Term 3 Unit 2 | Geography | 6th Social Science - Globe | 6th Social Science : Geography : Term 3 Unit 2 : Globe
Chapter: 6th Social Science : Geography : Term 3 Unit 2 : Globe
Globe
Unit 2
GLOBE

Learning Objectives
• To understand the four cardinal
directions.
• To learn about the shape of the
Earth.
• To understand about the model of
the Earth - the globe.
• To understand the significance of
lines of latitudes and longitudes.
• To know how standard time is
calculated around the world.
Surya and
Poovendhan are very good friends who study in the sixth standard and live in a
beautiful village called Thirunandriyur. Surya lives in South Street, while
Poovendhan lives in North Street. Every day they go to school together. One
day.........

Surya: Why are you coming so late, Poovendha?
Poovendhan: Please bear with me,
Surya! Come, let’s go.
Surya: What took you so long?
Poovendhan: You live on South Street.
But, I have to come from the North Street, which is so far away from here.
That’s why I’m late.
Surya: Yes, that’s true. But wherever
we live, don’t you remember that we all live on planet Earth?
Poovendhan: Yes! Yes! I do remember, Even our Ponni
Miss taught us about the Solar System.
Surya: But, I have a doubt ….
Poovendhan: Tell me, what is it?
Surya: We can see our house, the things
around us, the people, animals and birds with our eyes. But, why can’t we see
our Earth as a whole?
Poovendhan: Haven’t you seen it?
Surya: No, I haven’t. Have you ever
seen it?
Poovendhan: Yes, in our school only.
Surya: Did you say, in our school?
Poovendhan: Yes, on our Ponni Miss’ table. Big and
spherical!
Surya: Oh! Yes! Like a ball on a stand?
Poovendhan: Exactly! That is our
Earth
Surya: But........ But, our teacher
said that our Earth is in the Milky
Way Galaxy. But you say that our Earth is on our teacher’s
table. I am so confused. Come, let’s go and ask Ponni Miss.
The bell rang as they reached school. They
attended the morning assembly and went to the classroom. During the social
science period, Surya asks Ponni Miss to clear his doubts.
Surya: Good morning, Miss.
Teacher: Good morning.
Surya: Madam, you told us on the other
day that our Earth is in the Milky Way galaxy.
Teacher: Yes, it is true. This is
the model of the Earth.
Surya: A model of the earth, Madam?
Please explain!
Teacher: Sure, Surya.
The teacher asks all the students to sit down and
starts explaining.
Directions
The directions on
the ground are always shown with respect to the North. If we know the North,
then it is easy to find the other directions, namely South, East and West.
These are the four cardinal directions.
We know that the Sun rises in the East and sets in
the West. If we stand facing the sun in the morning, then we face the east. The
west is towards our back. The left hand points towards the north and the right
hand points towards the south. We should always keep this in mind.
Globe
We live on the
planet Earth, which is found third from the Sun. Since the Earth is huge and we
live on a very small area, we are not able to see the Earth as a whole. But,
when we travel to space, we can see the Earth as a whole.

So, in order
to see the shape of the Earth as a whole and to know its unique features, a
three dimensional model of the Earth was created with a specific scale.
The surface area of the Earth is
510.1 million square kilometres.
The Earth which
is spherical, is flat at the poles and bulges at the Equator. The Earth cannot
be compared with any other geometrical shape as it has a very unique shape.
Hence, its shape is called a geoid (earth shaped)
The Earth
moves around the Sun. It also rotates from the West to East on its axis at an
inclination of 23 ½°. The globe is also inclined at an angle of 23 ½°. The axis
is an imaginary line. It is not actually found on the Earth.
* The first globe was created by the
Greeks in the year 150 AD(CE).
* The Indian astronomer Aryabhatta -
I has mentioned in his book. ‘Aryabhatta Sidhantha’. ‘The
stars in the sky seem to move towards the West because of the Earth’s roation
on its axis’.
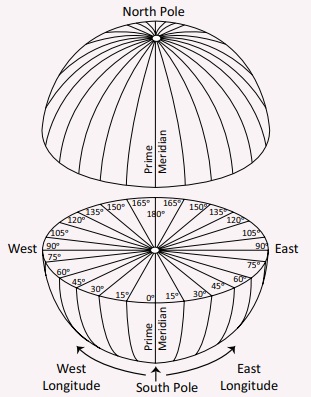
Lines on the
Globe
There are
imaginary lines which are drawn on the globe horizontally and vertically to
find a location and calculate distance and time. These imaginary lines are
called lines of latitudes and
longitudes.
