Chapter: Civil : Remote Sensing Techniques and GIS : Image Interpretation And Analysis
Digital Image Processing
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING
1 Introduction
As seen
in the earlier chapters, remote sensing data can be analysed using visual image
interpretation techniques if the data are in the hardcopy or pictorial form. It
is used extensively to locate specific features and conditions, which are then geocoded
for inclusion in GIS. Visual image interpretation techniques have certain
disadvantages and may require extensive training and are labour intensive. In this technique, the spectral
characteristics are not always fully evaluated because of the limited ability
of the eye to discern tonal values and analyse the spectral changes. If the data are in digital
mode, the remote sensing data can be analysed using digital image processing
techniques and such a database can be used in raster GIS. In applications where
spectral patterns are more informative, it is preferable to analyse digital data rather than pictorial
data.
In today's world of
advanced technology where most remote sensing data are recorded in digital
format, virtually all image interpretation and analysis involves some element
of digital processing. Digital image processing may involve numerous procedures
including formatting and correcting of the data, digital enhancement to
facilitate better visual interpretation, or even automated classification of
targets and features entirely by computer. In order to process remote sensing
imagery digitally, the data must be recorded and available in a digital form
suitable for storage on a computer tape or disk. Obviously, the other
requirement for digital image processing is a computer system, sometimes
referred to as an image analysis system, with the appropriate hardware
and software to process the data. Several commercially available
software systems have been developed specifically for remote sensing image
processing and analysis.
For discussion
purposes, most of the common image processing functions available in image
analysis systems can be categorized into the following four categories:
Preprocessing
Image Enhancement
Image Transformation
Image Classification and Analysis
2 PREPROCESSING
Preprocessing functions
involve those operations that are normally required prior tothe maindata
analysis and extraction of information, and are generally grouped as radiometric
orgeometric corrections. Radiometric corrections include correcting the
data for sensorirregularities and unwanted sensor or atmospheric noise,
and converting the data so they accurately represent the reflected or emitted
radiation measured by the sensor. Geometric corrections include correcting for
geometric distortions due to sensor-Earth geometry variations, and conversion of
the data to real world coordinates (e.g. latitude and longitude) on the Earth's
surface. The objective of the second group of image processing functions
grouped under the term of image enhancement, is solely to improve the
appearance of theimagery to assist in visual interpretation and
analysis. Examples of enhancement functionsinclude contrast stretching
to increase the tonal distinction between various features in a scene, and spatial
filtering to enhance (or suppress) specific spatial patterns in an image.
Image transformations are
operations similar in concept to those for image enhancement.However,
unlike image enhancement operations which are normally applied only to a single
channel of data at a time, image transformations usually involve combined
processing of data from multiple spectral bands. Arithmetic operations (i.e.
subtraction, addition, multiplication, division) are performed to combine and
transform the original bands into "new" images which better display
or highlight certain features in the scene. We will look at some of these
operations including various methods of spectral or band ratioing, and a
procedure called principal components analysis which is used to more
efficiently represent the information
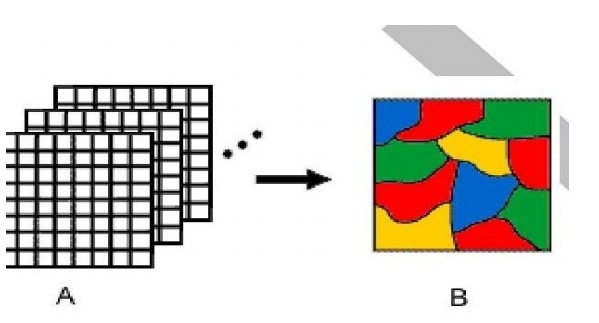
Image
classification and analysis operations are used to
digitally identify and classify pixelsin the data. Classification
is usually performed on multi-channel data sets (A) and this process assigns
each pixel in an image to a particular class or theme (B) based on statistical
characteristics of the pixel brightness values. There are a variety of
approaches taken to perform digital classification. We will briefly describe
the two generic approaches which are used most often, namely supervised
and unsupervised classification. In the following sections we will
describe each of these four categories of digital image processing functions in
more detail.
Pre-processing
operations, sometimes referred to as image restoration and rectification, are
intended to correct for sensor- and platform-specific radiometric and geometric
distortions of data. Radiometric corrections may be necessary due to variations
in scene illumination and viewing geometry, atmospheric conditions, and sensor
noise and response. Each of these will vary depending on the specific sensor
and platform used to acquire the data and the conditions during data
acquisition. Also, it may be desirable to convert and/or calibrate the data to
known (absolute) radiation or reflectance units to facilitate comparison
between data.
3 IMAGE ENHANCEMENT
TECHNIQUES
Low
sensitivity of the detectors, weak signal of the objects present on the earth surface, similar reflectance of
different objects and environmental conditions at the time of recording are the
major causes of low contrast of the image. Another problem that complicates photographic display of
digital image is that the human eye is poor at discriminating the slight
radiometric or spectral differences that may characterize the features. The
main aim of digital enhancement is to amplify these slight differences for
better clarity of the image scene. This means digital enhancement increases the
separability (contrast) between the interested classes or features. The digital image
enhancement may be defined as some mathematical operations that are to be
applied to digital remote sensing input data to improve the visual appearance
of an image for better interpretability or subsequent digital analysis
(Lillesand and Keifer, 1979). Since the image quality is a subjective measure varying from
person to person , there is no simple rule which may produce a single best result.
Normally, two or more operations on
the input image may suffice to fulfil the desire of the analyst, although the enhanced
product may have a fraction of the total information stored in the original
image. This will be realized
after seeing the different contrast enhancement techniques in this
chapter. There are a number of
general categories of enhancement techniques. As in many outer areas of
knowledge, the distinction between one type of analysis andanother is a matter
of personal taste and need of the interpreter. In remote sensing literature, many digital enhancement algorithms are available.
They are
contrast stretching enhancement, ratioing , linear combinations, principalcomponent analysis, and spatial filtering . Broadly, the enhancement
techniques are categorised as point operations and local operations. Point operations modify
the values of each pixel in an image data set independently, whereas local operations
modify the values of each pixel in the context of the pixel values surrounding
it. Point operations include contrast enhancement and band combinations, but spatial filtering is
an example of local operations. In this section, contrast enhancement, linear contrast stretch , histogram equalisation,
logarithmic contrast enhancement, and exponential contrast enhancement are considered.
Related Topics