Indus Civilisation | Term 1 Unit 3 | History | 6th Social Science - Exercises Questions with Answers | 6th Social Science : History : Term 1 Unit 3 : Indus Civilisation
Chapter: 6th Social Science : History : Term 1 Unit 3 : Indus Civilisation
Exercises Questions with Answers
Exercises
I. Choose the correct answer:
1. What metals were known to the people of Indus
Civilization?
a. Copper, bronze, silver,
gold, but not iron
b. Copper, silver, iron,
but not bronze
c. Copper, gold, iron,
but not silver
d. Copper, silver, iron,
but not gold
Answer: a. Copper, bronze, silver, gold, but not iron
2. Indus Civilisation belonged to
a. old Stone age
b. Medieval stone age
c. New stone age
d. Metal age
Answer: d. Metal age
3. River valleys are said to be the cradle of civilisation
because
a. Soil is very fertile.
b. They experience good
climate.
c. They are useful for
transportation.
d. Many civilisations
flourished on river valleys.
Answer: a. Soil is very fertile.
II. Match the Statement with the Reason. Tick the appropriate
answer :
1. Statement: Harappan civilization is said to be an urban civilization.
Reason: It
has well planned cities with advanced drainage system.
a. Statement and reason
are correct.
b. Statement is wrong.
c. Statement is true,
but the reason is wrong.
d. Both statement and reason are wrong.
Answer: a) Statement and reason are correct.
2. Statement: Harappan civilization belongs to Bronze Age.
Reason: Harappans
did not know the use of iron.
a. Statement and reason
are correct.
b. Statement is wrong.
c. Statement is correct,
but the reason is wrong.
d. Both statement and
reason are wrong.
Answer: a. Statement and reason are correct.
3. Statement: The engineering skill of Harappans was remarkable.
Reason: Building
of docks after a careful study of tides, waves and currents.
a. Statement and reason
are correct.
b. Statement is wrong.
c. Statement is correct,
but the reason is wrong.
d. Both statement and
reason are wrong.
Answer: a. Statement and reason are correct.
4. Which
of
the following statements about Mohenjo-Daro is correct?
a. Gold ornaments were
unknown.
b. Houses were made
of burnt bricks.
c. Implements were made
of iron.
d. Great Bath was made
water tight with the layers of natural bitumen
Answer: d. Great Bath was made water tight with the layers of
natural bitumen
5. Consider the following statements.
1. Uniformity in layout of town, streets, and brick sizes
2. An elaborate and well laid out drainage system
3. Granaries constituted
an important part of Harappan Cities
Which of the above statements
are correct?
a. 1&2
b. 1&3
c. 2&3
d. all the three
Answer: d. all the three
6. Circle the odd one
Oxen, sheep, buffaloes,
pigs, horses
Answer: (horses)
7. Find out the wrong
pair
a. ASI – John Marshall
b. Citadel – Granaries
c. Lothal – dockyard
d. Harappan
Civilizatio – River Cauvery
Answer: d. Harappan civilisation - River Cauvery
III. Fill in the Blanks
1. Indus valley is the oldest civilisation.
2. Archaeological Survey of India was founded by New Delhi.
3. Granaries were used to store grains.
4. Group
of people form civilisation.
IV. State True or False :
1. Mehergarh is a Neolithic site.
2. Archaeological survey
of India is responsible for preservation of cultural monuments in the country.
3. Granaries were used
to store grains
4. The earliest form
of writings was developed by Chinese.
V. Match the following :
1. Mohenjo-Daro - raised platform
2. Bronze - red quartz stone
3. Citadel - alloy
4. Carnelian - mound of dead
Answer:
1. Mohenjo - mound of
dead
2. Bronze - alloy
3. Citadel - Daro-raised
platform
4. Carnelian - red
quartz stone
VI. Answer
in one or two sentences:
1. What are the uses of metal?
The metals are used for making tools.
2. Make a list of baked and raw foods that we eat.
Vegetables and fruits
3. Do we have the practice of worshipping animals
and trees?
Yes, we have the practice of worshipping animals and
trees
4. River valleys are cradles of civilisation. Why?
Responsible for the growth of civilisation.
5. Just because a toy moves doesn’t mean its modern.
What did they use instead of batteries?
It is roly-poly toy made of terracotta material. The
centre of gravity and total weight of the doll is concentrated at its
bottom-most point, generating a dance like continuous movement with slow
oscillations.
6. Dog was the first animal to be tamed. Why?
Dogs could sniff other animals and chase them away
7. If you were an archaeologist, what will you do?
Research about the past ancient history
8. Name any two Indus sites located in the Indian
border?
