Chapter: Biochemistry: Vitamins
Folic acid
Folic
acid
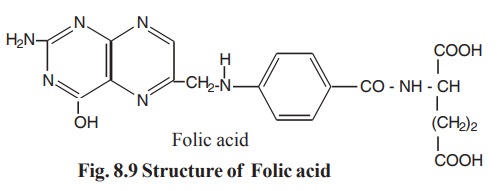
Folic acid contains a pteridine group linked to
para amino benzoic acid and l-glutamic acid (Fig. 8.9). It is slightly soluble
in water and stable to heat.
Functions
·
Folic
acid serve as coenzymes in reactions involving the transfer of one carbon units
like formyl and methyl groups.
·
It
participates in the reactions concerned with the synthesis of purine,
pyrimidine and nucleic acids.
·
It is
essential for maturation of red blood cells.
·
Folic
acid is required for the metabolism of amino acids like histidine.
·
Along
with vitamin B12, folic acid helps in the trans methylation
reactions. eg: uracil to thymine.
Sources
Folic acid is particularly present in green
leafy vegetables, cauliflower and dried yeast. Egg, liver and kidneys are rich
animal sources.
Requirements
There is no definite requirement for normal
human being. However, an increased amount is required during pregnancy and
lactation.
Infants - 50 μg / day
Children - 100 - 300 μg / day
Adults - 400 μg/day
Pregnant women - 800 μg / day
Lactating women - 600 μg/day
Absorption and storage
Absorption of folic acid takes place along the
whole length of the mucosa of the small intestine. Folic acid about (5-15 mg/g)
is in the liver and folate is also incorporated into the erythrocytes during
erythropoiesis (Red blood cells production).
Deficiency
Deficiency of vitamin B12 also leads
to functional folic acid deficiency.
·
Folic
acid deficiency leads to megaloblastic anemia characterised by the release of
large sized immature red blood cells into the circulation.
·
Sprue
and symptoms like glossitis and gastro intestinal disturbances have also been
reported.
·
Macrocytic
anemia of pregnancy responds to treatment with folic acid.
Related Topics