Ptolemy, a Greco – Roman mathematician, astronomer and geographer, was
the first person to draw the lines of latitude and longitude on a map.

In his book, ‘Geographia’ a detailed description about the Earth’s surface, its size and circumference and many locations based on the lines of latitude and longitude are given.
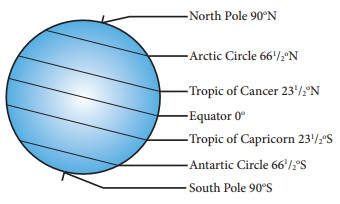
Latitudes
The imaginary
lines which are drawn horizontally on East - West direction on the Earth are
called the lines or parallels of
latitudes. The 0° line of latitude which
divides the Earth into two halves is known as the Equator.
From the Equator, parallel lines are drawn towards the North
and South poles at equal intervals. The latitudinal extent between 1° line
of latitude
on Earth is 111 km.
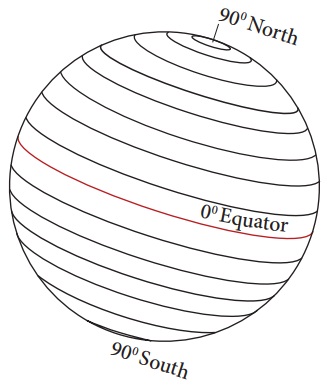
Since the Earth is
geoid shaped, the length of the lines of latitude decreases from the Equator towards
the South and North Poles. The 90° North and South Poles are not found as
lines, but as points.
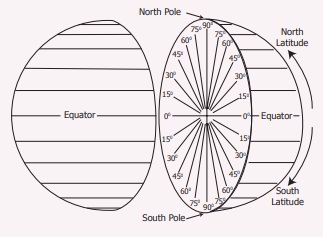
The lines of
latitude that are drawn horizontally between the Equator and the North Pole are
called ‘Northern latitudes’ and those which are found between
the Equator and the South Pole are called ‘Southern Latitudes’. The
lines of latitude consist of 89 parallels in the Northern Hemisphere and
89 parallels in the Southern Hemisphere, one at the Equator and
the two poles are found as points. Totally, there are 181 parallels
found on earth.
The Equator is the longest of all
lines of latitude. Hence, it is also known as ‘The Great
Circle’.
Activity :

Draw a circle on a paper. Draw a
horizontal line across the middle of a circle. Keeping this line as 0°, draw lines on both sides with an equal
interval of 15° with the help of a protractor. The lines you have drawn are
lines of latitudes.
Northern Hemisphere
The area of
the Earth from the equator (0°) to the South Pole (90°S) is called the Southern Hemisphere.
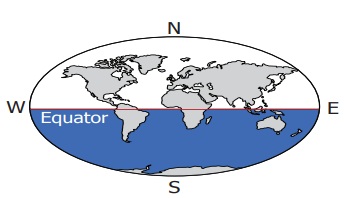
Southern Hemisphere
The area of
the Earth from the equator (0°) to the South Pole (90°S) is called the Southern Hemisphere.
The location
of any country or place is based on this division of the hemispheres
HOTS
Based on the latitudinal extent, in
which hemisphere is India located?
Important
lines of latitude
The earth
rotates on its axis at an inclination of 23½°. It also revolves around the sun
while rotating. Based on the angle at which the sun’s rays fall on the earth,
certain lines of latitude gain significance.
• 0°N and S – 23½°N and S
lines of latitudes are called – Low latitudes
• 23½°N and S – 66½°N and S
lines of latitudes are called – Middle Latitudes
• 66½°N and S – 90°N and S
lines of latitudes are called –High Latitudes
(Source : A
Dictionary of Geography – Susan Mayhew, Oxford University Press, Fifth
edition -2015)
The Sun’s
rays do not fall equally on all parts of the earth. They fall vertically over
the Equator and slanting towards the poles. Thus, all the places on earth do
not have the same amount of temperature. Based on the amount of heat received
from the Sun, the lines of latitude help in dividing the earth into different
climatic zones.