Manda, kalibangan
9. In Indus civilisation, which feature you like
the most? Why?
Town planning
10. What instrument is used nowadays to weigh things?
Spring scale, Weighing scale.
VII. Answer the following :
1. What method is used to explore buried buildings nowadays?
• Archaeologists study the physical objects such as
bricks, stones or bits of broken pottery (sherds) to ascertain the location of
the city and time that it belong to.
2. Why Indus Civilisation is called Bronze Age civilisation?
It is a historical period characterised by the use of
articles made of bronze.
3. Indus Civilisation is called urban civilisation.
Give reasons.
• Well-conceived town
planning
• Astonishing masonry
and architecture
• Priority for hygiene
and public health
• Standardised weights
and measures
• Solid agricultural
and artisanal base
4. Can you point out the special features of their
drainage system?
• Many of these cities
had covered drains. The drains were covered with slabs or bricks.
• Each drain had a
gentle slope so that water could flow.
• Holes were provided
at regular intervals to clear the drains.
• House drains passed,
below many lanes before finally emptying into the main drains.
• Every house had its
own soak pit, which collected all the sediments and allowed only the water to
flow into the street drain.
5. What do you know about the Great Bath?
• The great bath was a
large, rectangular tank in a courtyard.
• It may be the
earliest example of a water-proof structure.
• The bath was lined
with bricks, coated with plaster and made water-tight using layers of natural
bitumen.
• There were steps on
the north and south leading into the tank.
• There were rooms on
three sides.
• Water was drawn from
the well located in the courtyard and drained out after use.
6. How do you know that Indus people traded with
other countries?
• Harappans were great
traders.
• Standardised weights
and measures were used by them. They used sticks with marks to measure length.
• They used carts with
spokeless solid wheels.
• There is evidence
for extensive maritime trade with Mesopotamia. Indus Seals have been found as
far as Mesopotamia (Sumer) which are modern-day Iraq, Kuwait and parts of
Syria.
• King Naram-Sin of
Akkadian Empire (Sumerian) has written about buying jewellery from the land of
Melukha (a region of the Indus Valley).
• Cylindrical seals
similar to those found in Persian Gulf and Mesopotamia have also been found in
the Indus area. This shows the trade links between these two areas.
• A naval dockyard has
been discovered in Lothal in Gujarat. It shows the maritime activities of the
Indus people.
VIII. HOTS:
1. Observe the following features of Indus Civilisation
and compare that with the present day.
a. Lamp post
b. Burnt bricks
c. Underground drainage system
d. Weights and measurement
a. Lamp post: Some houses has lamp post in the Indus valley
b. Burnt bricks: Because they do not dissolve in water or rain.
c. Underground drainage system: the drainage was
covered with slabs. occasionally its cleaned by workmen
d. Weights and measurement: Indus people had
developed a system of standardised weights and measures. Ivory scale found in
Lothal in Gujarat is 1704mm (the smallest division evory recorded on a scale of
other contemporary civilisations).
e. Dockyard: Lothal A naval dockyard has been discovered in Lothal in
Gujarat. It shows the maritime activities of the Indus people.
2. Agriculture was one of their occupations. How
can you prove this? (with the findings)
• The seed of fruits
and the nuts they ate were thrown into the soil.
• During rains, the
soil gave it life. Some days later, the saplings sprouted from the soil.
• By observation and
logic, they learn that:
a. a plant grows from
a single seed and yields lots of fruits and vegetables.
b. seeds that fall in
the river beds sprout easily.
c. plants grows faster
in water fed areas.
d. alluvial soil is
more suitable for plant growth than any other.
With the above
knowledge they gained, they realised that with proper sowing and nurturing,
they could increase the number of plants more than the ones that grew
naturally. Thus agriculture and farming came into existence.
3. Many pottery and its pieces have been discovered
from Indus sites. What do you know from that?
The broken pieces of pottery have animal figures and
geometric designs on it. We can understand their significance and age period.
4. A naval dockyard has been discovered in Lothal.
What does it convey?
A naval dockyard has been discovered in Lothal in
Gujarat. It shows the maritime activities of the Indus people.
5. Can you guess what happened to the Harappans?
By 1900 BCE, the
Harappan culture had started declining.
It is assumed that the
civilisation met with
► repeated floods
► ecological changes
► invasions
► natural calamity
► climatic changes
► deforestation
► an epidemic
IX. Student Activity
1. Prepare a scrap book.
(Containing more information
about objects collected from Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa.)
2. You are a young archaeologist
working at a site that was once an Indus city. What will you collect?
Brunt bricks, potteries and weapons they used.
