Our Environment | Term 3 Unit 4 | 6th Science - Food Chain and Food Web | 6th Science : Term 3 Unit 4 : Our Environment
Chapter: 6th Science : Term 3 Unit 4 : Our Environment
Food Chain and Food Web
Food Chain and
Food Web
Living organisms need food to perform their
life processes. Some organisms can produce their own food, such as plants,
while other organisms cannot do this
and need to feed on other organisms to obtain their energy.
We can therefore identify different feeding
types in an ecosystem, based on how the organism obtain (gets) its food. They
are producers and consumers.
Producers
Producers are organisms that are able to produce their own organic food.
They do not need to eat other organisms to do this. Producers are also called autotrophs.
Can you name an organism that prepare it’s own food?
Plants are producers because they make their
own food by photosynthesis.
What do plants need in order to photosynthesis?
Consumers
Organisms which cannot produce their own food,
need to eat other organisms as food. These organisms are called consumers.
All animals are consumers as they cannot produce their own food. Consumers are
also called heterotrophs.
There are many types of consumers and we can
classify them into specific groups depending on the food that they consume.
These are:
* herbivores
Animals which eat plants or plant products e.g:
cattle, deer, goat and rat.
* carnivores
Animals that eat other animals e.g: Lion, tiger, frog and owl.
* omnivores
Animals that eat both plants and animals e.g:
Humans, dog and crow
* decomposers
Micro-organisms that obtain energy from the
chemical breakdown of dead organisms (both plants and animals). They break
complex organic substances into simple organic substances that goes into the
soil and are used by plants. (e.g) Bacterium, Fungi
Food chain
In a forest, deer eats grass; and in turn we
know tiger eats deers. In any ecosystem there is a chain like relationship
between the organisms that live there. This sequence of who eats whom in an
ecosystem is called as food chain.
It describes how organisms get energy and
nutrients by eating other organisms.
A food chain shows the relationship between
producers (e.g. grass) and consumers (e.g. deer, goats, cows and tiger).
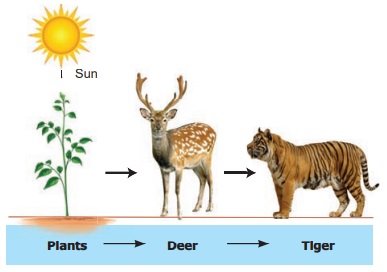
E.g. Food chain in a terrestrial (grassland)
ecosystem
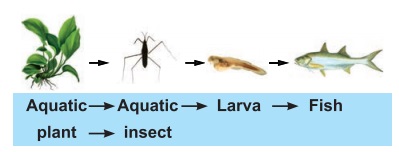
E.g. Food chain in an aquatic (lake) ecosystem
Energy flow
The food chain begins with the energy given by
the Sun. Sunlight triggers photosynthesis in plants. The energy from the Sun is
stored in the plant parts. When the grasshopper eats the grass, the energy
flows from grass to grasshopper. Frog gets energy by eating grasshopper. This
energy is transferred to a crow, when the frog is eaten by a crow. Thus we
conclude the primary energy production in the world of living things is made by
plants; that is by photosynthesis.
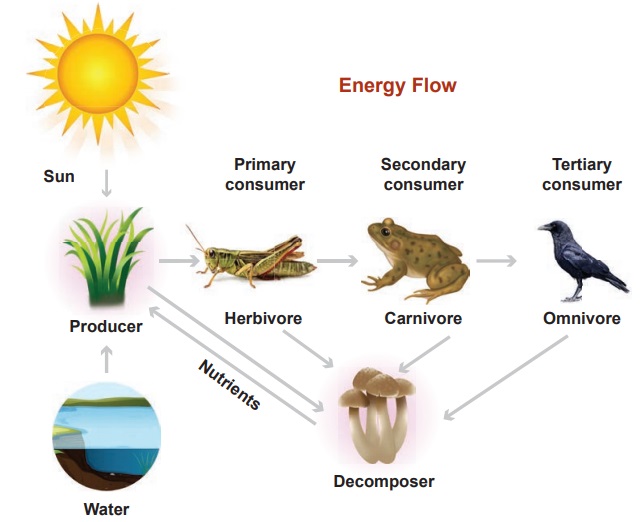
The micro organism reduce the excreata and the
dead bodies of animals into primary simple components and puts them back into
soil. It is this material that help the plants to grow. Thus we can see that
there is a cycle of materials from primary producers to highest level
predators, then back to soil.