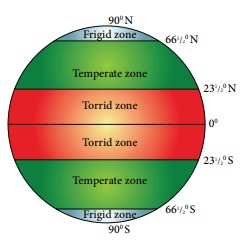
Torrid Zone
The region
from the Equator towards the Tropic of Cancer (23½°N) and the Tropic of
Capricorn (23½°S) is called the Torrid Zone. The Sun’s rays fall vertically
over this region and the average temperature is very high. Hence this region is
known as the Torrid Zone.
Temperate
Zone
From the Tropic of
Cancer (23½°N) to the Arctic Circle (66½°N) and from the Tropic of Capricorn
(23½°S) to the Antarctic Circle (66½°S), the Sun’s rays fall slantingly.
Moderate temperature prevails in this region. Hence, this region is called Temperate
Zone.
Frigid Zone
From the Arctic
Circle (66½°N) to the North Pole (900N) and from the Antarctic Circle (66½°S)
to the South Pole (90°S), the Sun’s rays fall further inclined, through out the
year. The temperature is very low. Hence, this region is known as Frigid
Zone.
Some lines of latitude are also
called by the following names in Tamil.
Latitude – ahalangu (அகலாங்கு)
Longitude – nettangu (நெட்டாங்கு)
Equator - nilanaduvarai (நிலநடுவரை)
Tropic of Cancer - kadagavarai (கடகவரை)
Tropic of Capricorn - magaravarai (மகரவரை)
(Source:
Ariviyal Kalanjiyam, The Tamil University)
Longitudes
The imaginary lines
drawn vertically connecting the North Pole and the South Pole are called lines
or meridians of longitude. These lines of longitude are seen as semi circles.
The 0° line of longitude is called the Prime Meridian.
There are 180 lines of longitude towards the East and West from the Prime
Meridian. So, there are totally 360 lines of longitude. These
lines converge at the poles. The 180° W and 180° E line of longitude are
the same line.
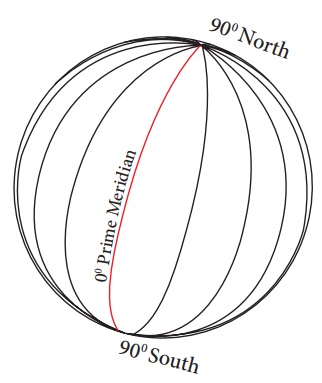
The lines of
longitude that are found between the Prime Meridian and the 180° East line of
longitude are called ‘Eastern Longitudes’ and the lines of longitude
that are found between the Prime Meridian (0°) and the 180° West line of
longitude are called ‘Western Longitudes’. Two opposite meridians
form a great circle
The lines of longitude are found as
semi circles covering 111 km at the Equator, 79 km at 45° latitude and no space
between the lines at the poles.
Activity
:

Take
a ball and a thin iron wire. Pierce the ball with the wire from one end to the
other end through the middle. Remove the wire. Draw circles around the points.
Name the northern most point as North Pole and the southern most point as South
Pole. The angle of a circle is 360°. Mark points on the circle at an interval
of 15° using a protractor. Then draw lines joining these points on the top and
bottom of the ball. The lines that you have drawn are lines of longitudes.
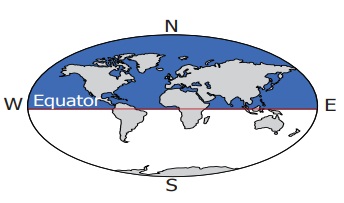
Eastern Hemisphere
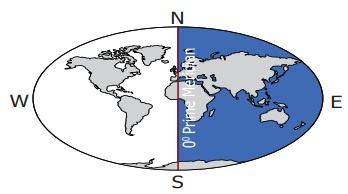
The part of the
Earth between the 0° line of longitude and the 180° East line of longitude is
known as the Eastern Hemisphere.
Western Hemisphere
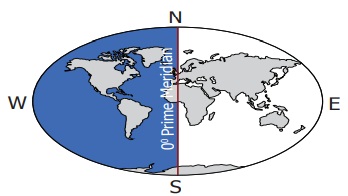
The part of the
Earth from 0° line of longitude to 180° West line of longitude is called as Western
Hemisphere.
Activity
Based on the longitudinal extent, in
which hemisphere is our country located? Look at the globe and answer.
Significant Lines of Longitude
Greenwich Meridian
The Royal
Astronomical Observatory is located at Greenwich near London in England.