3. Make flash cards.
(Take square cards and
stick picture in one card and the information for the same picture in another card.
Circulate among the groups and tell them to match the picture with information.)
4. Draw your imaginary
town planning in a chart.
5. Make a model of any
one structure of Indus Civilisation using clay, broken pieces of bangles, matchsticks,
woollen thread and ice cream sticks.
6. Can you imagine how
toys have changed through the ages? Collect toys made of
Clay -> stone ->
wood -> metal -> plastic -> fur -> electric -> electronic ->???
7. Crossword puzzle.
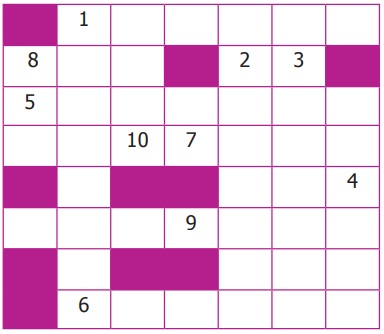
Top to Bottom
1. Director General
of ASI
2. ____________ is older
than Mohenjo-Daro
3. This is____________
age civilisation
4. Each house had a
____________.
Left to Right
5. Place used to store grains
6. A dockyard has been found
7. ____________ is unknown
to Indus people
8. It is used to make
water tight.
Right to Left
9. From this we can
get lot of information
10. This is responsible
for research
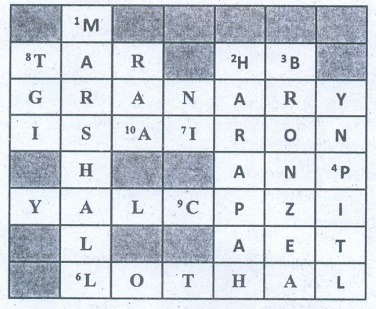
Top To Bottom
1. Marshal
2. Harapa
3. Bronze
4. Pit
Left To Right
5. Granary
6. Lothal
7. Iron
8. Tar
Right
To Left
9. Clay
10. ASI
Rapid Fire Quiz (Do it in groups)
1. Which crop did Indus
people use to make clothes?
Cotton
2. Which was the first
Indus city discovered?
Harappa
3. Where was Indus Civilisation?
River Indus
4. Which animal was
used to pull carts?
Oxen
5. Which metal was unknown
to Indus people?
Iron
6. What was used to
make pots?
Wheels
7. Which is considered
the largest civilisation among four ancient civilisations of the world?
Indus valley civilization
X. Life skill
1. Making an animal
or a pot out of clay.
2. Making terracotta toy with movable limbs.
3. Pot painting (with geometric pattern).
4. Make informational charts and posters.
XI. Map Work
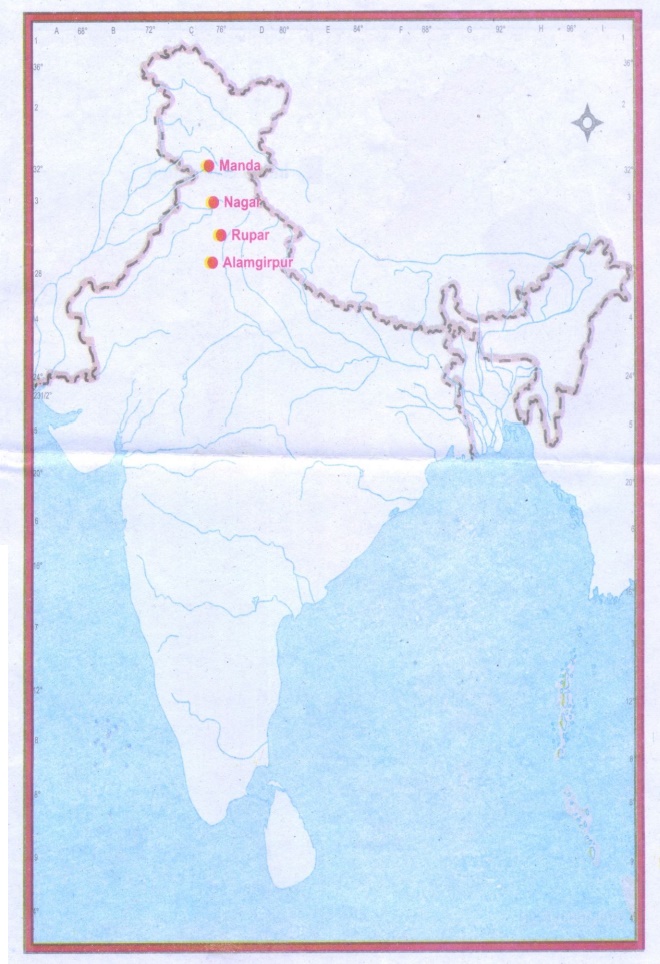
1. Mark any four Indus sites located within the
Indian border.
