Chapter: Business Science : Financial Management : Foundations of Finance
Foundations of Finance
FOUNDATIONS OF FINANCE
1 Introduction
1.1Meaning of Finance
1.2Definition of Finance
1.3Types of Finance
2 Overview
2.1 Scope of Financial Management
2.2 Objectives of Financial Management
2.3 Approaches to Financial Management
2.4 Importance of Financial Management
3 Time Value Of Money
3.1 Concept
3.2 Compound Interest
3.3 Present Value
4 Introduction To The Concept Of Return Of A Single
Asset
4.1 Introduction
4.2 Concept and Types of Risk
4.3 Risk and Return of the Portfolio
4.4. Relationship Between The Risk And Return
5 Valuation Of Bonds And Shares
5.1 Valuation of Bonds
5.2 Valuation of Shares
6 Option Valuation
6.1 Factors Affecting Value Of Options
1 Introduction
Business
concern needs finance to meet their requirements in the economic world. Any
kind of business activity depends on the finance. Hence, it is called as
lifeblood of business organization. Whether the business concerns are big or
small, they need finance to fulfill their business activities.
In the
modern world, all the activities are concerned with the economic activities and
very particular to earning profit through any venture or activities. The entire
business activities are directly related with making profit. According to the
economics concept of factors of production, rent given to landlord, wage given
to labour, interest given to capital and profit given to shareholders or
proprietors, a business concern needs finance to meet all the requirements.
Hence finance may be called as capital, investment, fund etc., but each term is
having different meanings and unique characters. Increasing the profit is the
main aim of any kind of economic activity.
1.1 Meaning Of Finance
Finance
may be defined as the art and science of managing money. It includes financial
service and financial instruments. Finance also is referred as the provision of
money at the time when it is needed. Finance function is the procurement of
funds and their effective utilization in business concerns. The concept of
finance includes capital, funds, money, and amount. But each word is having
unique meaning. Studying and understanding the concept of finance become an
important part of the business concern.
1.2 Definition Of Finance
v According
to Khan and Jain, ―Finance is the
art and science of managing money‖.
v Webster’s Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary
defines finance as ―the Science on study
of the management of funds‘ and the management of fund as the system that
includes the circulation of money, the granting of credit, the making of
investments, and the provision of
banking
facilities.
Definition Of Business Finance
According
to the Guthumann and Dougall,
―Business finance can broadly be defined as the activity concerned with
planning, raising, controlling, administering of the funds used in the
business‖.
Corporate
finance is concerned with budgeting, financial forecasting, cash management,
credit administration, investment analysis and fund procurement of the business
concern and the business concern needs to adopt modern technology and
application suitable to the global environment.
1.3 Types Of Finance
Finance
is one of the important and integral part of business concerns, hence, it plays
a major role in every part of the business activities. It is used in all the
area of the activities under the different names.
v
Private Finance
v
Public Finance
Types of Finance
Private Finance, which includes the Individual,
Firms, Business or Corporate Financial activities to meet the requirements.
Public Finance
which concerns with revenue and disbursement of Government such as Central
Government, State Government and Semi-Government Financial matters.
2 OVERVIEW
Definition
The most
popular and acceptable definition of financial management as given by S.C. Kuchal is that ―Financial Management deals with procurement of
funds and their effective utilization
in the business‖.
Joshep and Massie: Financial
management ―is the operational activity of a business that is responsible for obtaining and effectively utilizing the
funds necessary for efficient operations.
2.1 Scope Of Financial Management
1. Financial Manage ment and Economics
Economic
concepts like micro and macroeconomics are directly applied with the financial
management approaches. Investment decisions, micro and macro environmental
factors are closely associated with the functions of financial manager.
Financial management also uses the economic equations like money value discount
factor, economic order quantity etc. Financial economics is one of the emerging
area, which provides immense opportunities to finance, and economical areas.
2. Financial Management and Accounting
Accounting
records includes the financial information of the business concern. Hence, we
can easily understand the relationship between the financial management and
accounting. In the olden periods, both financial management and accounting are
treated as a same discipline and then it has been merged as Management
Accounting because this part is very much helpful to finance manager to take
decisions. But nowadays financial management and accounting discipline are
separate and interrelated.