According to the International Meridian Conference held in 1884 in

This line of longitude is called the
Prime Meridian and it is also known as the Greenwich Meridian because it
passes through Greenwich.
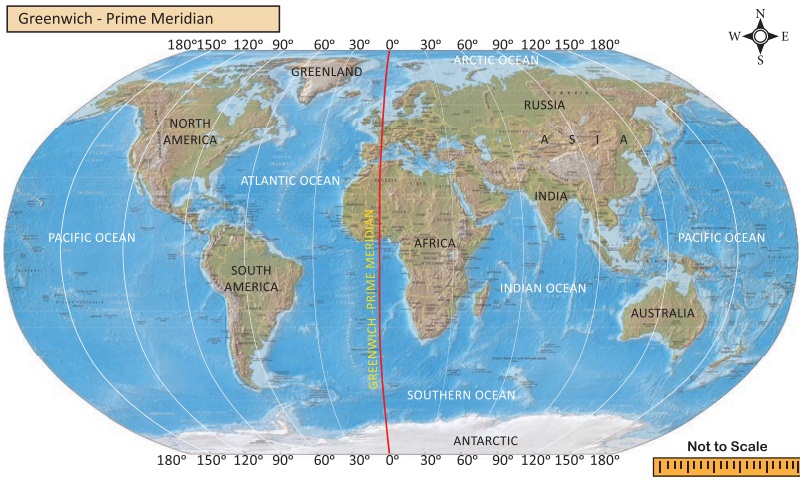
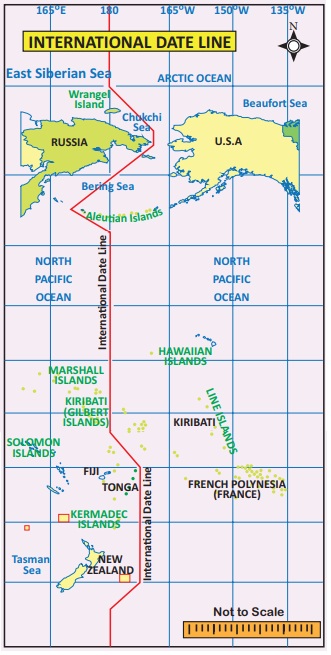
International Date Line
The 180º line of
longitude has been fixed as the International Date Line, drawn on the Pacific
Ocean between Alaska and Russia through Bering Strait. If a person crosses this
line from the West to East, he loses a day. On the other hand, when he crosses
from the East to West, he gains a day. Based on this, the date is fixed for
different countries or regions of the world.
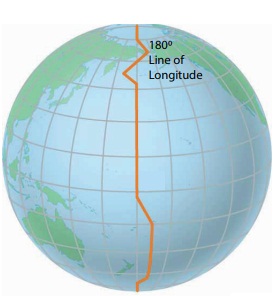
The International Date Line is not straight. If the line is drawn straight, two places in
the same country would have different dates.
So the International Date
Line is found
zigzag in certain places to avoid confusion.
Earth Grid
The imaginary
lines of latitude and longitude form a grid like pattern on the surface of the
earth, known as the ‘Earth grid’ or
‘Geographic grid’.
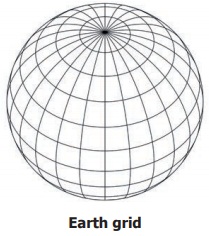
To locate a
place exactly on earth, the latitudinal and longitudinal extensions are required.
Longitude
and Time
As many as 360 lines of longitude are drawn to connect the North and South
Poles around the Earth 180° on the Eastern Hemisphere and 180° on the Western
Hemisphere. Time is calculated on the basis of the lines of longitude.
Fact
* The Earth takes one day to rotate on its
axis.
* 1 day = 24 hours
* 1 hour = 60 minutes
* 24 hours = 24 x 60 = 1440 minutes
* The angle of the earth = 360°
* 360° = 360 Longitudes
* 360° = 1440 minutes
* So 1° = 1440/360 = 4 minutes
* In 4 minutes = 1° rotation
* In 60 minutes = 60/4 = 15°rotation
* So, in an hour (60 minutes) the
earth rotates 15°
Local Time
When the sun is
overhead on a particular line of longitude, it is 12 noon at all the places
located on that line of longitude. This is called local time.
