Chapter: Civil : Mechanics Of Fluids : Fluid Kinematics And Dynamics
Fluid Kinematics And Dynamics: Introduction
KINEMATICS AND DYNAMICS
INTRODUCTION
Fluid kinematics refers to the
features of a fluid in motion. It only deals with the motion of fluid particles
without taking into account the forces causing the motion. Considerations of
velocity, acceleration, flow rate, nature of flow and flow visualization are
taken up under fluid kinematics.
A fluid motion can be analyzed by
one of the two alternative approaches, called Lagrangian and Eulerian.
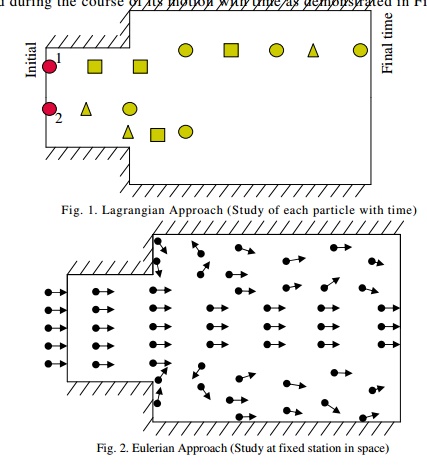
In Lagrangian approach, a particle or a fluid
element is identified and followed during the course of its motion with time as
demonstrated in Fig.1
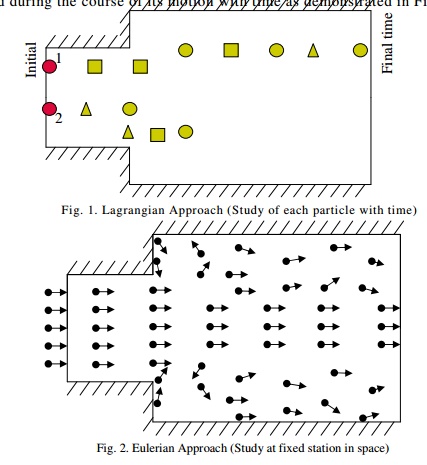
Fig. 1. Lagrangian Approach (Study of each
particle with time)
Fig. 2. Eulerian Approach (Study at fixed station
in space)
Eg: To know the attributes of a
vehicle to be purchased, you can follow the specific vehicle in the traffic
flow all along its path over a period of time.
Difficulty in tracing a fluid
particle (s) makes it nearly impossible to apply the Lagrangian approach. The
alternative approach, called Eulerian approach consists of observing the fluid
by setting up fixed stations (sections) in the flow field (Fig. 2).
Motion of the fluid is specified by velocity
components as functions of space and time. This is considerably easier than the
previous approach and is followed in Fluid Mechanics.
Eg: Observing the variation of flow properties in
a channel like velocity, depth etc, at a section.
Related Topics