Chapter: Maternal and Child Health Nursing : The Male Reproductive System
External Organs - Male Reproductive System
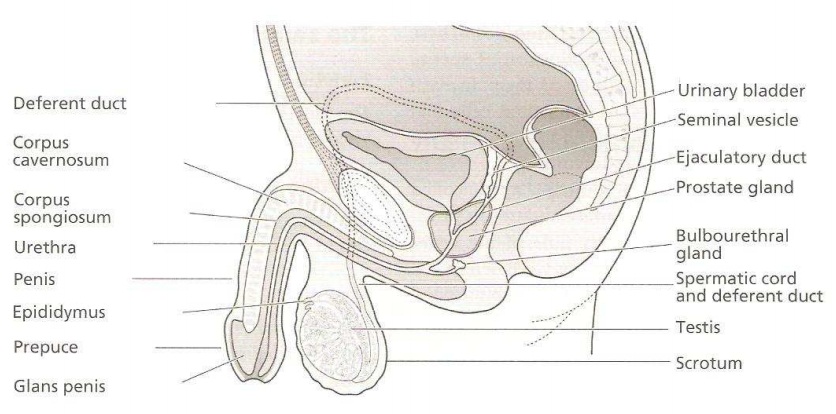
The Male Reproductive System
The male
reproductive system is made up two main parts.
1.
The External
2.
The internal parts
The External Organs
The Penis
It has
its root in the perineum with the lower 2/3rd of the body suspended outside in
front of the scrotal sac. It is made up of three bundles of spong-like
erectitle tissues:
1.
2 the corporal cavernosa on the lateral columns in
front of the urethra
2.
The corpus spongiosum on the posterior column which
contains the urethra enclosed in a firm sheath of firm tissue with rich blood
supply and covered with the skin. The skin continues with the scrotum and the
groins. The skin double fold backwards on itself at the glans penis to form the
prepuce (foreskin) which is usually removed during circumcision. The penis
transmites a portion of the urethra which acts as a passage for semen as well
as excretion of urine… During sexual excitement the pe nis becomes larger,
rounder, firmer and erect to be able to penetrate and deposit semen near the
cervix. Stimulation of the nervous system increases blood supply to the organ.
This
erections tart at puberty and may result in wet dream in adolescent boy. There
is a small sphincter in the urethra which prevent semen from entering the
bladder and urine from the urethra mixing with the semen during intercourse.
The Scrotum
It is a
sensitive pouch-like sac covered with wrinkled skin and hair from which the
penis hangs. It lies in front of the thighs, behind the penis and is thickly
pigmented. The scrotum is divided by a fibrous septum called Dartos muscle into
two cavities each of which contain a testis epididymis and initial portion of
the vas deference. The muscles contract in cold weather and relax in hot
weather to ensure normal temperature around the testes. Next to the clartos
muscle lies the cremaster muscle and fascia. It protects the testes from
injuries.
Related Topics