3. Financial Management or Mathematics
Modern
approaches of the financial management applied large number of mathematical and
statistical tools and techniques. They are also called as econometrics.
Economic order quantity, discount factor, time value of money, present value of
money, cost of capital, capital structure theories, dividend theories, ratio
analysis and working capital analysis are used as mathematical and statistical
tools and techniques in the field of financial management.
4. Financial Management and Production Management
Production
management is the operational part of the business concern, which helps to
multiple the money into profit. Profit of the concern depends upon the
production performance. Production performance needs finance, because
production department requires raw material, machinery, wages, operating
expenses etc. These expenditures are decided and estimated by the financial
department and the finance manager allocates the appropriate finance to
production department. The financial manager must be aware of the operational
process and finance required for each process of production activities.
5. Financial Management and Marketing
Produced
goods are sold in the market with innovative and modern approaches. For this,
the marketing department needs finance to meet their requirements. The
financial manager or finance department is responsible to allocate the adequate
finance to the marketing department. Hence, marketing and financial management
are interrelated and depends on each other.
6. Financial Management and Human Resource
Financial
management is also related with human resource department, which provides
manpower to all the functional areas of the management. Financial manager
should carefully evaluate the requirement of manpower to each department and
allocate the finance to the human resource department as wages, salary,
remuneration, commission, bonus, pension and other monetary benefits to the
human resource department. Hence, financial management is directly related with
human resource management.
2.2 Objectives Of Financial Management
Effective
procurement and efficient use of finance lead to proper utilization of the
finance by the business concern. It is the essential part of the financial
manager. Hence, the financial manager must determine the basic objectives of
the financial management. Objectives of Financial Management may be broadly divided
into two parts such as:
1. Profit
maximization
2. Wealth
maximization.
Profit Maximization
v
Profit maximization is also called as cashing per
share maximization. It leads to maximize the business operation for profit
maximization.
v Ultimate aim of the business concern is earning
profit, hence, it considers all the possible
ways to
increase the profitability of the concern.
v
Profit is the parameter of measuring the efficiency
of the business concern. So it shows the entire position of the business
concern.
v
Profit maximization objectives help to reduce the
risk of the business.
Favourable Arguments for Profit Maximization
(i) Main aim
is earning profit.
(ii) Profit is
the parameter of the business operation.
(iii)Profit
reduces risk of the business concern.
(iv)Profit is
the main source of finance.
(v) Profitability
meets the social needs also.
Unfavourable Arguments for Profit Maximization
(i)
Profit maximization leads to exploiting workers and consumers.
(ii) Profit
maximization creates immoral practices such as corrupt practice, unfair trade
practice, etc.
(iii) Profit
maximization objectives leads to
inequalities among the stake
holders such as
customers,
suppliers, public shareholders, etc.
Drawbacks of Profit Maximization
(i)
It is
vague: In this objective, profit is not defined precisely or correctly. It
creates some unnecessary opinion
regarding earning habits of the business concern.
(ii)
It
ignores the time value of money: Profit maximization does not
consider the time
value of
money or the net present value of the cash inflow. It leads certain differences
between the actual cash inflow and net present cash flow during a particular
period.
(iii)
It
ignores risk: Profit maximization does not consider risk of the
business concern.
Risks may
be internal or external which will affect the overall operation of the business
concern
.
Wealth Maximization
Wealth
maximization is one of the modern approaches, which involves latest innovations
and improvements in the field of the business concern. The term wealth means
shareholder wealth or the wealth of the persons those who are involved in the
business concern. Wealth maximization is also known as value maximization or
net present worth maximization. This objective is an universally accepted
concept in the field of business.
Favourable Arguments for Wealth Maximization
(i) Wealth
maximization is superior to the profit maximization because the main aim of the
business concern under this concept is to improve the value or wealth of the
shareholders.
(ii) Wealth maximization
considers the comparison of the value to cost associated with the business
concern. Total value detected from the total cost incurred for the business
operation.
