Interior of the Earth | Term 1 Unit 1 | Geography | 7th Social Science - Earthquake | 7th Social Science : Geography : Term 1 Unit 1 : Interior of the Earth
Chapter: 7th Social Science : Geography : Term 1 Unit 1 : Interior of the Earth
Earthquake
Earthquake
A
sudden movement of a portion of the earth’s crust which produces a shaking or
trembling is known as an earthquake.
Earthquakes may cause widespread damage to life and property. The point where
these vibrations originate is called the focus
of the earthquake. The point of the earth’s surface directly above the focus is
called the epicentre of the earthquake. From
the focus, the earthquake vibrations travel in different directions in the form
of seismic waves.
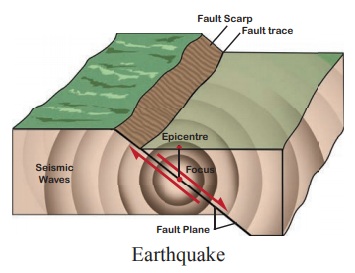
The
earthquake waves are recorded by an instrument known as seismograph. The magnitude of an earthquake is measured by the Richter scale. The
numbers on this scale range from 0 to 9.
An earthquake of 2.0 on
Richter scale or less can be felt only a little. An earthquake over 5.0 on
Richter scale can cause damage from things falling. A 6.0 on Richter scale or
higher magnitude is considered very strong and 7.0 on Richter scale is
classified as a major earthquake.
Causes of Earthquake
The
chief cause of earthquake is the sudden slipping of the portion of the earth’s
crust along fractures or faults. The movement of the molten rocks underneath
the surface produce strains which break the rocks apart. The sudden shifting of
landmass causes upheavals in the crust of the earth sending vibrations or waves
into the surrounding portions of the earth. Sometimes the surface of the earth
itself cracks.
Another
cause of earthquake is volcanic activity. A violent or explosive eruption often
causes the earth in its vicinity to quake. Earthquakes are often common in most
volcanic areas.
Effects of Earthquakes
Earthquakes
may cause changes in the earth’s surface. Vibrations often set landslides in
mountainous regions.A greater danger in an earthquake is the falling of
buildings. Most of the houses which collapsed were made of mud and bricks and
proved to be death traps. Fire is another great danger. Underground water
system is naturally disturbed by such movements.
There are three types of earthquake
waves:
1. P waves or
longitudinal waves
2. S waves or transverse
waves
3.
L waves or surface waves
An
earthquake which originates below or near the sea causes great disturbance in
the water. The floods and waves cause great loss of life, sometimes more than
the earthquake itself. Tsunami, a Japanese
term, is the name given to the huge wave caused in the sea by an earthquake.
Tsunamis are quite common along the coasts of Japan and other regions in the
Pacific Ocean.
On 26th Dec 2004 Tsunami in
the Indian Ocean swept coastal area of Indonesia, India, Srilanka, Thailand
etc., They caused immense damage to lifeand property in the coastal area
Distribution of
Earthquakes
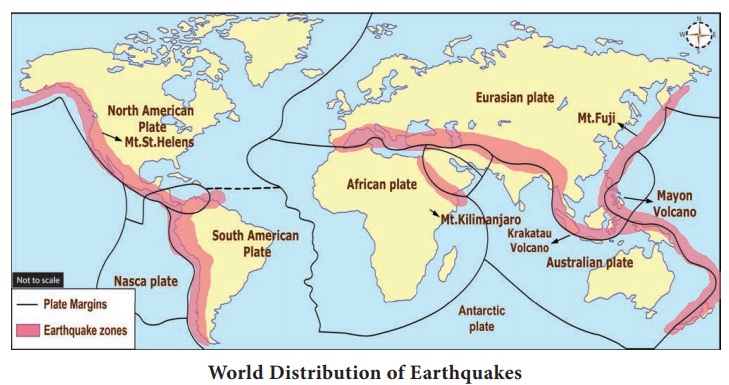
The
world’s distribution of earthquakes coincide very closely with that of
volcanoes. Regions of greatest seismicity are circum-Pacific areas, with the
epicenters and the most frequent occurrences along the Pacific
Ring of Fire. It is said that about 68 percent of earthquakes occur in
this belt. Another 31 % of earthquakes take place in the
Mediterranean-Himalayan belt including Asia Minor, the Himalayas and parts of
north-west China. The remaining percent of earthquakes are occur in Northen
Africa and Rift valley areas of the Red sea and Dead sea.
In
India, the Himalayan region and the Ganga-Brahamaputra valley are prone to
earthquakes. A number of earthquakes have been experienced in this region. Some
of them were very severe and caused extensive damage, e.g., the earthquake of
Uttar Kashi in 1991 and Chamoli in 1999.
The Deccan Plateau, which was supposed to be comparatively free from the dangers of the earthquakes, has experienced two severe earthquakes in the past, the Koyna earthquake in 1967 and the Latur earthquake in 1993.
Related Topics