Chapter: Introduction to Botany: Plants and Earth
Geography of Vegetation
Geography of Vegetation
Plants are main components of terrestrial ecosystems, they are primary pro-ducers, and almost all terrestrial life if based on plants. Consequently, plants will determine how a particular territory might look, which could be, for exam-ple, grassland, tundra, or forest. These types of vegetation (i.e., visually different plant communities) will have different occurrence on Earth. Below is the list of the most important types (they also called biomes):
Tundra
Small-sized plants adapted to the short season, wet soils and some-times also permafrost
Taiga
Conifer forests
Deciduous forest
Broadleaved temperate forests. The other type of deciduousforests are dry forests of tropical climates.
Grassland
Prairie (North America), steppe (Eurasia), savanna (Africa and Aus-tralia), llanos (north South America), pampas (south South America)
Shrubland
Chaparral (North America), maquis (Mediterranean), fynbos (SouthAfrica), bush (Australia)
Desert
Different from shrubland by plants staying apart and soil surface visible
Tropical forest
Selva, tropical rain forest: humid and warm environment, thepeak of Earth biodiversity
Naturally, these biomes are directly related with the climate, mostly with the coldest temperatures and amount of precipitation. If the Earth would be one continent, then these vegetation types will be arranged from a pole to equator exactly in the order from the list above. However, the real picture is more com-plicated (Fig. 9.1.)
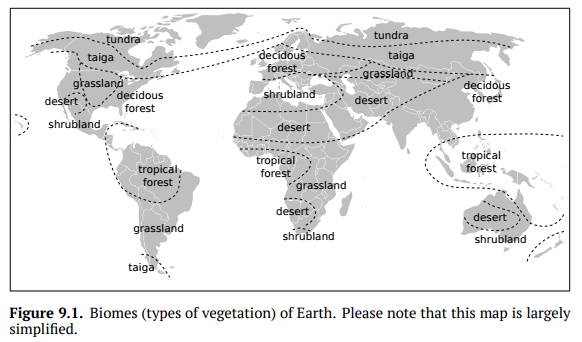
Some smaller biomes, especially different kinds of wetlands (like sphagnum bogs or mangroves) are significantly dispersed, sometimes even intra-zonal (occur in different climatic zones).
Related Topics