It
provides extract value of the business concern.
(iii)Wealth
maximization considers both time and risk of the business concern.
(iv)Wealth
maximization provides efficient allocation of resources.
(v) It
ensures the economic interest of the society.
Unfavourable Arguments for Wealth Maximization
(i) Wealth
maximization leads to prescriptive idea of the business concern but it may not
be suitable to present day business activities.
(ii) Wealth
maximization is nothing, it is also profit maximization, it is the indirect
name of the profit maximization.
(iii)Wealth
maximization creates ownership- management controversy.
(iv)Management
alone enjoys certain benefits.
(v) The
ultimate aim of the wealth maximization objectives is to maximize the profit.
(vi)Wealth
maximization can be activated only with the help of the profitable position of
the business concern.
2.3 Approaches To Financial Management
Theoretical
points of view, financial management approach may be broadly divided into two
major parts.
v Traditional Approach
v Modern Approach
Traditional Approach
Traditional
approach is the initial stage of financial management, which was followed, in
the early part of during the year 1920 to 1950. This approach is based on the
past experience and the traditionally accepted methods. Main part of the
traditional approach is rising of funds for the business concern. Traditional
approach consists of the following important area.
v Arrangement
of funds from lending body.
v Arrangement
of funds through various financial instruments.
v Finding
out the various sources of funds.
Functions Of Finance Manager
1. Forecasting Financial Require ments
It is the
primary function of the Finance Manager. He is responsible to estimate the
financial requirement of the business concern. He should estimate, how much
finances required to acquire fixed assets and forecast the amount needed to
meet the working capital requirements in future.
2. Acquiring Necessary Capital
After
deciding the financial requirement, the finance manager should concentrate how
the finance is mobilized and where it will be available. It is also highly
critical in nature.
3. Investment Decision
The
finance manager must carefully select best investment alternatives and consider
the reasonable and stable return from the investment. He must be well versed in
the field of capital budgeting techniques to determine the effective
utilization of investment. The finance manager must concentrate to principles
of safety, liquidity and profitability while investing capital.
4. Cash Management
Present
day‘s cash management plays a major role in the area of finance because proper
cash management is not only essential for effective utilization of cash but it
also helps to meet the short-term liquidity position of the concern.
5. Interrelation with Other Departments
Finance
manager deals with various functional departments such as marketing,
production, personnel, system, research, development, etc. Finance manager
should have sound knowledge not only in finance related area but also well
versed in other areas. He must maintain a good relationship with all the
functional departments of the business organization.
2.4 Importance Of Financial Management
Financial Planning
Financial
management helps to determine the financial requirement of the business concern
and leads to take financial planning of the concern. Financial planning is an
important part of the business concern, which helps to promotion of an
enterprise.
Acquisition of Funds
Financial
management involves the acquisition of required finance to the business concern.
Acquiring needed funds play a major part of the financial management, which
involve possible source of finance at minimum cost.
Proper Use of Funds
Proper
use and allocation of funds leads to improve the operational efficiency of the
business concern. When the finance manager uses the funds properly, they can
reduce the cost of capital and increase the value of the firm.
Financial Decision
Financial
management helps to take sound financial decision in the business concern.
Financial decision will affect the entire business operation of the concern.
Because there is a direct relationship with various department functions such
as marketing, production personnel, etc.
Improve Profitability
Profitability
of the concern purely depends on the effectiveness and proper utilization of
funds by the business concern. Financial management helps to improve the
profitability position of the concern with the help of strong financial control
devices such as budgetary control, ratio analysis and cost volume profit
analysis.
Increase the Value of the Firm
Financial
management is very important in the field of increasing the wealth of the
investors and the business concern. Ultimate aim of any business concern will
achieve the maximum profit and higher profitability leads to maximize the
wealth of the investors as well as the nation.
Promoting Savings
Savings
are possible only when the business concern earns higher profitability and
maximizing wealth. Effective financial management helps to promoting and mobilizing
individual and corporate savings.
