Chapter: Programming and Data Structures : Linear Data structures- List
Doubly linked lists
DOUBLY LINKED LIST
Doubly linked list
In a doubly-circularly-linked list,
each node has two links, similar to a doubly-linked list, except that
the previous link of the first node points to the last node and the next link
of the last node points to the first node. As in doubly-linked lists,
insertions and removals can be done at any point with access to any nearby
node.
Sentinel nodes
Linked lists sometimes have a special
dummy or sentinel node at the beginning
and/or at the end of the list, which is not used to store data.
Basic
Operations on Linked Lists
1. Insertion
a. At
first
b. At
last
c. At
a given location (At middle)
2. Deletion
a. First
Node
b. Last
Node
c. Node
in given location or having given data item
Initial
Condition
HEAD
= NULL;
/* Address of the first node in the list is stored
in HEAD. Initially there is no node in the list. So, HEAD is initialized to
NULL (No address) */
What
are the Applications of linked list?
v To
implement of Stack, Queue, Tree, Graph etc.,
v Used
by the Memory Manager
v To
maintain Free-Storage List
Doubly Linked Lists (or) Two –Way Lists
There are some problems in using the Single linked
list. They are
1. A
singly linked list allows traversal of the list in only one direction. (Forward
only)
2. Deleting
a node from a list requires keeping track of the previous node, that is, the
node
whose
link points to the node to be deleted.
These major drawbacks
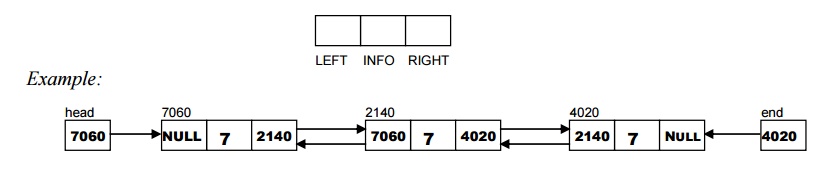
can be avoided by using the double linked list. The doubly linked list is a linear
collection of data elements, called nodes, where each
node is divided into three parts. They are:
1. A
pointer field LEFT which contains the address of the preceding node in the list
2. An
information field INFO which contains the data of the Node
3. A
pointer field RIGHT which contains the address of the next node in the list
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node
{
struct node *previous; int data;
struct node *next;
}*head, *r;
void insert_begning(int value)
{
struct
node *tem,*t;
tem=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
tem->data=value;
if(head==NULL)
{
head=tem; head->previous=NULL;
head->next=NULL; r=head;
}
else
{
t=tem;
t->previous=NULL;
t->next=head;
head->previous=t; head=t;
}
}
void insert_end(int value)
{
struct
node *tem,*t;
tem=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct
node)); tem->data=value;
if(head==NULL)
{
head=tem; head->previous=NULL;
head->next=NULL; r=head;
}
else
{
r=head;
while(r!=NULL)
{
t=r; r=r->next;
}
r=tem; t->next=r; r->previous=t;
r->next=NULL;
}
}
int insert_after(int value, int loc)
{
struct
node *t,*tem,*t1;
tem=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
tem->data=value;
if(head==NULL)
{
head=tem; head->previous=NULL;
head->next=NULL;
}
else
{
t=head;
while(t!=NULL
&& t->data!=loc)
{
t=t->next;
}
if(t==NULL)
{
printf("\n%d
is not present in list ",loc);
}
else
{
t1=t->next; t->next=tem;
tem->previous=t; tem->next=t1; t1->previous=tem;
}
}
r=head; while(r->next!=NULL)
{
r=r->next;
}
return;
}
int delete_from_end()
{
struct node *t; t=r;
if(t->previous==NULL)
{
free(t);
head=NULL;
r=NULL; return 0;
}
printf("\nData deleted from list is %d
\n",r->data); r=t->previous;
r->next=NULL; free(t);
return
0;
}
int delete_from_middle(int value)
{
struct node *temp,*var,*t, *temp1;
temp=head;
while(temp!=NULL)
{
if(temp->data
== value)
{
if(temp->previous==NULL)
{
free(temp);
head=NULL; return 0;
}
else
{
var->next=temp1;
temp1->previous=var; free(temp);
return
0;
}
}
else
{
var=temp; temp=temp->next;
temp1=temp->next;
}
}
printf("data deleted from list is
%d",value); return 0;
}
void display()
{
struct node *t; t=head; if(t==NULL)
{
printf("List
is Empty");
}
while(t!=NULL)
{
printf("-> %d
",t->data); t=t->next;
}
}
void main()
{
int value, ch, loc;
clrscr();
head=NULL;
printf("Doubly
Linked List");
printf("\n1.insert at begning\n2. insert at
end\n3.insert at middle"); printf("\n4.delete from end\n5.delete
middle\n6.display list\n7.exit"); while(1)
{
printf("\n\nenter the choice ");
scanf("%d",&ch);
switch(ch)
{
case
1:
{
printf("enter the value to insert in node
"); scanf("%d",&value); insert_begning(value);
display();
break;
}
case
2:
{
printf("enter the value to insert in node at
end "); scanf("%d",&value);
insert_end(value); display();
break;
}
case
3:
{
printf("after which data you want to insert
data "); scanf("%d",&loc);
printf("enter the data you want to insert in
list "); scanf("%d",&value);
insert_after(value,loc); display();
break;
}
case
4:
{
delete_from_end(); display();
break;
}
case
5:
{
printf("enter the
position to delete");
scanf("%d",value);
delete_from_middle(value);
display();
break;
}
case
6 :
{
display();
break;
}
case
7 :
{
exit(0);
break;
}
}
}
getch();
}
Array
Static memory
Insertion and deletion
required to modify the existing element location
Elements stored as
contiguous memory as on block.
Accessing element is
fast
Linked
list
Dynamic memory
Insertion and deletion
are made easy.
Element stored as
Non-contiguous memory as pointers
Accessing element is
slow
Related Topics