Chapter: Introduction to the Design and Analysis of Algorithms : Dynamic Programming
Dynamic Programming: Three Basic Examples
Three Basic Examples
The goal of this section is
to introduce dynamic programming via three typical examples.
EXAMPLE
1 Coin-row problem There is a row of n coins whose values are some positive integers c1, c2, . . . , cn, not necessarily distinct. The goal is to pick
up the maximum amount of money subject to the constraint that no two coins
adjacent in the initial row can be picked up.
Let F (n) be the maximum amount that can be picked up
from the row of n coins. To derive a
recurrence for F
(n), we partition all the allowed coin selections into two groups:
those that include the last coin and those without it. The largest amount we
can get from the first group is equal to cn + F
(n ŌłÆ 2)ŌĆöthe value of the nth coin plus the maximum amount we can pick up
from the first n
ŌłÆ 2 coins. The maximum amount we can get from the second group
is equal to F (n ŌłÆ 1) by the definition of F (n). Thus, we have the following recurrence subject
to the obvious initial conditions:
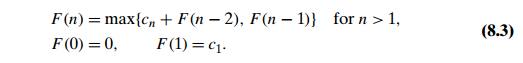
We can compute F (n) by filling the one-row table left to right in
the manner similar to the way it was done for the nth Fibonacci number by Algorithm Fib(n)
in Section 2.5.
ALGORITHM CoinRow(C[1..n])
//Applies formula (8.3)
bottom up to find the maximum amount of money //that can be picked up from a
coin row without picking two adjacent coins //Input: Array C[1..n] of positive integers
indicating the coin values //Output: The maximum amount of money that can be
picked up
F [0] ŌåÉ 0; F
[1] ŌåÉ C[1] for i ŌåÉ 2 to n do
F [i] ŌåÉ max(C[i] + F [i ŌłÆ 2],
F [i ŌłÆ 1])
return F [n]
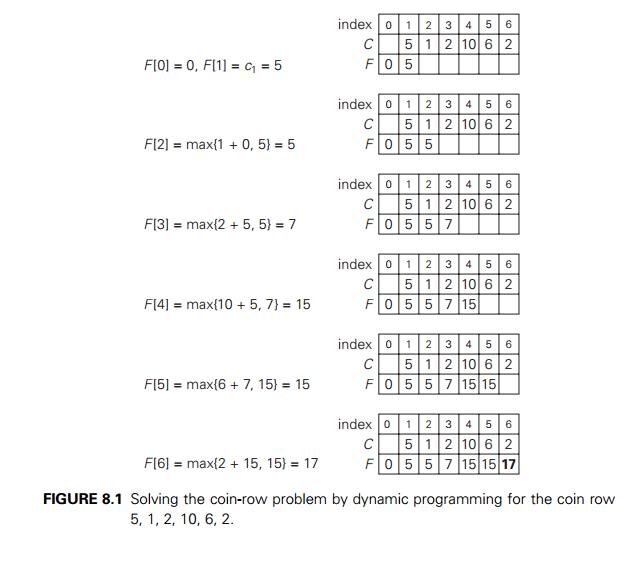
The application of the
algorithm to the coin row of denominations 5, 1, 2, 10, 6, 2 is shown in Figure
8.1. It yields the maximum amount of 17. It is worth pointing
out that, in fact, we also
solved the problem for the first i coins in the row given for
every 1 Ōēż i Ōēż 6. For example, for i = 3, the maximum amount is F (3) = 7.
To find the coins with the
maximum total value found, we need to back-trace the computations to see which
of the two possibilitiesŌĆöcn + F
(n ŌłÆ 2) or F
(n ŌłÆ 1)ŌĆöproduced the maxima in formula (8.3). In the
last application of the formula, it was the sum c6 + F
(4), which means that the coin c6 = 2 is a part of an optimal solution. Moving to
computing F (4), the maximum was produced by the sum c4 + F
(2), which means that the coin c4 = 10 is a part of an optimal solution as well.
Finally, the maximum in computing F
(2) was produced by F (1), implying that the coin c2 is not the part of an optimal solution and the
coin c1 = 5 is. Thus, the optimal solution is {c1, c4, c6}. To avoid repeating the same computations
during the backtracing, the information about which of the two terms in (8.3)
was larger can be recorded in an extra array when the values of F are computed.
