Chapter 6 | Civics | 8th Social Science - Foreign Policy of India | 8th Social Science : Civics : Chapter 6 : Defence & Foreign Policy
Chapter: 8th Social Science : Civics : Chapter 6 : Defence & Foreign Policy
Foreign Policy of India
Foreign Policy of India
A foreign policy is a set of
political goals that define how a sovereign country will interact with other
countries in the world. It seeks to secure the best interest of the people,
territory and economy of the country. Our country’s external relation is based
on certain principles and policies. India’s foreign policy was evolved with the
background of her colonial sufferings.
Basic Principles of Foreign
Policy
* Preservation of national interest
* Achievement of world peace
* Disarmament
* Abolition of Colonialism, Racism
and Imperialism
* Incresing the number of friendly
nations
* Economic development
Panchsheel
Jawaharlal Nehru, the first Prime
Minister of India was the chief architect of India’s foreign policy. Nehru was
a supporter of world peace. Hence he gave utmost importance to world peace in
his policy planning. He declared the five principles of peace, known as
Panchsheel.
These principles included
1. Mutual
respect for each other’s territorial integrity and sovereignty
2. Mutual
non-aggression
3. Mutual
non-interference in each other’s internal affairs
4. Equality
and mutual benefit
5. Peaceful co-existence.
Non-Alignment
The word Non-Alignment was coined by
V.K. Krishna Menon. Non-alignment has been regarded as the most important
feature of India’s foreign policy. Non-alignment aimed to maintain national
independence in foreign affairs by not joining any military alliance formed by
the USA or Soviet Union in the aftermath of the Second World War. Non-alignment
was neither neutrality nor non-involvement nor isolationism. It was a dynamic
concept which meant not committing to any military bloc but taking an
independent stand on international issues.
The founding fathers of Non-Aligned Movement: Jawaharlal Nehru of India, Tito of
Yugoslavia, Nasser of Egypt, Sukarno of Indonesia, and Kwame Nkumarah of Ghana.

Nelson Mandela – Leader of the African
National Council of South Africa. A determined fighter against apartheid.
Apartheid is the worst form of racial discrimination. It is against humanism
and democracy. India fought against Apartheid and opposed all types of racial
discrimination. The end of racialism in South Africa in 1990 was a great
success for India’s policy.
India’s Relation with
Neighbouring Countries
India’s position is unique in its
neighbourhood. India has always favoured international and regional
cooperation, because she believes that through cooperation all disputes and
problems among nations can be sorted out peacefully. India's foreign policy is
based on the principle of developing friendly relations and cooperation with
her neighbours.
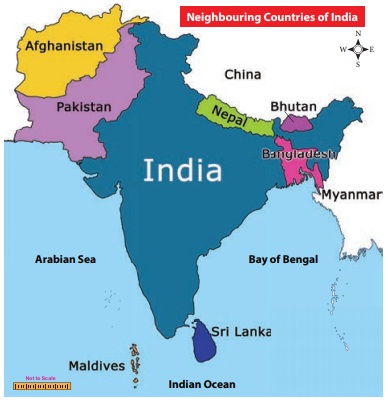
India shares a common
land border with Pakistan, Afghanistan, Nepal, China, Bhutan, Bangladesh and
Burma. It also shares a common sea border with Sri Lanka.
India is a vast country with
• Pakistan and Afghanistan to the
north-west
• China, Nepal, Bhutan to the north
• Bangladesh to the east
• Myanmar to the far east
• Sri Lanka (south-east) and
• Maldives (south-west)
Neighbourhood First policy
It is part of India’s foreign policy
that actively focuses on improving ties with India’s immediate neighbours.
India provides neighbours with support as needed in the form of resources,
equipment and training. Greater connectivity and integration is provided so as
to improve the free flow of goods, people, energy, capital and information.
Act East Policy
South East Asia begins with North
East India. Myanmar is our land bridge to the countries of the Association of
the Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). The purpose is to ensure a stable and
multipolar balance of power in the Indo-Pacific and to become an integral part
of Asia.
India is actively engaged in general
economic diplomacy with its neighbouring countries as below.
SAARC
India believes in regional
co-operation. To foster the bonds of brotherhood, co-operation and peaceful
co-existence SAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation) was
established. India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Sri Lanka, Maldives
and Afghanistan are the eight members of the SAARC.
BCIM
This Bangladesh – China – India -
Myanmar Economic corridor envisages the formation of a thriving economic belt,
focusing on cross- border transport, energy and telecommunication networks.
BIMSTEC
It refers Bay of Bengal Initiative
for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation. Its main objectives are
to strengthen and improve the technological economic cooperation, international
trade and foreign direct investment cooperation. The member countries are
Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Bhutan and Nepal.
BBIN
Bangladesh – Bhutan - India – Nepal
has signed a framework to enable movement of passengers, cargo vehicles and for
energy development.
To summarise, India is a huge
country with manifold cultures. It has high status in the South East Asia.
India’s foreign policy is to maintain peace, freedom and mutual co-operation
among the nations. Though India is not in any major military alliance, our
relations with the major powers have acquired a strategic depth.
Related Topics