Nowadays
financial management is also popularly known as business finance or corporate
finances. The business concern or corporate sectors cannot function without the
importance of the financial management.
3 Time Value Of Money
3.1 Concept
Time value of money shows the relation of
value of money with time. Time value of money is also value of interest which we have
earned for giving money to other for specific period. Value of Rs. 1 which you have today is more valuable than
what Rs. 1 you will receive after one year because you can invest today receive
Rs. 1 in any scheme and you can earn minimum interest on it. It means today
received money is important than tomorrow receivable money. Interest rate is the cost of borrowing money as a yearly
percentage. For investors, interest rate is the
rate earned on an investment as a yearly percentage.
Time
value of money results from the concept of interest. So it now time to discuss
Interest.
1. Simple Interest
It may be
defined as Interest that is calculated as a simple percentage of the original
principal amount. The formula for calculating simple interest is
SI = P0
(i)(n)
Future value of an account at the end of n period
FVn = P0+ SI = P0 + P0(i)(n)
3.2 Compound Interest
If
interest is calculated on original principal amount it is simple interest. When
interest is calculated on total of previously earned interest and the original
principal it compound interest. Naturally, the amount calculated on the basis
of compound interest rate is higher than when calculated with the simple rate.
FV n
= Po (1+ i) n
Where,
i = Annual rate of interest / Number of
payment periods per year
= r/k
So, FV n
= P0 (1 + r/k)n
When
compounding is done k times a year at an annual interest rate r.
Or
FVn
= Po (i + FVIF) in
Where,
Effective Rate of Interest
It is the
actual equivalent annual rate of interest at which an investment grows in value
when interest is credited more often than once a year. If interest is paid m
times in a year it can be found by calculating:
Ei = (1+
i/m) m -1
3.3 Present Value
―Present
Value‖ is the current value of a ―Future Amount‖. It can also be defined as the
amount to be invested today (Present Value) at a given rate over specified
period to equal the ―Future Amount‖.
The
present value of a sum of money to be received at a future date is determined
by discounting the future value at the interest rate that the money could earn
over the period. This process is known as Discounting.
The present value interest factor declines as the interest rate rises and as
the length of time increases.
Po =
FVn /(1+ i) n
Po =
FVn (1+ i) -n
Where,
FVn = Future value n years hence
I = Rate of interest per annum
n = Number of years for which discounting
is done.
B. Discount (or) present value technique: -
= (1+ )
![]()
Present
value Vo = Future value (Vn) x DFin
4 Introduction To The Concept Of Return Of A Single
Asset
4.1 Introduction
Risk and
Return of the investments are interrelated covenants in the selection any
investments, which should be studied through the meaning and definition of risk
and return and their classification of themselves in the first part of this
chapter and the relationship in between them is illustrated in the second half
of the chapter.
Meaning Of Return & Rate Of Return
Return is
the combination of both the regular income and capital appreciation of the
investments.The regular income is nothing but dividend/interest income of the
investments. The capital appreciations of the investments are nothing but the
capital gains of the investments i.e. the difference in between the closing and
opening price of the investments.
Return
symbolized as follows D1 + Pt – Pt – 1 / Pt – 1
These two
categories, Earnings yield and Capital gains yield *Earnings Yield = Earnings
per share / Market price per share***
4.2Concept And Types Of Risk
v The
variability of the actual return from the expected return which is associated
with the investment/asset known as risk of the investment. Variability of
return means that the Deviation in between actual return and expected return
which is in other words as variance i.e., the measure of statistics.
v Greater
the variability means that Riskier the security/ investment. Lesser the
variability means that More certain the returns, nothing but Least risky
.
Interest Rate Risk
It is
risk – variability in a security's return resulting from the changes in the
level of interest rates.
Market Risk
It refers
to variability of returns due to fluctuations in the securities market which is
more particularly to equities market due to the effect from the wars,
depressions etc.
Inflation Risk
Rise in
inflation leads to Reduction in the purchasing power which influences only few
people to invest due to Interest Rate Risk which is nothing but the variability
of return of the investment due to oscillation of interest rates due to
deflationary and inflationary pressures.