The Sun is overhead
on a line of longitude only once in a day. So the local time differs for every
line of longitude.
When the Sun is
overhead the Greenwich Meridian at 12 noon, it is the local time of that place.
The world time is calculated by this standard line of longitude. It is known as
the Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
For example, if the
time is 12 noon at Greenwich Meridian, it is 12:04 p.m. at 1°E line of
longitude and 11:56 a.m. at 1°W line of longitude. So, as one moves
towards the east from any meridian the time increases. And if one moves towards
the west from any meridian, time decreases.
1. The word meridian is derived from
the Latin word ‘Meridianus’. It means mid day. (Medius – Middle, dies
– day). So, meridian means the position of the Sun found overhead at a
place at noon.
2. a.m. means 'anti Meridiem'
(anti – before) – Before Noon.
3. p.m. means 'post Meridiem'
(Post after/later) – After noon.
Standard
Time
Local time is
calculated when the sun is overhead at noon. Many lines of longitude may pass
through a country. Countries may or may not observe a common time. The standard
time of a country or a part of it is calculated keeping a particular meridian as a standard one.
The meridians are
selected in multiples of 15° or 7 ½°. It is done in such a way that the
variation of standard time from the Greenwich is expressed either as 1 hour or
½ an hour.
Indian
Standard Time
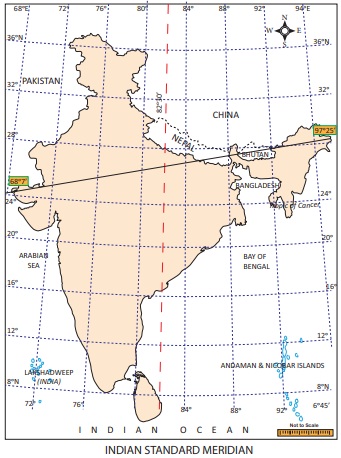
The longitudinal
extent of India is from 68°7’ E to 97°25’ E. As many as twenty nine lines of
longitude pass through India. Having 29 standard time is not logical. Hence
82½° E line of longitude is observed as the Prime Meridian to calculate the
Indian Standard Time (IST).
The 82½° E line of longitude passes
throughMirzapur near Allahabad in Uttar Pradesh. This is
located at an equal distance from Ghuar Mota in Gujarat and Kibithu
in Arunachal Pradesh.
Time Zones
The world has 24 time zones. Some countries have a
great longitudinal extent. So they have more than one standard time. Example:
Russia has 7 time zones.
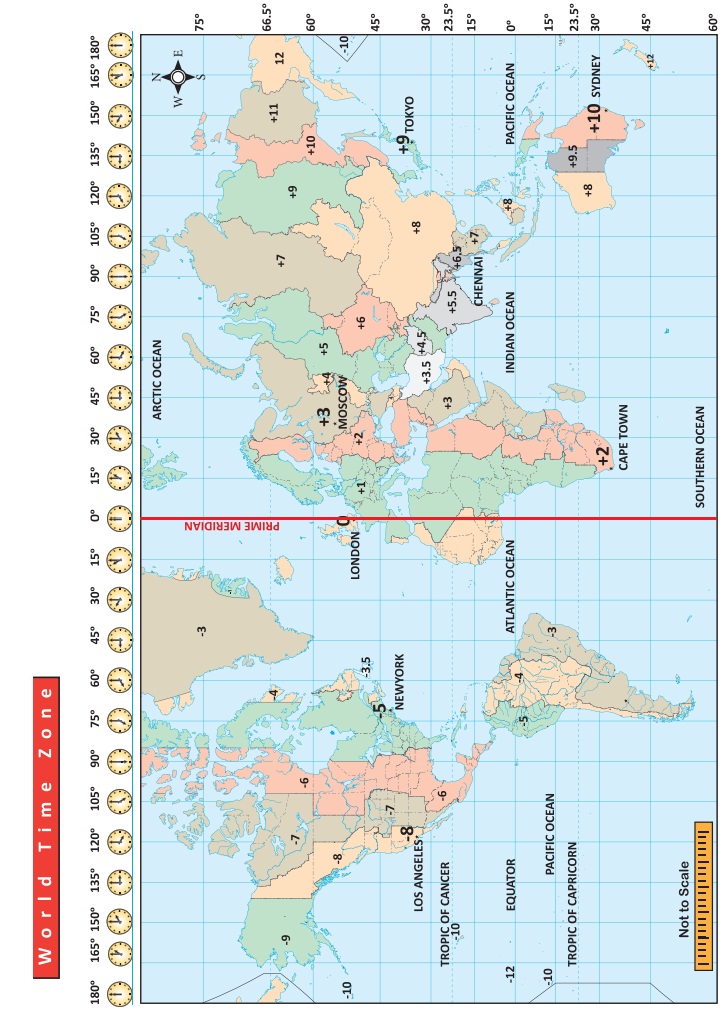
Activity:
1. What is the difference in time
between the GMT and IST?