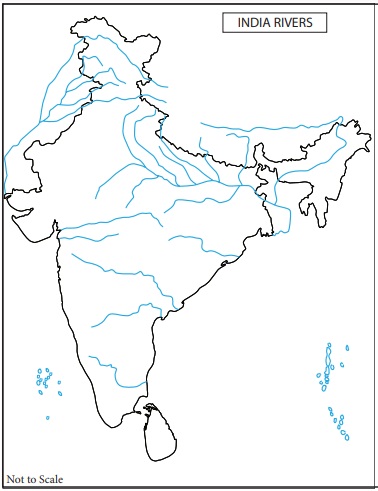
2. On the river map of India, colour the places
where Indus civilisation spread.
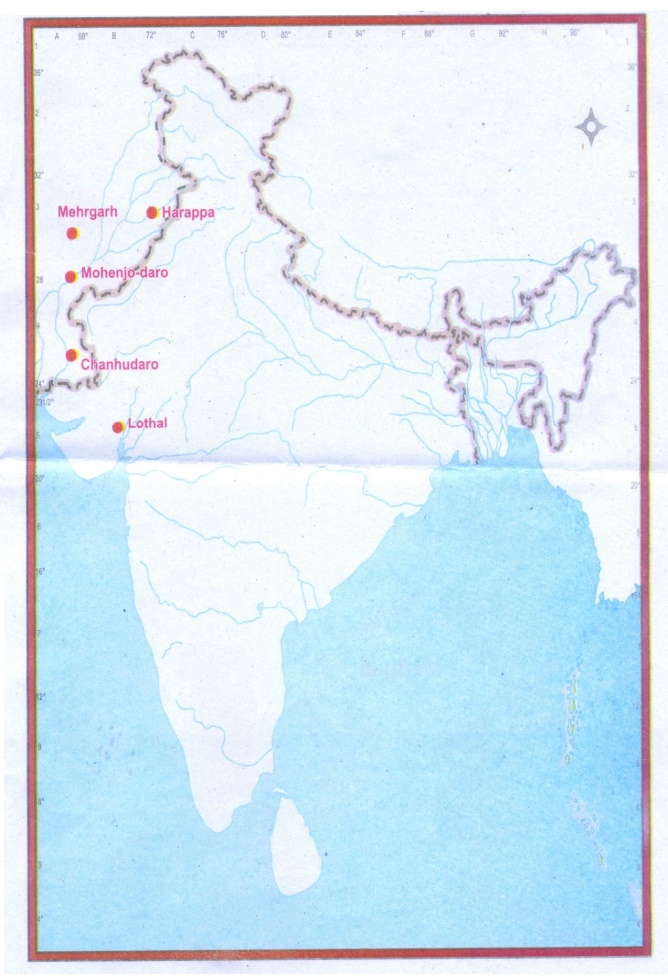
3. Mark the following places in the given India map:
a. Mohenjo-Daro
b. Chanhudaro
c. Harappa
d. Mehergarh
e. Lothal
XII. Answer Grid
• What did Charles Masson see?
He saw,’’ruined brick
castle with very high walls and towers built on a hill”.
• List three things people used
which we use today?
Granary, Toilets,
Lamppost
• What else has been found?
The Indus valley
people did not leave great structures, like the pyramids of Egypt or the great
walls of china. Their cities have almost vanished. Today , visitors see ruins
dug into by archaeologists. Skills such as trading , farming and brick-makiing
were passed on. Indus people helped shape the later cultures of India and
Pakistan.
• Can you say three things
unknown to Indus people?
Horse, iron
• Which metal was unknown to
Indus people?
Iron
• Which is the oldest
civilisation in the world?
Indus valley
Civilization
• Why dog was the first animal to
be tamed?
Sniff of dog helped
them to identify the dangerous animals
• Who were the first people to
grow cotton?
Indus people
• Which institution is
responsible for archaeological research?
The Archaeological
Survey of India
• Was there any river valley
civilisation found in TamilNadu?
Kaveri delta
• Name any two Harappan sites
which were found in Indian border?
Manda, Mitathai
• Can we say the Indus cities as
cities of children?
Toys like carts, cows
with movable heads and limbs, clay balls, tiny doll, a small clay monkey,
terracotta squirrels eating a nut, clay dogs and male dancer have been found.
They made various types of toys using terracotta, which show that they enjoyed
playing.
Related Topics