Business Risk
.
Business risk is nothing but Operational risk which arises only due to the
presence of the fixed cost of operations.
Financial Risk
Connected
with the raising of fixed charge of funds viz Debt finance & Preference
share capital. More the application of fixed charge of financial will lead to
Greater the financial Risk which is nothing but the Trading on Equity.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity
risk reflects only due to the quality of benefits with reference to certainty
of return to receive after some period which is normally revealed in terms of quality
of benefits.
Measurement of Risk
Standard Deviation:
v Greater
the standard deviation - Greater the risk
v Does not
consider the variability of return to the expected value
v This may
be misleading - if they differ in the size of expected values
Coefficient
of variation = S.D/ Mean
4.3 Risk And Return Of The Portfolio
v Portfolio
is the Combination of two or more assets or investments.
v Portfolio
Expected Return is the weighted average of the expected returns of the
securities or assets in the portfolio.Weights are the Proportion of total funds
in each
security
which form the portfolio Wj Kj.
v Wj =
funds proportion invested in the security.
v Kj =
expected return for security J.
v Benefits
of portfolio holdings are bearing certain benefits to single assets.
v Including
the various types of industry securities - Diversification of assets.
v It is not
the simple weighted average of individual security.
v Risk is
studied through the correlation/co-variance of the constituting assets of the
portfolio. The Correlation among the securities should be relatively considered
to maximize the return at the given level of risk or to minimize the risk.
v Correlation
of the expected returns of the constituent securities in the portfolio.
It is a
Statistical expression which reveals the securities earning pattern in the
portfolio as
together.
Diversification of the Risk of Portfolio
v Diversification of the portfolio
can be done through the selection of the securities which have negative
correlation among them which formed the portfolio. The return of the risky and
riskless assets is only having the possibilities to bring down the risk of the
portfolio.
v The risk of the portfolio cannot
be simply reduced by way adopting the principle of correlation of returns among
the securities in the portfolio. To reduce the risk of the portfolio, the
classification of the risk has to be studied, which are as follows:
v The risk can be further
classified into two categories viz Systematic and Unsystematic risk of the
securities
Systematic Risk: Which only requires the investors
to expect additional return/ compensation
to bear the
Unsystematic Risk: The investors are not given any such additional
compensation to bear unlike the
earlier. The relationship could be obviously understood through the study of
Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM).
Ø Developed
by William F. Sharpe
Ø Explains
the relationship in between the risk and expected / required return
Ø Behaviour
of the security prices
Ø Extends
the mechanism to assess the dominance of a security on the total risk and
return
Ø Highlights
the importance of bearing risk through some premium
Ø No
transaction costs - No intermediation cost during the transaction
Ø No single
investor is to influence the market Risk and Return
Ø Highest return for given level of risk
OrLowest risk for a give n level of return
Ø Risk - Expected value, standard deviation
4.4 Relationship Between The Risk And Return
v Total
Return - Risk free rate of return= Excess return (Risk premium)
v Total
return = Risk free return + Risk premium
v Kj = Rf +
bj (Km–Rf)
v Bj is
nothing but Beta of the security i.e., market responsiveness of the security.
It is normally expressed as a b
v b = Non
Diversifiable risk of asset or Portfolio/ Risk of the Market Portfolio
v Risk of
the portfolio = after diversification, the risk of the market portfolio is non
v diversifiable
5 Valuation Of Bonds And Shares
5.1Valuation Of Bonds
A bond or
a debenture is a long-term debt instrument or security. It is issued by
business enterprises or government agencies to raise long-term capital. A bond
usually carries a fixed rate of interest. It is called as coupon payment and
the interest rate is called as the coupon rate. The coupon payment can be
either annually or semi-annually.
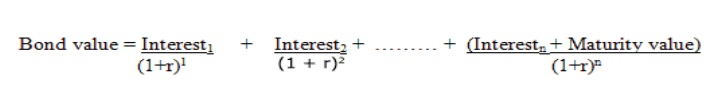
Where:
Interest
1 to n = Interests in periods 1 to n.
