Chapter: Mechanical : Automobile Engineering : Alternative Energy Sources
Fuel Cell
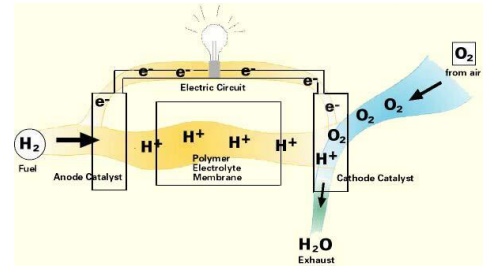
Fuel Cell
A Fuel Cell is an electrochemical device that combines
hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity, with water and heat as its
by-product. Since conversion of the fuel to energy takes place via an
electrochemical process, not combustion. It is a clean, quiet and highly
efficient process- two to three times more efficient than fuel burning.
It operates similarly to a battery, but it does not run down
nor does it require recharging As long as fuel is supplied, a Fuel Cell will
produce both energy and heat A Fuel Cell consists of two catalyst coated
electrodes surrounding an electrolyte. One electrode is an anode and the other
is a
cathode
The process begins when Hydrogen molecules enter the anode The catalyst coating
separates
hydrogen’s negatively charged electrons from the positively charged protons The
electrolyte allows the protons to
pass through to the cathode, but not the electrons.
Instead the electrons are directed through an external circuit
which creates electrical current. While the electrons pass through the external
circuit, oxygen molecules pass through the cathode. There the oxygen and the
protons combine with the electrons after they have passed through the external
circuit. When the oxygen and the protons combine with the electrons it produces
water and heat. Individual fuel cells can then be placed in a series to form a
fuel cell stack. The stack can be used in a system to power a vehicle or to
provide stationary power to a building
Related Topics