2. If it is 5 a.m. at New York City,
USA. what would be the time at NewDelhi, the capital of India?
3. If it is 12 Midnight at London,
what would be the time in India?
4. The standard time of Sydney city
in Australia is found to be at a difference of _________ hours from that of the
GMT.
5. Mr. Senthamizh travels by flight
from Chennai to London. He boarded the aeroplane at 9a.m After 12 hours of
travel, at what time (GMT) would he have reach London?
We saw about the lines of latitude and longitude
drawn on the globe. Besides these, physical land forms, seas, oceans, countries
etc., are also found on the globe
Wrap up
1. The imaginary lines drawn horizontally from the
East to West on the globe and maps are called lines of latitude or parallels.
2. The imaginary lines drawn vertically from the North
to South on the globe and maps are known as lines of longitude or meridians.
3. The 0° line of latitude is called theEquator.
4. The 0° line of longitude is called the
Greenwich Meridian or the Prime Meridian.
5. The part of the Earth from the Equator (0°) to
North Pole (90°) is called the Northern Hemisphere and from the Equator (0°) to
South Pole (90°) is called the Southern Hemisphere.
6. The part of the Earth from the Greenwich
Meridian (0°) to 180° East line of longitude is called the Eastern Hemisphere
and from Equator (0°) to 180° West line of longitude is called the Western
Hemisphere.
7. Lines of latitude are circles which are drawn
at a distance of about 111 km. The poles are shown as points.
8. Lines of longitude are drawn as semi circles. The
distance between the lines of longitude at the Equator is 111 km. It is found
at a distance of 79 km at 45° latitude and they converge at the poles.
9. Lines of latitude do not merge, while lines of
longitude converge at the poles.
10. Time is calculated on the basis of the lines
of longitude. The 180° line of longitude is the International Date Line.
Glossary
1. Globe – A model of the earth
2. Lines of Latitude / Parallels– Imaginary lines drawn
horizontally on the Earth from the East to West
3. Lines of Longitude / Meridians – Imaginary line
drawn vertically on the Earth from the North to South
4. Geoid – The shape of the Earth
5. Hemisphere – Dividing the earth on the basis of
0° lines of latitude and longitude with regard to directions
6. Equator– The line of latitude drawn
horizontally at the centre of theEarth
7. Tropic of Cancer – 23 ½° N line of latitude
8. Tropic of Capricorn – 23 ½° S line of latitude
9. Arctic Circle – 66 ½° N line of latitude
10. AntarcticCircle– 66 ½° S line of latitude
Reference
1. Goh Cheng Leong, Certificate Physical and Human
Geography (2009), Oxford University Press, New Delhi, India.
2. A Dictionary of Geography – Susan Mayhew,
Oxford University Press, Fifth edition -2015.
3. அறிவியல்
களஞ்சியம் (தொகுதிகள்), தஞ்சை தமிழ்ப்பல்கலைக்க வெளியீடு.
4. The earth shape and gravity (1965) Oxford
Degman Press.
5. Strahler, Physical Geopraphy 4th Edition (1965)
New York MC Graw – Hill Book Co.
Web Links
1. https://www.britannica.com
ICT CORNER
Geography
- Globe
Through
this activity you will know about the globemodel!.
Steps:
Step -1 Use the URL or scan the QR code to open
the activity page.
Step -2 Click the red “hot spot” area to see the
main landmarks of the globe.
Step -3 In the view box Click the “Core” option to
view the Earth's inner layers.
Step -4 Drag and rotate the Globe you can rotate
the Globe.
*Pictures are indicatives
only.
Browse in
the link
Web:
https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/planets/earth/overview/ (or) scan the QR Code
Related Topics