Unless
otherwise mentioned, the maturity value of the bond is the face value.
When the
required rate of return is equal to the coupon rate, the bond value equals the
par value.
When the
required rate of return is more than the coupon rate, the bond value would be
less than its par value. The bond in this case would sell at a discount.
When the
required rate of return is less than the coupon rate, the bond value would be
more than its par value. The bond in this case would sell at a premium.
5.2 Valuation Of Shares
Factors Which Influence The Value Of Shares
The
factors which influence the value of shares can be broadly classified into two
groups- internal and external factors. They are stated below-
(i)
Internal
factors
v Earning
capacity of assets
v Return on
investments
v Profit
after tax
v Profit
available to equity shareholders
v Earnings
per share
v Dividend
per share or Rate of dividend.
(ii) External Factors
v General
economic condition of the country.
v Political
and social environment.
v International
economic scenario.
v International
political environment.
METHODS OF VALUATION OF SHARES
The
methods of valuation depend on the purpose for which valuation is required.
Generally, there are three methods of valuation of shares:
1.Net Assets Method of Valuation of Shares
Under
this method, the net value of assets of the company is divided by the number of
shares to arrive at the value of each share. For the determination of net value
of assets, it is necessary to estimate the worth of the assets and liabilities.
The goodwill as well as non-trading assets should also be included in total
assets.
Value per
Share= (Net Assets-Preference Share Capital)/Number of Equity Shares
2. Yield or Market Value Method of Valuation Of
Shares
The
expected rate of return in investment is denoted by yield. The term "rate
of return" refers to the return which a shareholder earns on his
investment. Further it can be classified as
(a) Rate
of earning and (b) Rate of dividend. In other words, yield may be earning yield
and dividend yield.
a. Earning Yield
Value per
Share = (Expected rate of earning/Normal rate of return) X Paid up value of
equity share
Expected
rate of earning = (Profit after tax/paid up value of equity share) X 100
b. Dividend Yield
Expected
rate of dividend = (profit available for dividend/paid up equity share capital)
X 100 Value per share = (Expected rate of dividend/normal rate of return) X 100
3. Earning Capacity Method Of Valuation Of Shares
Under
this method, the value per share is calculated on the basis of disposable
profit of the company. The disposable profit is found out by deducting reserves
and taxes from net profit.
Value per
share = Capitalized Value/Number of Shares
6 Option Valuation
An option
is a contract, or a provision of a contract, that gives one party (the option
holder) the right, but not the obligation, to perform a specified transaction
with another party (the option issuer or option writer) according to the
specified terms. The owner of a property might sell another party an option to
purchase the property any time during the next three months at a specified
price.
There are
two options which can be exercised:
v Call
option, the right to buy is referred to as a call option.
v Put
option, the right to sell is referred as a put option.
There are
two types of options: the European options, which can be exercised only at
expiration, and the American options, which may be exercised any time prior to
expiration.
The
American option offers greater flexibility and hence its value, in general, is
greater than the European one.
At this point, we are examining options on stocks
that are not paying any dividends. When a stock pays a dividend then the value
of the stock drops on the ex dividend
date. This predictable drop in the price of a stock will have an effect on the
price of the options on that stock.
6.1 Factors Affecting Value Of
Options
• Price – value
of the call option is directly proportionate to the change in the price of the
underlying.
• Time – as
options expire in future, time has an effect on the value of the options.
• Interest
rates and Volatility – in case where the underlying asset is a bond or
interest rate, interest rate volatility would have an impact on the option
prices.
Properties of Option Values
1. The
minimum value of an option is zero.
This is
because an option is only a choice, not an obligation. The value of an option
cannot be negative, because you do not have to do anything to get rid of it.
The option will always have a zero, or a positive value.
2. The
maximum value of a call option is equal to the value of the underlying asset.
This
makes a lot of economic sense. An option allows you to buy a given asset at a
certain exercise price. The most valuable option will be the one that allows
you to acquire the asset at no cost, and the value of this option will be equal
to the value of the underlying asset.
3. The
total value of an option is the sum of its intrinsic value and its time
premium.
Related Topics