / you / am / as
I am as healthy as you are.
2. your / today / put on / new / since / is / birthday /dress / the
Since today is your birthday, put on the new
dress.
3. allergic / dogs / Rani / though / is / to / of / six / she / them / has
Though Rani is allergic to dogs, she has six of
them.
4. speaks / Ruben / besides / German / languages / two
Ruben speaks two languages besides German.
5. loan/apply/you/if/for/you/a/get/will/immediately/it/
If you apply for a loan, you will get it
immediately.
Nominalisation
The term "nominalisation" refers to he process of producing a noun from another part of speech by adding a derivational affix.
A grammatical expression is turned into a noun phrase when we nominalise a sentence. For example,
(A) After 1885, trade with Europe grew. (Verb)
(B) After 1885, there was a growth in trade with Europe. (Noun)
In sentence B, we have used the word ‘growth’ which is the noun form of the verb ‘grow’ by adding the suffix ‘th’.
Nominalisation can be done in three different ways.
1. We can add suffixes like -ment, -tion, -sion, -ness, -ation, -ity, -al to verbs and adjectives.
Examples:
admire – admiration
arrive – arrival
careless – carelessness
fail – failure
include – inclusion
intense – intensity
punish – punishment
2. Some words are turned into nouns without any adding suffix.
Examples:
bleed – blood
lose – loss
prove – proof
sell – sale
speak – speech
3. Some words do not undergo any change when they are used as nouns.
Examples:
attempt – attempt
change – change
control – control
desire – desire
escape – escape
G. Write the noun forms of the following words.
1. beautiful 2. breathe 3. enter 4. know 5. deafen 6. zealous 7. familiar 8. accept 9. dangerous
Word : Noun forms
1. beautiful : beauty
2. breathe : breath
3. enter : entry
4. know : knowledge
5. deafen : deaf
6. zealous : zeal
7. familiar : familiarity
8. accept : acceptance
9. dangerous : danger
More examples:
We have learnt how we derive noun forms from verbs and adjectives. Now, let us transform complete sentences by converting verbs and adjectives into nouns. In this process, we nominalise them, without changing the meaning of the given sentences.
1. He decided to turn down her request.
He made a decision to turn down her request.
2. The team members reviewed the matter. It helped them solve the problem.
The review of the matter by the team members helped them solve the problem.
H. Complete the following sentences using the noun form of the words given in brackets
1. The boy had to give a proper explanation for being late. (explain)
2. They could make prediction about the future.(predict)
3. At one point in life, he had no choice but to trust his friend. (choose)
4. The monuments are to be preserved because of their historical significance. (significant)
5. It is very difficult to work with so many distractions.(distract)
I. Rewrite the sentences nominalising the underlined words. The first one has been done for you.
Ex: Students work diligently to score well in exams.
Students work with diligence to score well in exams.
1. We succeeded in our attempt.
We got success in our attempt.
2. Nalini leads a happy life.
Nalini has happiness in her life.
3. She failed and it disappointed her.
Her failure gave her disappointment.
4. India became an independent country in the year 1947.
India got independence in the year
1947.
5. The child resembles her father.
The child has a resemblance to her
father.
J. Combine the pairs of sentences given below into a single sentence using the noun form of the highlighted words.
1. He is an honest person. Everyone likes him.
Answer: Everyone likes him for his honesty.
2. Sathya gave an explanation. The police wanted her to prove it.
Answer: Though Sathya gave an explanation, the police wanted the proof.
3. He speaks well. It attracts all.
Answer: His speech is
an attraction to all.
4. Suresh is always punctual and regular. It has earned him a good job.
Answer: Punctuality and regularity of Suresh have earned him a good job.
5. The policeman arrived quickly. It made us happy.
Answer: The quick arrival of the policeman made us happy.
K. Complete the sentences in the paragraph using the appropriate form of words given in brackets.
1. My sister wanted to go to Mumbai last week. She made a decision (decide) to buy a ticket at once. As reservation (reserve) could be done online, she gave preference (prefer) to book a ticket that way. First, she collected information (inform) about the arrival (arrive) and departure (depart) of trains and airplanes.
