Democracy | Term 3 Unit 1 | Civics | 6th Social Science - Exercises Questions with Answers | 6th Social Science : Civics : Term 3 Unit 1 : Democracy
Chapter: 6th Social Science : Civics : Term 3 Unit 1 : Democracy
Exercises Questions with Answers
EXERCISES
I. Choose the correct answer.
1. Early
man settled near ________
and practiced agriculture.
a. plains
b. bank of rivers
c. mountains
d. hills
Answer: b) bank of rivers
2. The birth
place of democracy is ________
a. China
b. America
c. Greece
d. Rome
Answer: c) Greece
3. ________ is celebrated as the International
Democracy Day.
a. September 15
b. October 15
c. November 15
d. December 15
Answer: a) September 15
4. Who has the
right to work in a direct Democracy?
a. Men
b. Women
c. Representatives
d. All eligible voters
Answer: d) All eligible voters
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. Direct Democracy is practised in Switzerland
2. The definition
of democracy is defined by Abraham Lincoln.
3. People choose
their representatives by giving their Votes.
4. In our country Representative democracy is in practice.
III. Answer
the following.
1. What is Democracy?
Democracy is 'Government of the
people, by the people, for the people'.
2. What
are the types of democracy?
Direct democracy and Representative
democracy.
3.
Define: Direct Democracy.
In a Direct Democracy, only the
citizens can make laws. All changes have, to be approved by the citizen. The
politicians only rule over parliamentary procedure.
4.
Define: Representative Democracy.
The Representative government is
elected by the people to form a democratic system. All those who attain the age
of 18 are given the voting rights to elect the representatives.
5. What are the salient features of our
constitution that you have understood?
The Constitution of India plays an important role in maintaining
law and order.
"Our Constitution ensures freedom, equality and justice to
everyone."
"It defines the political principles, the structure of the
government institutions and methods to follow these rules and regulations, the
powers and responsibilities. And also, it fixes the Rights and Duties and the
Directive Principles of the citizens. Thus our Constitution provides a
structure to us."
Indian Constitution is the longest
written constitution in the world.
IV. HOTs
1. Compare and contrast direct democracy and
representative democracy.
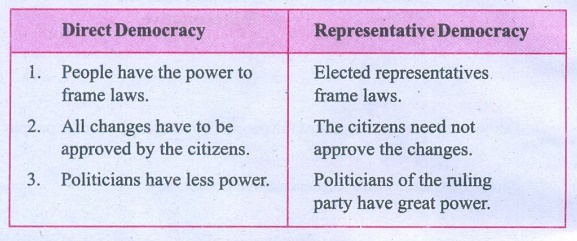
Direct Democracy
1. People have the power to frame laws.
2. All changes have to be approved by the citizens.
3. Politicians have less power.
Representative
Democracy
1. Elected representatives frame laws.
2. The citizens need not approve the changes.
3. Politicians of the ruling party have great power.
V. Activity.
1. Find out your area's representative’s names
and write down
a. MP b. MLA
C.
Local body member
2. Discuss about the merits and demerits of
democracy.
Related Topics