Using the CoinRow to find F (n), the largest amount of money that can be picked
up, as well as the coins composing an optimal set, clearly takes $(n) time and $ (n) space. This is by far superior to the alternatives:
the straightforward top- down application of recurrence (8.3) and solving the problem
by exhaustive search (Problem 3 in this sectionŌĆÖs exercises).
EXAMPLE
2 Change-making problem Consider the general instance
of the following well-known problem. Give change for
amount n using the minimum number of
coins of denominations d1 < d2 < . . . < dm. For the coin denominations used in the United
States, as for those used in most if not all other countries, there is a very
simple and efficient algorithm discussed in the next chapter. Here, we consider
a dynamic programming algorithm for the general case, assuming availability of
unlimited quantities of coins for each of the m denominations
d1 < d2 < . . . < dm where d1 = 1.
Let F (n) be the minimum number of coins whose values
add up to n; it is convenient to define F (0) = 0. The amount n can only be obtained by adding one coin of
denomination dj to the amount n ŌłÆ dj for j = 1, 2, . . . , m such that n Ōēź dj . Therefore, we can consider all such
denominations and select the one minimizing F (n ŌłÆ dj ) + 1. Since 1 is a constant, we
can, of course, find the smallest F
(n ŌłÆ dj ) first and then add 1 to it. Hence, we have the
following recurrence for F
(n):
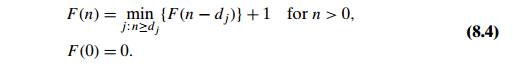
We can compute F (n) by filling a one-row table left to right in
the manner similar to the way it was done above for the coin-row problem, but
computing a table entry here requires finding the minimum of up to m numbers.
ALGORITHM ChangeMaking(D[1..m], n)
//Applies dynamic programming
to find the minimum number of coins //of denominations d1 <
d2 < . . . < dm where d1 = 1 that add up to a //given amount n
//Input: Positive integer n and array D[1..m] of increasing positive //
integers indicating the coin denominations where D[1] = 1 //Output: The minimum number of coins that
add up to n
F [0] ŌåÉ 0
for i ŌåÉ 1 to n do
t emp ŌåÉ Ōł×; j
ŌåÉ 1
while j Ōēż m and i Ōēź D[j ] do
t emp ŌåÉ min(F
[i ŌłÆ D[j ]], t emp) j ŌåÉ j + 1
F [i] ŌåÉ t emp + 1 return F [n]
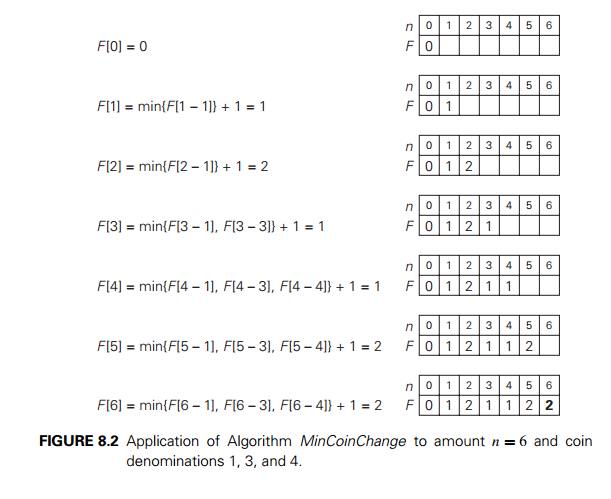
The application of the
algorithm to amount n = 6 and denominations 1, 3, 4 is shown in Figure
8.2. The answer it yields is two coins. The time and space efficiencies of the
algorithm are obviously O(nm) and $(n), respectively.
To find the coins of an
optimal solution, we need to backtrace the computa-tions to see which of the
denominations produced the minima in formula (8.4). For the instance
considered, the last application of the formula (for n = 6), the minimum was produced by d2 = 3. The second minimum (for n = 6 ŌłÆ 3) was also produced for a coin
of that denomination. Thus, the minimum-coin set for n = 6 is two 3ŌĆÖs.