2. A few days later, Androcles was captured by his master. He had to suffer all kinds of punishment (punish). At last, he was thrown to a lion which was in great hunger (hungry).It had been kept in an enclosure (enclose) and had not been fed for several days. His friends stood there with tearfull (tear) eyes as the lion rushed towards him. The lion stopped near him and stood for a while looking (look) at him. Then it lay down by his side like a pet dog. Obviously (obvious), the lion recognized Androcles and the help (help) he had given it.
Phrases and Clauses
Finite And Non-Finite Verbs:
Words which denote an action are known as verbs. We classify verbs into two types. They are
1. Finite verbs:
a. My brother goes to temple daily.
b. We have already finished the project.
The words printed in bold letters are finite verbs.
1. Finite verbs indicate the tense and time of actions.
2. Finite verbs undergo a change as and when the Subject (number or person) changes.
2. Non-Finite Verbs:
1. Non-finite verbs do not indicate the tense and time of actions.
2. Non-finite verbs do not change even when the Subject (number or person) changes.
There are three kinds of non-finite verbs.
1. An infinitive ( to + verb )
2. A gerund ( verb + ing )
3. A participle
Example:
a. My son likes to watch cricket matches.(Infinitive)
b. Playing chess is my hobby. (Gerund)
c. Driven out of the kingdom, the king hid himself in a forest. (Participle)
PHRASE:
Example 1:
an intelligent boy
a costly pen
an interesting story
The above group of words are known as phrases. It doesn’t contain a finite verb.
A Phrase is a group of words without a finite verb
CLAUSE:
Example 1:
a boy who is intelligent
a pen which is costly
a story which is interesting
The groups of words given above are clauses
A Clause is a group of words which consists of a finite verb.
More Examples:
Example 1:
Having completed the work, the boy went out to play.
The underlined part of the sentence, doesn’t contain a Finite verb. This group of words is a Phrase.
Example 1:
After the boy had completed the work, he went out to play.
The underlined part of the sentence contains a finite verb. Hence, we call it a clause.
Kinds Of Phrases:
We have three kinds of phrases according to their functions in sentences.
1. Adjective Phrase: It is a group of words that does the work of an adjective. It describes the noun.
Example 1:
We bought chairs made of wood for our auditorium.
2. Adverb Phrase: It is a phrase which functions as an adverb. This Phrase supplies some information about the action.
Example 1:
When the patient was taken to the Emergency ward, the doctors rushed there in a hurried manner.
3. Noun Phrase: This is a phrase which acts as a noun.
Example 1:
A boy of class X became the house captain.
L. Identify the phrases in the following sentences and classify them as Adjective, Adverb or Noun phrases.
1. The girl in blue saree is my sister.
2. Kohli hopes to win the trophy.
3. The train halts at every junction.
4. I have never seen such a picture.
5. She worked in an enthusiastic manner.
Kinds Of Clauses
1. Adverb Clause: It modifies the verb, that is, it tells something about the action. This Clause gives details about the action.
Example:
The students were sitting quietly in the classroom until the teacher arrived.
(The highlighted part of the sentence speaks about the time of the action)
2. Noun Clause: This clause functions as a noun.
Example:
Whoever wins the contest will get a prize.
(The highlighted portion acts as a noun here)
3. Adjective Clause: It acts as an adjective and describes a noun.
Example:
I went to the place where I was born.
(The highlighted words describes the place)
M. Identify the clauses and classify them accordingly.
1. Ram bought a pen that doesn’t write well. - Adjective clause
2. Come back as soon as possible.
3. Most of her friends whom she had invited attended her wedding.
4. My brother visits my father whenever he comes to Chennai.
5. Call me in case there is an emergency.
6. Until the sun sets, the old woman cannot step out of her house.
7. She knows where I go.
8. You can go wherever you want. - Adverb clause
Related Topics