Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 5 : Acoustics
Echoes
ECHOES
An echo is the sound
reproduced due to the reflection of the original sound from various rigid
surfaces such as walls, ceilings, surfaces of mountains, etc.
If you shout or clap
near a mountain or near a reflecting surface, like a building you can hear the
same sound again. The sound, which you hear is called an echo. It is due to the
reflection of sound. One does not experience any echo sound in a small room.
This does not mean that sound is not reflected in a small room. This is because
smaller rooms do not satisfy the basic conditions for hearing an echo.
1. Conditions necessary for hearing echo
1. The persistence of
hearing for human ears is 0.1 second. This means that you can hear two sound
waves clearly, if the time interval between the two sounds is at least 0.1 s.
Thus, the minimum time gap between the original sound and an echo must be 0.1
s.
2. The above criterion
can be satisfied only when the distance between the source of sound and the
reflecting surface would satisfy the following equation:
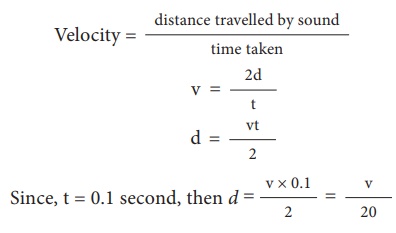
Since, t = 0.1 second, then d = [v ×
0.1] / 2 = v/20
Thus the minimum
distance required to hear an echo is 1/20 th part of the magnitude
of the velocity of sound in air. If you consider the velocity of sound as 344 m
s–1, the minimum distance required to hear an echo is 17.2 m.
2. Applications of echo
·
Some animals communicate with each other over long distances and
also locate objects by sending the sound signals and receiving the echo as
reflected from the targets.
·
The principle of echo is used in obstetric ultrasonography, which
is used to create real-time visual images of the developing embryo or fetus in
the mother’s uterus. This is a safe testing tool, as it does not use any
harmful radiations.
·
Echo is used to determine the velocity of sound waves in any
medium.
3. Measuring velocity of sound by echo method
Apparatus required:
A source of sound
pulses, a measuring tape, a sound receiver, and a stop watch.
Procedure:
1.
Measure the distance ‘d’ between the source of sound pulse and the
reflecting surface using the measuring tape.
2.
The receiver is also placed adjacent to the source. A sound pulse
is emitted by the source.
3.
The stopwatch is used to note the time interval between the
instant at which the sound pulse is sent and the instant at which the echo is
received by the receiver. Note the time interval as ‘t’.
4.
Repeat the experiment for three or four times. The average time
taken for the given number of pulses is calculated.
Calculation of speed of sound:
The sound pulse emitted
by the source travels a total distance of 2d while travelling from the source
to the wall and then back to the receiver. The time taken for this has been
observed to be ‘t’. Hence, the speed of sound wave is given by:
Speed of sound =
distance travelled / time taken = 2d/t
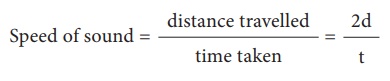
Related Topics