EXAMPLE
3 Coin-collecting problem Several coins are placed in
cells of an n ├Ś m board, no more than one coin per cell. A robot,
located in the upper left cell of the board, needs to
collect as many of the coins as possible and bring them to the bottom right
cell. On each step, the robot can move either one cell to the right or one cell
down from its current location. When the robot visits a cell with a coin, it always
picks up that coin. Design an algorithm to find the maximum number of coins the
robot can collect and a path it needs to follow to do this.
Let F (i, j ) be the largest number of coins the robot can
collect and bring to the cell (i,
j ) in the ith row and j th column of the board. It can reach this cell
either from the adjacent cell (i ŌłÆ 1,
j ) above it or from the adjacent cell (i, j ŌłÆ 1) to the left of it. The
largest numbers of coins that can be brought to these cells are F (i ŌłÆ 1,
j ) and F
(i, j ŌłÆ 1), respectively. Of course, there are no
adjacent cells above the cells in the first row, and there are no adjacent
cells to the left of the cells in the first column. For those cells, we assume
that F (i ŌłÆ 1,
j ) and F
(i, j ŌłÆ 1) are equal to 0 for their nonexistent
neighbors. Therefore, the largest number of coins the robot can bring to cell (i, j ) is the maximum of these two numbers plus one
possible coin at cell (i,
j ) itself. In other words, we have the following formula for F (i, j ):
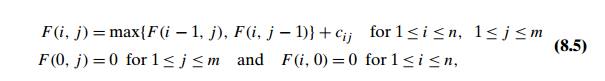
where cij = 1 if there is a coin in cell (i, j ), and cij = 0 otherwise.
Using these formulas, we can
fill in the n ├Ś m table of F (i, j ) values either row by row or column by column,
as is typical for dynamic programming algorithms involving two-dimensional
tables.
ALGORITHM RobotCoinCollection(C[1..n, 1..m])
//Applies dynamic programming
to compute the largest number of //coins a robot can collect on an n ├Ś m board by starting at (1, 1) //and moving right and down from upper left
to down right corner //Input: Matrix C[1..n, 1..m] whose elements are equal to 1 and 0 //for
cells with and without a coin, respectively
//Output: Largest number of
coins the robot can bring to cell (n,
m) F [1, 1] ŌåÉ C[1, 1]; for j ŌåÉ 2 to m
do F [1,
j ] ŌåÉ F [1,
j ŌłÆ 1] + C[1,
j ] for i ŌåÉ 2 to n do
F [i,
1] ŌåÉ F [i ŌłÆ 1, 1] + C[i,
1] for j ŌåÉ 2 to m do
F [i,
j ] ŌåÉ max(F
[i ŌłÆ 1,
j ], F [i, j ŌłÆ 1]) + C[i,
j ] return F [n, m]
The algorithm is illustrated
in Figure 8.3b for the coin setup in Figure 8.3a. Since computing the value of F (i, j ) by formula (8.5) for each cell of the table
takes constant time, the time efficiency of the algorithm is (nm). Its space efficiency is,
obviously, also (nm).
Tracing the computations
backward makes it possible to get an optimal path: if F (i ŌłÆ 1,
j ) > F (i, j ŌłÆ 1), an optimal path to cell (i, j ) must come down from the adjacent cell above
it; if F (i ŌłÆ 1,
j ) < F (i, j ŌłÆ 1), an optimal path to cell (i, j ) must come from the adjacent cell on the left;
and if F (i ŌłÆ 1,
j ) = F (i, j ŌłÆ 1), it can reach cell (i, j ) from either direction. This yields two optimal
paths for the instance in Figure 8.3a, which are shown in Figure 8.3c. If ties
are ignored, one optimal path can be obtained in (n + m) time.
Exercises 8.1
What does dynamic programming have in common with
divide-and-conquer? What is a principal difference between them?
Solve the instance 5, 1, 2, 10, 6 of the coin-row problem.
a. Show that the time efficiency
of solving the coin-row problem by straight-forward application of recurrence
(8.3) is exponential.
Show that the time efficiency of solving the coin-row problem by
exhaustive search is at least exponential.
Apply the dynamic programming
algorithm to find all the solutions to the change-making problem for the
denominations 1, 3, 5 and the amount n = 9.