Trophic levels
We see that the energy is passed along from the
producer to the consumers. But, there are three different consumers in any food
chain. How can we distinguish different consumers?
Animals that eat plants are primary consumers.
Animals that eat primary consumers are called secondary
consumers.
Animals that eat the secondary consumers
(mostly predators) are the tertiary consumers.
There may even be large predators that eat
tertiary consumers. They are called as quaternary consumers.
Each of these levels in the food chain is
called a trophic level.
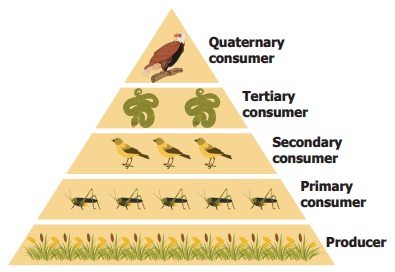
Organism uses up to 90% of its food energy for
its life processes. Only about 10% of energy goes into new body cells and will
be available to the next animal when it gets eaten. This loss of energy at each
trophic level can be shown by an energy pyramid.
A rat eats grains; and in turn we know snake
eats rat. Now snake is a prey for peacock and in turn peacocks are easy prey
for tigers and leopards. Now think? Do tigers have any natural predators?
In all food chain there is a top level predator
that has no natural predators. In an aquatic ecosystem there are no natural
predator for alligator; in a forest there are no natural predators for tigers.
Importance of food chain
1 .Learning food
chain help us to understand the feeding relationship and interaction between
organisms in any ecosystem.
2. Understanding
the food chain also helps us to appreciate the energy flow and nutrient
circulation in an ecosystem. This is important because pollution impacts the
ecosystem. The food chain can be used to understand the movement of toxic
substances and their impacts.
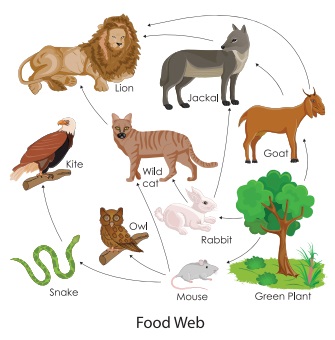
Food web
Consumers have different sources of food in an
ecosystem and do not rely on only one species for their food. If we put all the
food chains within an ecosystem together, then we end up with many
interconnected food chains. This is called a food web.
A food web is very useful to show the many
different feeding relationships between different species within an ecosystem.
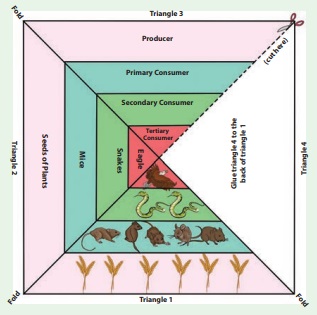
Activity 2: Take a square paper. Fold its
diagonals. Draw three lines in three triangles as shown in the picture.
Cut from the edge of the diagonal
to the center as shown in the picture.
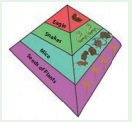
If you fold this triangle and
paste behind the third triangle you get a pyramidal shape.
In one of the triangles, draw
images of each of the organisms in the different levels.
In another triangle write the
names of the organisms. In the last triangle, write the energy level of the
organism. Have a look at the following example. You must come up with different
organisms!.
Related Topics