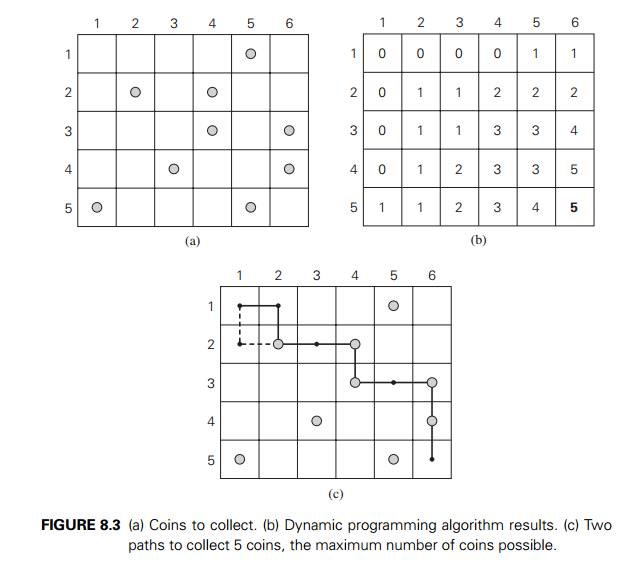
How would you modify the
dynamic programming algorithm for the coin-collecting problem if some cells on
the board are inaccessible for the robot? Apply your algorithm to the board
below, where the inaccessible cells are shown by XŌĆÖs. How many optimal paths
are there for this board?
Rod-cutting problem Design a dynamic programming
algorithm for the fol-lowing problem. Find the maximum total sale price that
can be obtained by cutting a rod of n units long into
integer-length pieces if the sale price of a piece i units long is pi for i
= 1, 2,
. . . , n. What are the time and space efficiencies of your algorithm?
Shortest-path counting A chess rook can move
horizontally or vertically to any
square in the same row or in the same column of a chessboard. Find the number
of shortest paths by which a rook can move from one corner of a chessboard to the
diagonally opposite corner. The length of a path is measured by the number of
squares it passes through, including the first and the last squares. Solve the
problem
by a dynamic programming algorithm.
by using elementary combinatorics.
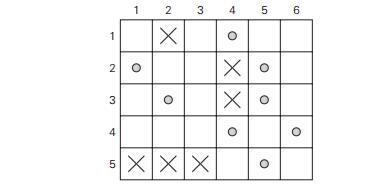
Minimum-sum descent Some positive integers are
arranged in an equilateral triangle
with n numbers in its base like the
one shown in the figure below for n = 4. The problem is to find the smallest sum in a
descent from the triangle apex to its base through a
sequence of adjacent numbers (shown in the figure by the circles). Design a
dynamic programming algorithm for this problem and indicate its time
efficiency.
Binomial coefficient Design an efficient algorithm
for computing the bino-mial coefficient C(n, k) that uses no multiplications. What are the
time and space efficiencies of your algorithm?
Longest path in a dag
Design an efficient algorithm for finding the length of the longest
path in a dag. (This problem is important both as a prototype of many other
dynamic programming applications and in its own right because it determines the
minimal time needed for completing a project comprising precedence-constrained
tasks.)
Show how to reduce the coin-row problem discussed in this section
to the problem of finding a longest path in a dag.
Maximum square submatrix Given an m ├Ś n boolean matrix B, find its largest square submatrix whose elements are all zeros. Design a
dynamic programming algorithm and indicate its time efficiency. (The algorithm
may be useful for, say, finding the largest free square area on a computer
screen or for selecting a construction site.)
World Series odds Consider two teams, A and B, playing a series of games
until one of the teams wins n games. Assume that the
probability of A winning a game is the same
for each game and equal to p, and the probability of A losing a game is q = 1 ŌłÆ p. (Hence, there are no ties.) Let P (i, j ) be the probability of A winning the series if A needs i more games to win the series and B needs j more games to win the series.
Set up a recurrence relation for P (i, j ) that can be used by a dynamic programming algorithm.
Find the probability of team A
winning a seven-game series if the proba-bility of it winning a game is 0.4.
Write pseudocode of the dynamic programming algorithm for solving
this problem and determine its time and space efficiencies.
Related Topics